- 安装pheatmap包
- 创建测试矩阵
- 画个热图
- 显示色块的数值或文本
- 调整色块或文本大小
- 行列注释
- 列名的文本角度调整
- 切分热图
- 自定义显示哪些行列的名字
- 用距离矩阵的方法来聚类
- 练习
1. 安装pheatmap包
install.packages("pheatmap")
library(pheatmap)
2. 创建测试矩阵
test = matrix(rnorm(200), 20, 10) #test为一个20*10的矩阵,200个元素满足参数为0和1的正态分布
test[1:10, seq(1, 10, 2)] = test[1:10, seq(1, 10, 2)] + 3
test[11:20, seq(2, 10, 2)] = test[11:20, seq(2, 10, 2)] + 2
test[15:20, seq(2, 10, 2)] = test[15:20, seq(2, 10, 2)] + 4
colnames(test) = paste("Test", 1:10, sep = "") #定义列名,注意paste的用法
rownames(test) = paste("Gene", 1:20, sep = "") #定义行名
3. 画个热图
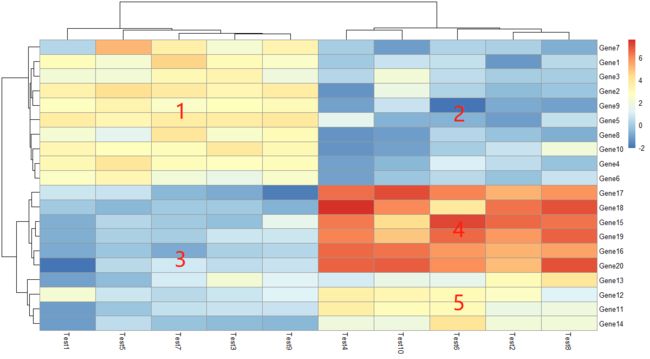
3.1 pheatmap(test)
基本用法,根据“2. 创建测试矩阵”中的局部赋值运算可以得到明显的分区。
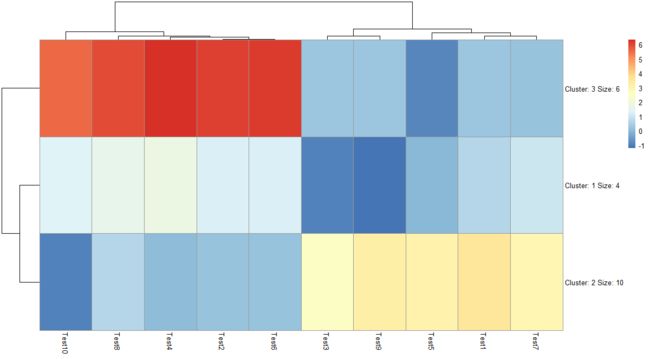
3.2 pheatmap(test, kmeans_k = 3)
将行聚为几类
kmeans是一种聚类算法,详见https://www.cnblogs.com/bourneli/p/3645049.html
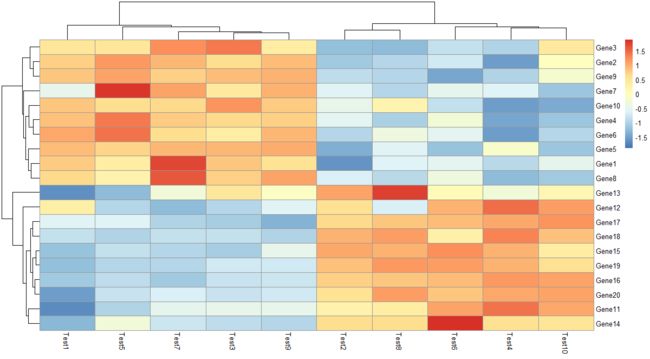
3.3 pheatmap(test, scale = "row")
标准化
为什么要标准化? 原始数据中,每个基因表达变化范围对应的数值大小不同,导致图片中色彩变化难以显示基因在不同样本中的变化趋势,可以对基因在每个样本中基因表达数据进行标准化,使其数值在一定范围内,从而实现热图的优化,而控制参数为scale,对基因(行,row)进行处理
可以与第一张图比较一下,例如Gene3这一行,在这张图中可以看出样本之间的差异明显了许多。
3.4 pheatmap(test, clustering_distance_rows = "correlation")
聚类线长度优化,可能不一样的算法有不一样的枝长。
clustering_distance_cols同理。
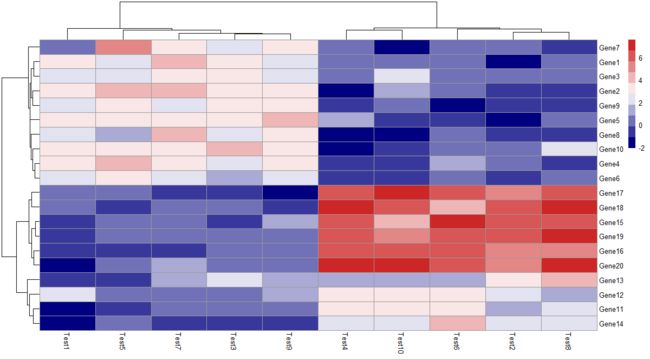
3.5 pheatmap(test, color = colorRampPalette(c("navy", "white", "firebrick3"))(10))
设置颜色,后面括号里的数字表示梯度,10就是将这三种颜色设置为10个梯度
3.6 pheatmap(test, cluster_row = FALSE)
是否显示行的聚类,cluster_col同理
3.7 pheatmap(test, legend = FALSE)
是否显示图例
4. 显示色块的数值或文本
基本用法:pheatmap(test, display_numbers = TRUE)
此外还可添加如下参数
number_format = "%.3e"表示保留3位小数,且用科学计数法显示
number_format = "%.3f"表示保留3位小数,用小数显示
display_numbers除了赋布尔值,还能赋矩阵(其维度与原矩阵相同),此时可以人为添加文本(有点像R画图的图层叠加)。
pheatmap(test, display_numbers = matrix(ifelse(test > 5, "*", ""), 20,10))
legend_breaks设置图例的显示范围,间隔为1;legend_labels重写刻度的标签, 需与legend_breaks同时使用。
pheatmap(test, legend_breaks = -1:4, legend_labels = c("0","1e-4", "1e-3", "1e-2", "1e-1", "1"))
5. 调整色块或文本大小
pheatmap(test, cellwidth = 15, cellheight = 12, main = "Example heatmap", fontsize = 8, filename = "test.pdf")
dev.off()
这五个参数分别表示:
色块的宽度、色块的高度、标题、行列名及图例字体的大小、保存为当前工作目录下的图片的文件名
6. 行列注释
对于每一行每一列都添加一些注释信息,本质还是"分类"。
annotation_col = data.frame(
CellType = factor(rep(c("CT1", "CT2"), 5)),
Time = 1:5
) #注意rep()的用法;为什么要定义为因子;R可以自动补全Time变量
rownames(annotation_col) = paste("Test", 1:10, sep = "")
annotation_row = data.frame(
GeneClass = factor(rep(c("Path1", "Path2", "Path3"), c(10, 4, 6)))
)
rownames(annotation_row) = paste("Gene", 1:20, sep = "")
> annotation_col
CellType Time
Test1 CT1 1
Test2 CT2 2
Test3 CT1 3
Test4 CT2 4
Test5 CT1 5
> annotation_row
GeneClass
Gene1 Path1
Gene2 Path1
Gene3 Path1
Gene4 Path1
Gene5 Path1
在实际操作中,这些数据框表示的信息需要我们自己记录。
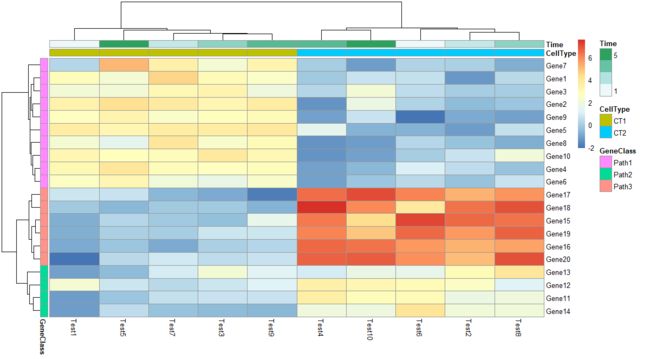
pheatmap(test, annotation_col = annotation_col, annotation_row = annotation_row)
自定义注释色块的颜色
ann_colors = list(
Time = c("white", "firebrick"),
CellType = c(CT1 = "#1B9E77", CT2 = "#D95F02"),
GeneClass = c(Path1 = "#7570B3", Path2 = "#E7298A", Path3 = "#66A61E")
) #注意ann_colors是列表
pheatmap(test, annotation_col = annotation_col, annotation_row = annotation_row,
annotation_colors = ann_colors)
7. 列名的文本角度调整
angle_col = "45",文本与从左向右水平线的夹角,只能是“270”, “0”, “45”, “90”, “315”这几个值。
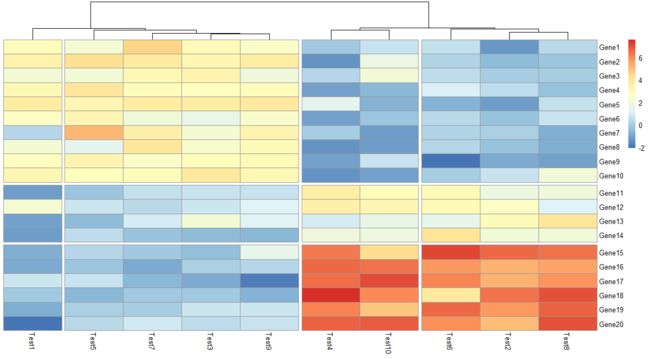
8. 切分热图
pheatmap(test, cluster_rows = F, gaps_row = c(10, 14), cluster_cols = T,
cutree_col = 4)
gaps_row有效的前提是cluster_rows = F;cutree_col有效的前提是cluster_cols = T
效果图如下:
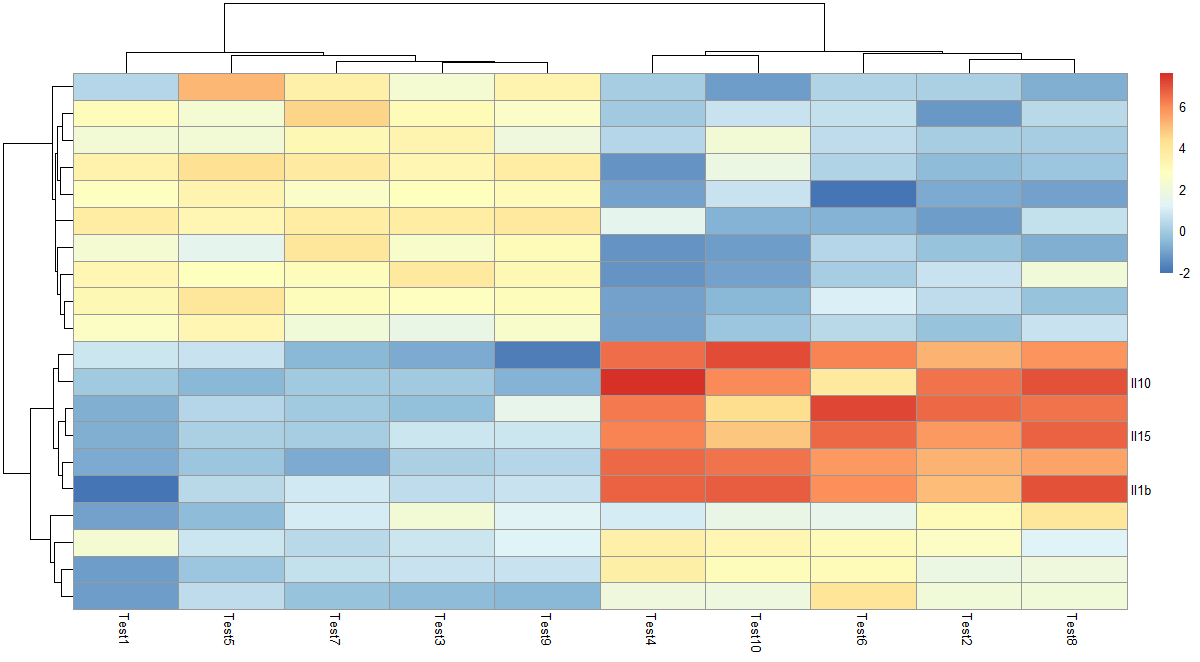
9. 自定义显示哪些行列的名字
labels_row = c("", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "", "",
"", "", "Il10", "Il15", "Il1b")
pheatmap(test, labels_row = labels_row)
10. 用距离矩阵的方法来聚类
?dist()
This function computes and returns the distance matrix computed by using the specified distance measure to compute the distances between the rows of a data matrix.
?t()
求矩阵的转置
drows = dist(test, method = "minkowski")
dcols = dist(t(test), method = "minkowski")
pheatmap(test, clustering_distance_rows = drows, clustering_distance_cols = dcols)
minkowski度量我目前还不理解是什么。
我试了一下,和pheatmap(test)在图片上看不出区别。
11. 练习
#将原文本文件的第一列作为行名
a <- read.table("GSE17215_series_matrix.txt",comment.char = "!",sep = "\t",header = T)
rownames(a)=a[,1]
a=a[,-1]
# 或者如下
# a <- read.table("GSE17215_series_matrix.txt",comment.char = "!",sep = "\t",header = T,row.names = 1)
# View(a)
a <- log2(a)
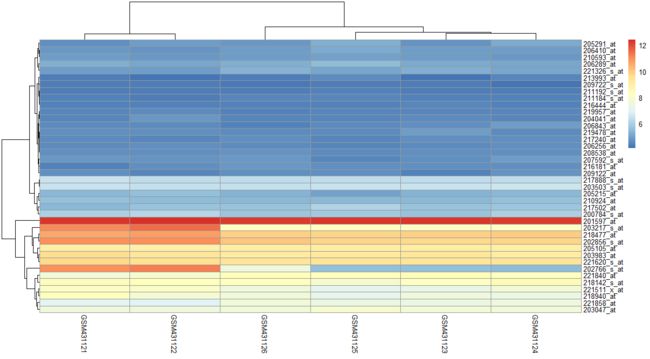
随机取40行画热图,探针在各样本中区别不明显。
pheatmap::pheatmap(a[sample(1:nrow(a),40),])
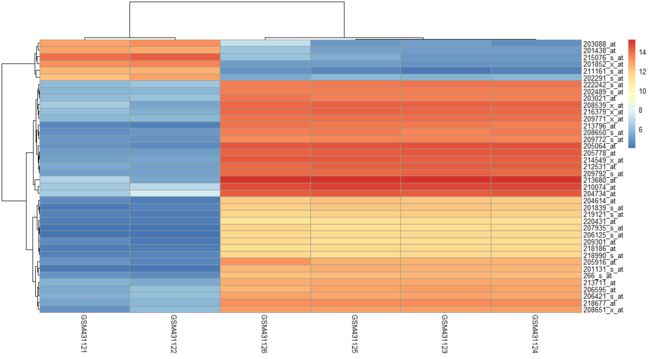
取行标准差最大的40行画热图,差别出来了。
sd_top_40 <- names(sort(apply(a,1,sd),decreasing = T)[1:40])
sd_top_40
pheatmap(a[sd_top_40,])