K-means、K-means ++、K-modes和K-prototype聚类算法简述 附Python代码
K-means
K-means属于聚类算法中最简单的一种,也是一种无监督学习的算法。
步骤:
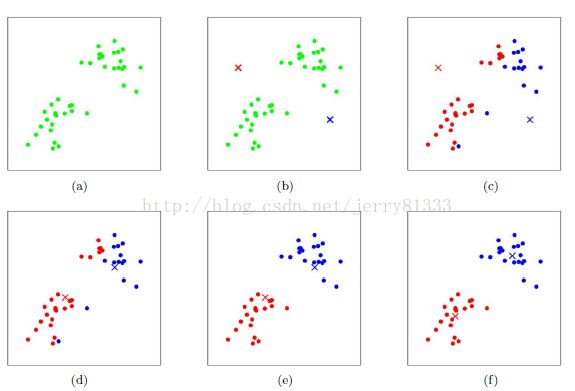
按上图所示,具体步骤如下:
1. 设定初始簇的个数,上图为2
2. 使用欧式距离对簇进行分类,与最近的簇为一类,如上图所示,分为红蓝两类
3. 对已分类的所有数据区均值,取X/Y坐标的平均值,设为新的中心点,如上图c-d的操作
4. 重新对簇进行分类(如步骤2),如上图d-c的操作
5. 迭代直到结束。
结束迭代的方法有很多,比如收敛达到一定程度后结束迭代,如无法收敛可以设置迭代次数
问题:
1. 需要先验知识,必须给定一个簇,簇多簇少效果是截然不同的。
2. 初始簇中心点对算法影响较大,如果初始值不太好,可能对结果产生较大的影响。
3. 去噪点能力差,误差数据可能会对结果造成较大的影响。
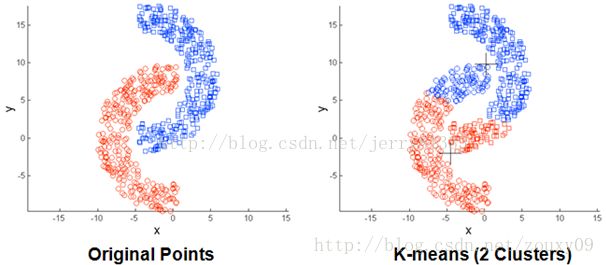
4. 仅适用于球心数据分布
5. 数据比较大时收敛比较慢
解决:
对于中心点的收敛问题,可以使用特殊的求中心点公式:
1. Minkowski Distance 公式 —— λ 可以随意取值,可以是负数,也可以是正数,或是无穷大
2. Euclidean Distance 公式 —— 也就是第一个公式 λ=2 的情况
3. CityBlock Distance 公式 —— 也就是第一个公式 λ=1 的情况
K-means ++
为了解决随机初始点不好并且不知道初始中心点数量的问题,这里可以引入K-means++。
1. 先从数据库随机挑个随机点当“种子点”。
2. 对于每个点,都计算其和最近的一个“种子点”的距离D(x)并保存在一个数组里,然后把这些距离加起来得到Sum(D(x))。
3. 然后,再取一个随机值,用权重的方式来取计算下一个“种子点”。这个算法的实现是,先取一个能落在Sum(D(x))中的随机值Random,然后用Random -= D(x),直到其<=0,此时的点就是下一个“种子点”。
4. 重复第(2)和第(3)步直到所有的K个种子点都被选出来。
5. 进行K-Means算法。
2. 对于每个点,都计算其和最近的一个“种子点”的距离D(x)并保存在一个数组里,然后把这些距离加起来得到Sum(D(x))。
3. 然后,再取一个随机值,用权重的方式来取计算下一个“种子点”。这个算法的实现是,先取一个能落在Sum(D(x))中的随机值Random,然后用Random -= D(x),直到其<=0,此时的点就是下一个“种子点”。
4. 重复第(2)和第(3)步直到所有的K个种子点都被选出来。
5. 进行K-Means算法。
K-modes
K-modes是K-means用在非数值集合上的一种方法,将原本K-means使用的欧式距离替换成字符间的汉明距离。
K-prototype
K-prototype是K-means与K-modes的一种集合形式,适用于数值类型与字符类型集合的数据。
1. 度量具有混合属性的方法是,数值属性采用K-means方法得到P1,分类属性采用K-modes方法P2,那么D=P1+a*P2,a是权重。如果觉得分类属性重要,则增加a,否则减少a,a=0时即只有数值属性
2. 更新一个簇的中心的方法,方法是结合K-means与K-modes的更新。
Python代码
以下基于Python 3.6,修改自http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09/article/details/17589329这篇博客:
from numpy import *
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# calculate Euclidean distance
def euclDistance(vector1, vector2):
return sqrt(sum(power(vector2 - vector1, 2)))
# init centroids with random samples
def initCentroids(dataSet, k):
numSamples, dim = dataSet.shape
centroids = zeros((k, dim))
for i in range(k):
index = int(random.uniform(0, numSamples))
centroids[i, :] = dataSet[index, :]
return centroids
# k-means cluster
def kmeans(dataSet, k):
numSamples = dataSet.shape[0]
# first column stores which cluster this sample belongs to,
# second column stores the error between this sample and its centroid
clusterAssment = mat(zeros((numSamples, 2)))
clusterChanged = True
## step 1: init centroids
centroids = initCentroids(dataSet, k)
while clusterChanged:
clusterChanged = False
## for each sample
for i in range(numSamples):
minDist = 100000.0
minIndex = 0
## for each centroid
## step 2: find the centroid who is closest
for j in range(k):
distance = euclDistance(centroids[j, :], dataSet[i, :])
if distance < minDist:
minDist = distance
minIndex = j
## step 3: update its cluster
if clusterAssment[i, 0] != minIndex:
clusterChanged = True
clusterAssment[i, :] = minIndex, minDist**2
## step 4: update centroids
for j in range(k):
pointsInCluster = dataSet[nonzero(clusterAssment[:, 0].A == j)[0]]
centroids[j, :] = mean(pointsInCluster, axis = 0)
print ('Congratulations, cluster complete!')
