FFmpeg开发必备的C语言
文章目录
- HelloWorld
- 常用基本类型
- 常量与变量
- 指针与数组
- 结构体
- 枚举
- 文件操作
- C语言编译器
- C语言调试器
HelloWorld
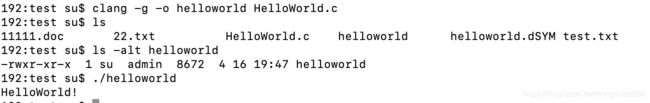
vi HelloWorld.c
#include clang -g -o helloworld HelloWorld.c
ls -alt helloworld
./helloworld
常用基本类型
- short、 int、 long
- float、double
- char
- void
#include clang -g -o helloworld1 HelloWorld.c
./helloworld1
打印:
Hello World!
a = 100
b = 1.230000
c = C
常量与变量
- int a = 0; //变量,可以再赋值
- const int len = 256; //常量定义
指针与数组
- 指针就是内存地址:void* 、 char*
- 数组 如:char c[2] 、 int arr[10]
指针:
#includegcc -g -o testpoint testpoint.c
./testpoint
打印结果:
addr of a:0x7ffee1cb1830,0x7fa99b402b60,1
addr of b:0x7ffee1cb1828,0x7fa99b402b70,2
addr of c:0x7ffee1cb184c,0x7ffee1cb184c,0,1,2
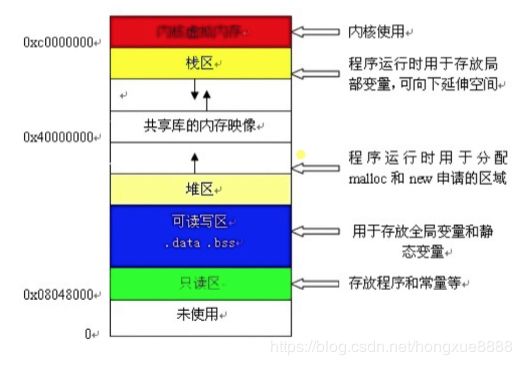
操作系统时如何管理内存的?
- 栈空间
- 堆空间
- 内存映射
内存的分配与释放
- 分配内存
void* mem = malloc(size); - 释放内存
free(mem);
内存泄漏与野指针
- 不断向系统申请内存
- 申请的内存不用,也不释放
- 占用别人的内存称为野指针
函数指针
- 返回值类型(*指针变量名)([形参列表]);
int func(int x);//声明一个函数
int(*f)(int x);//声明一个函数指针
f = func;//将func函数的首地址赋给指针f
函数指针示例:
vi testfunc.c
#includeclang -g -o testfunc testfunc.c
./testfunc
打印:
3+5 = 8
8-3 = 5
结构体
vi testst.c
#includeclang -g -o testst testst.c
./testst
打印结果:
struct content is :10,20
枚举
vi testenum.c
#includeclang -g -o testenum testenum.c
./testenum
打印结果:
the color is: 0
the color is: 2
文件操作
- 文件类型
FILE* file; - 打开文件
FILE* fopen(path,mode); - 关闭文件
fclose(FILE*)
#includeclang -g -o testfile testfile.c
./testfile
buf : hello world!
C语言编译器
gcc/clang -g -O2 -o test test.c -I... -L... -l
- -g: 输出文件中的调试信息
- -O:对输出文件做指令优化
- -o: 输出文件
- -I: 指定头文件
- -L:指定库文件位置
- -l :指定使用哪个库
编译过程
- 预编译
- 编译
- 链接,动态链接/静态链接
vi add.h
int add(int a,int b);
vi add.c
int add(int a,int b){
return (a + b);
}
vi add.c
#includeclang -g -c add.c
libtool -static -o libmylib.a add.o
clang -g -o testlib testlib.c -I. -L. -lmylib
./testlib
打印结果:
add = 5
或者:
clang -g -c testlib.c
clang -o testlib1 testlib.o -L . -lmylib
./testlib1
打印结果:
add = 5
C语言调试器
调试器原理
- 编译输出带调试信息的程序
- 调试信息包含:指令地址、对应源代码和行号
- 指令完成后,回调
gdb和lldb
| 命令 | gdb | lldb |
|---|---|---|
| 设置断点 | b | b |
| 运行程序 | r | r |
| 单步执行 | n | n |
| 跳入函数 | s | s |
| 跳出函数 | finish | finish |
| 打印内容 | p | p |
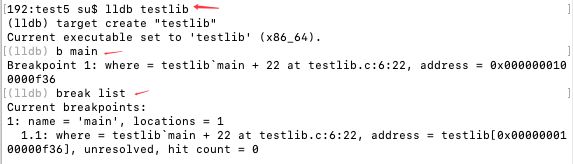
lldb testlib
b main
break list
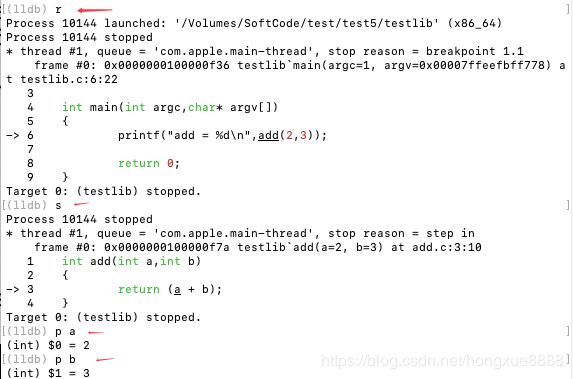
r
s
p a
p b
finish
n
c #continue执行完之后的
quit # 退出
cd testlib.dSYM/Contents/Resources/DWARF
dwarfdump testlib