return centroids, clusterAssment
# show your cluster only available with 2-D data
def showCluster(dataSet, k, centroids, clusterAssment):
numSamples, dim = dataSet.shape
if dim != 2:
print ("Sorry! I can not draw because the dimension of your data is not 2!")
return 1
mark = ['or', 'ob', 'og', 'ok', '^r', '+r', 'sr', 'dr', ' len(mark):
print ("Sorry! Your k is too large! please contact Zouxy" )
return 1
# draw all samples
for i in range(numSamples):
markIndex = int(clusterAssment[i, 0])
plt.plot(dataSet[i, 0], dataSet[i, 1], mark[markIndex])
mark = ['Dr', 'Db', 'Dg', 'Dk', '^b', '+b', 'sb', 'db', '
此为数据集:
1.658985 4.285136
-3.453687 3.424321
4.838138 -1.151539
-5.379713 -3.362104
0.972564 2.924086
-3.567919 1.531611
0.450614 -3.302219
-3.487105 -1.724432
2.668759 1.594842
-3.156485 3.191137
3.165506 -3.999838
-2.786837 -3.099354
4.208187 2.984927
-2.123337 2.943366
0.704199 -0.479481
-0.392370 -3.963704
2.831667 1.574018
-0.790153 3.343144
2.943496 -3.357075
-3.195883 -2.283926
2.336445 2.875106
-1.786345 2.554248
2.190101 -1.906020
-3.403367 -2.778288
1.778124 3.880832
-1.688346 2.230267
2.592976 -2.054368
-4.007257 -3.207066
2.257734 3.387564
-2.679011 0.785119
0.939512 -4.023563
-3.674424 -2.261084
2.046259 2.735279
-3.189470 1.780269
4.372646 -0.822248
-2.579316 -3.497576
1.889034 5.190400
-0.798747 2.185588
2.836520 -2.658556
-3.837877 -3.253815
2.096701 3.886007
-2.709034 2.923887
3.367037 -3.184789
-2.121479 -4.232586
2.329546 3.179764
-3.284816 3.273099
3.091414 -3.815232
-3.762093 -2.432191
3.542056 2.778832
-1.736822 4.241041
2.127073 -2.983680
-4.323818 -3.938116
3.792121 5.135768
-4.786473 3.358547
2.624081 -3.260715
-4.009299 -2.978115
2.493525 1.963710
-2.513661 2.642162
1.864375 -3.176309
-3.171184 -3.572452
2.894220 2.489128
-2.562539 2.884438
3.491078 -3.947487
-2.565729 -2.012114
3.332948 3.983102
-1.616805 3.573188
2.280615 -2.559444
-2.651229 -3.103198
2.321395 3.154987
-1.685703 2.939697
3.031012 -3.620252
-4.599622 -2.185829
4.196223 1.126677
-2.133863 3.093686
4.668892 -2.562705
-2.793241 -2.149706
2.884105 3.043438
-2.967647 2.848696
4.479332 -1.764772
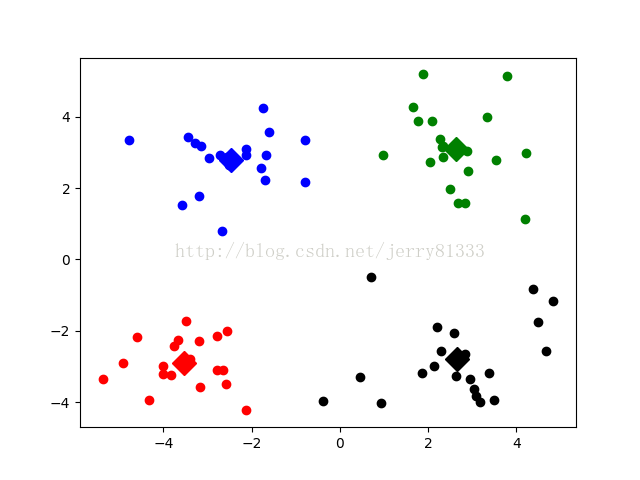
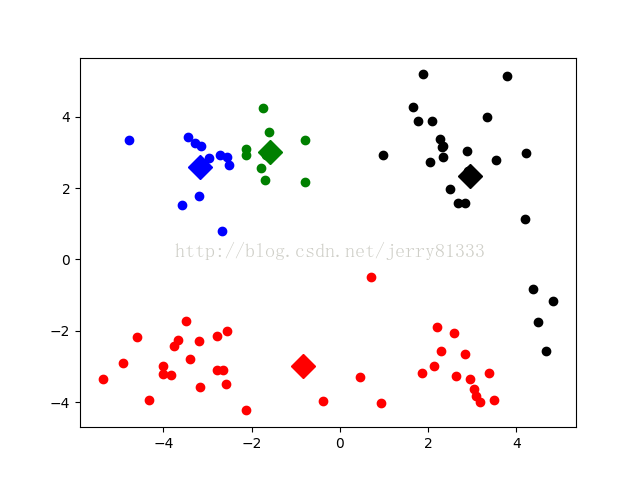
-4.905566 -2.911070 效果图:
因为仅使用了最基础的K-means算法,并且随机初始点,因此有一定概率出现不好的聚类情况,如下图: