- (五)PS识别:压缩痕迹挖掘-压缩量化表与 DCT 系数分析
超龄超能程序猿
机器学习python图像处理人工智能计算机视觉
(一)PS识别:Python图像分析PS识别之道(二)PS识别:特征识别-直方图分析的从原理到实现(三)PS识别:基于噪声分析PS识别的技术实现(四)PS识别:基于边缘纹理检测分析PS识别的技术实现一介绍本文将介绍一种基于量化表分析和DCT系数分析的图片PS检测方法,帮助你判断图片是否经过处理。二实现原理量化表分析在JPEG图片的压缩过程中,量化表起着关键作用。不同的软件或处理操作可能会改变量化表
- Python高频面试题(四)
Irene-HQ
测试python自动化测试python开发语言面试测试工具githubpycharm
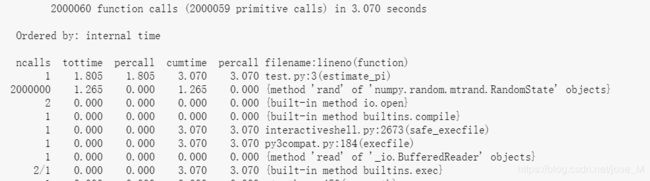
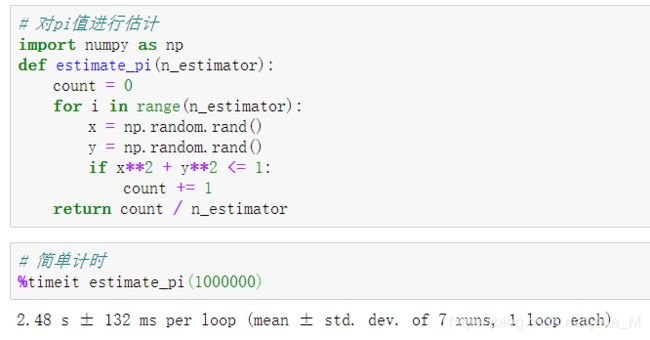
以下是Python研发和自动化测试面试中更高阶的专项考点及典型问题一、并发与异步编程(高级)GIL全局解释器锁的应对策略问题:GIL如何影响Python多线程性能?如何绕过GIL限制?答案:GIL使同一时刻仅一个线程执行字节码,CPU密集型任务性能受限绕过方案:使用多进程(multiprocessing)、C扩展(如Cython)、异步IO(asyncio)46协程异步调用示例问题:
- Python常考面试题汇总(附答案)
TT图图
面试职场和发展
写在前面本文面向中高级Python开发,太基本的题目不收录。本文只涉及Python相关的面试题,关于网络、MySQL、算法等其他面试必考题会另外开专题整理。不是单纯的提供答案,抵制八股文!!更希望通过代码演示,原理探究等来深入讲解某一知识点,做到融会贯通。部分演示代码也放在了我的github的该目录下。语言基础篇Python的基本数据类型Python3中有六个标准的数据类型:Number(数字)(
- Python 编程基础作业总结
本周主要围绕Python基础编程展开了学习,通过一系列的作业题来巩固所学知识。这些题目涵盖了输入输出、条件判断、循环结构等多个基础知识点,下面将对每道作业题进行详细分析。1.计算指定月份第一天是星期几题目描述编写一个程序,接受用户输入的一个年份和一个月份,输出该月份的第一天是星期几。使用蔡乐公式计算星期。提示:使用蔡乐公式计算星期。W=((26*M-2)/10+D+Y+Y/4+C/4-2*C)%7
- 交叉编译Python-3.6.0到aarch64/aarch32 —— 支持sqlite3
参考https://datko.net/2013/05/10/cross-compiling-python-3-3-1-for-beaglebone-arm-angstrom/平台主机:ubuntu14.0464bit开发板:qemu+aarch64(参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/pengdonglin137/p/6442583.html)工具链:aarch64-linux-
- python# python:3.5 aarch64构建镜像
Ling丶落
centos
构建失败从ubuntu中尝试构建FROMpython:3.5-slimLABELMAINTAINER="
[email protected]"#installrelatedpackagesENVENVIRONMENTDOCKER_PRODWORKDIR/workCOPY./dataset.py/work/dataset.pyCOPY./model.py/work/model.pyCOPY./PyA
- opencv-python与opencv-contrib-python的区别联系
剑心缘
零碎小知识pythonopencv
opencv-python包含基本的opencvopencv-contrib-python是高配版,带一些收费或者专利的算法,还有一些比较新的算法的高级版本,这些算法稳定之后会加入上面那个。官网对contrib模块的简介(点击链接跳转)参考链接
- 【计算机毕业设计】基于Springboot的办公用品管理系统+LW
枫叶学长(专业接毕设)
Java毕业设计实战案例课程设计springboot后端
博主介绍:✌全网粉丝3W+,csdn特邀作者、CSDN新星计划导师、Java领域优质创作者,掘金/华为云/阿里云/InfoQ等平台优质作者、专注于Java技术领域和学生毕业项目实战,高校老师/讲师/同行前辈交流✌技术范围:SpringBoot、Vue、SSM、HLMT、Jsp、PHP、Nodejs、Python、爬虫、数据可视化、小程序、安卓app、大数据、物联网、机器学习等设计与开发。主要内容:
- 两步移动搜索法(2SFCA)python
我在北京coding
pythonpython开发语言
实现两步移动搜索法(Two-StepFloatingCatchmentAreaMethod,2SFCA)是一种广泛应用于地理信息系统(GIS)领域的方法,用于评估设施的空间可达性。以下是基于Python和GeoPandas的一种实现方式。准备工作为了实现2SFCA方法,需要准备以下数据集:供给点:表示服务提供方的位置及其服务能力。需求点:表示潜在使用者的位置及其需求量。距离矩阵:描述供给点与需求点
- Java、python中高级开发工程师岗位框架要求统计
爱吃土豆的马铃薯ㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤㅤ
javapython开发语言
一、主流框架使用频率框架/技术出现频率说明SpringBoot89%几乎成为Java后端开发的标配,用于快速构建微服务和独立应用。SpringCloud76%微服务架构必备,提供服务发现、配置管理、网关等核心组件。MyBatis/MyBatis-Plus72%最流行的ORM框架,MyBatis-Plus进一步简化开发。Spring68%基础框架,中高级岗位要求深入理解IoC、AOP原理。Hiber
- PPOCRLabel 环境配置教程
ysh9888
人工智能算法计算机视觉opencv
PPOCRLabel环境配置教程_哔哩哔哩_bilibili1安装conda2新建环境condacreate--nameppocrpython=3.8--channelhttps://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/anaconda/pkgs/free/condaactivateppocrpipinstall-rrequirements.txt-ihttps://pypi
- response.split(“\n“)[0].strip() 是什么
ZhangJiQun&MXP
教学2021AIpythonpython机器学习人工智能语言模型自然语言处理
response.split(“\n”)[0].strip()是什么returnresponse.split("\n")[0].strip()这行代码在Python中通常用于对字符串进行处理并返回处理后的结果response.split("\n"):split()是Python字符串对象的一个方法,用于根据指定的分隔符将字符串拆分成一个列表。在这行代码中,"\n"作为分隔符,表示按照换行符来拆分字
- Python函数
python知识
1文档字符串函数定义下的第一个字符串是文档字符串,用于解释函数。可以通过help(function_name)或function_name.__doc__来查看。2函数返回单个返回值:return一个值无返回值:函数执行完毕没有return语句,或者return后面没有值,会隐式地返回None返回多个值:实际上是返回一个包含所有值的元组(tuple)3参数函数声明:使用def关键字来创建函数默认参
- Python-selenium爬取
藏在歌词里
pythonselenium开发语言
selenium前言使用python的requests模块还是存在很大的局限性,例如:只发一次请求;针对ajax动态加载的网页则无法获取数据等等问题。特此,本章节将通过selenium模拟浏览器来完成更高级的爬虫抓取任务。什么是seleniumSelenium是一个用于自动化Web应用程序测试的开源工具集。它提供了一组API和工具,可以与多种编程语言一起使用,如Java、Python、C#等,用于
- python --飞浆离线ocr使用/paddleocr
依赖#python==3.7.3paddleocr==2.7.0.2paddlepaddle==2.5.2loguru==0.7.3frompaddleocrimportPaddleOCRimportcv2importnumpyasnpif__name__=='__main__':OCR=PaddleOCR(use_doc_orientation_classify=False,#检测文档方向use
- 【PaddleOCR】OCR文本检测与文本识别数据集整理,持续更新......
博主简介:曾任某智慧城市类企业算法总监,目前在美国市场的物流公司从事高级算法工程师一职,深耕人工智能领域,精通python数据挖掘、可视化、机器学习等,发表过AI相关的专利并多次在AI类比赛中获奖。CSDN人工智能领域的优质创作者,提供AI相关的技术咨询、项目开发和个性化解决方案等服务,如有需要请站内私信或者联系任意文章底部的的VX名片(ID:xf982831907)博主粉丝群介绍:①群内初中生、
- 说话人识别python_基于各种分类算法的说话人识别(年龄段识别)
weixin_39673184
说话人识别python
基于各种分类算法的语音分类(年龄段识别)概述实习期间作为帮手打杂进行了一段时间的语音识别研究,内容是基于各种分类算法的语音的年龄段识别,总结一下大致框架,基本思想是:获取语料库TIMIT提取数据特征,进行处理MFCC/i-vectorLDA/PLDA/PCA语料提取,基于分类算法进行分类SVM/SVR/GMM/GBDT...用到的工具有HTK(C,shell)/Kaldi(C++,shell)/L
- llama-cpp-python使用教程
try2find
llamapython开发语言
以下是llama-cpp-python的完整使用教程,涵盖安装、基础用法、高级功能(如GPU加速、多模态等)和常见问题解决。1.安装1.1基础安装(CPU版)pipinstallllama-cpp-python-ihttps://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple1.2启用GPU加速(CUDA)CMAKE_ARGS="-DGGML_CUDA=ON"pipinstall
- 【Python】列表嵌套字典多规则排序
魔都吴所谓
Python算法工具python服务器java
数据a=[{"project":"pro_613","branchList":[]},{"project":"pro_614","branchList":[]},{"project":"pro_612","branchList":[]},{"project":"pro_631","branchList":[]},{"project":"pro_617","branchList":[]},{"pro
- Redis存储Cookie实现爬虫保持登录 requests | selenium
前言前面已经介绍了requests和selenium这两种方式的基础知识和模拟登录,但是我们需要每次都进行登录,这明显是很麻烦并且不合理的,所以这次我分享一下怎么可以让我们的程序进行一次登录之后,和普通浏览器一样下次不进行登录直接进行对网站数据的爬取下面的我分享的内容需要前置知识,如果同志有知识不理解,可以查看我以前写的文章Python爬虫request三方库实战-CSDN博客Python爬虫XP
- Requestium - 将Requests和Selenium合并在一起的自动化测试工具
测试界晓晓
软件测试测试工具selenium自动化软件测试功能测试自动化测试程序人生
Requests是Python的第三方库,主要用于发送http请求,常用于接口自动化测试等。Selenium是一个用于Web应用程序的自动化测试工具。Selenium测试直接运行在浏览器中,就像真正的用户在操作一样。本篇介绍一款将Requests和Selenium结合在一起的自动化测试工具-Requestium简介Requestium是一个Python库,它将Requests、Selenium和P
- 深度解析:venv和conda如何解决依赖冲突难题
咕咕日志
condapython
文章目录前言一、虚拟环境的核心价值1.1依赖冲突的典型场景1.2隔离机制实现原理二、venv与conda的架构对比2.1工具定位差异2.2性能基准测试(以创建环境+安装numpy为例)三、venv的配置与最佳实践3.1基础工作流3.2多版本Python管理四、conda的进阶应用4.1环境创建与通道配置4.2混合使用conda与pip的风险控制4.3跨平台环境导出五、工具选型决策树5.1场景化推荐
- 冒泡排序算法详解(含Python代码实现)
算法_小学生
算法
冒泡排序(BubbleSort)是最基础的排序算法之一,通常用于学习排序算法的入门理解。本文将通过Python代码实现冒泡排序,并详细讲解其原理、执行流程、复杂度分析及适用情况。✨一、算法简介冒泡排序的核心思想是:相邻两个元素比较,将较大的元素不断“冒泡”至右侧,最终实现排序。其基本过程是重复比较相邻的元素,如果顺序错误就交换,重复这一过程,直到没有任何需要交换的为止。二、Python代码实现下面
- PyTorch中 item()、tolist()使用详解和实战示例
点云SLAM
PyTorch深度学习pytorch人工智能python深度学习张量的操作itemtolist
在PyTorch中,.item()和.tolist()是两个常用于从Tensor中提取Python原生数据的方法,尤其在调试、日志记录或将结果传给非张量库时非常有用。下面是它们的详解与代码示例。1..item()方法用途:将仅包含一个元素的张量(即标量张量)转换为对应的Python原生数据类型(float,int,等)。限制:只能用于只包含一个元素的Tensor,否则会报错。示例代码:import
- Github 2025-07-05 Rust开源项目日报Top10
老孙正经胡说
githubrust开源Github趋势分析开源项目PythonGolang
根据GithubTrendings的统计,今日(2025-07-05统计)共有10个项目上榜。根据开发语言中项目的数量,汇总情况如下:开发语言项目数量Rust项目10TypeScript项目1uv:极快的Python软件包安装程序和解析器创建周期:147天开发语言:Rust协议类型:ApacheLicense2.0Star数量:7066个Fork数量:200次关注人数:7066人贡献人数:45人O
- JSONLines和JSON数据格式使用教程
Cachel wood
现代程序设计技术jsonjsonlines贪心算法算法sparkajax大数据
文章目录一、核心区别二、JSONLines的优势三、Python中使用JSONLines1.写入JSONLines文件2.读取JSONLines文件3.处理大文件示例四、常见工具支持1.命令行工具2.编程语言库五、适用场景选择六、注意事项总结JSONLines(简称jsonl或jl)和传统JSON都是用于存储结构化数据的格式,但它们的设计目标和使用场景有所不同。以下是详细对比和使用指南:一、核心区
- 图像分割技术详解:从原理到实践
lanjieying
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:图像分割是图像处理领域将图像分解为多个区域的过程,用于图像分析、特征提取等。文章介绍了图像分割的原理,并通过一个将图像划分为2*4子块的示例,展示了如何使用Python和matplotlib库中的tight_subplot函数进行图像分割和展示。文章还探讨了图像分割在不同领域的应用,以及如何在机器学习项目中作为数据预处理步骤。1.图像分割基本概念在图像处理领域
- 【机器学习笔记Ⅰ】7 向量化
巴伦是只猫
机器学习机器学习笔记人工智能
向量化(Vectorization)详解向量化是将数据或操作转换为向量(或矩阵)形式,并利用并行计算高效处理的技术。它是机器学习和数值计算中的核心优化手段,能显著提升代码运行效率(尤其在Python中避免显式循环)。1.为什么需要向量化?(1)传统循环的缺陷低效:Python的for循环逐元素操作,速度慢。代码冗长:需手动处理每个元素。示例:计算两个数组的点积(非向量化)a=[1,2,3]b=[4
- 【Python】python_jwt
宅男很神经
python开发语言
1.1传统会话(Session)机制的黄金时代与黄昏在Web应用的黎明时期,身份验证的范式几乎完全由**基于服务器端会话(Session-BasedAuthentication)**的机制所主导。这是一个直观且在单体应用时代极其有效的模型,其工作流程如同一场精密的双人舞:凭证交换与“储物柜钥匙”的签发:用户在登录页面输入用户名和密码。这些凭证被发送到服务器。服务器验证其有效性后,会在自己的“储物间
- 【Python】simulink与python联合仿真
1.1Simulink的边界:事件驱动、算法复杂性与AI集成瓶颈Simulink的核心优势在于其强大的微分方程求解器和对连续时间系统、离散时间系统的精确描述能力。其基于“信号流”和“框图”的建模范式,使得工程师可以直观地构建与物理现实高度对应的数学模型。然而,这种优势也带来了其天然的局限性:基于时间的驱动核心(Time-BasedCoreEngine):Simulink的“心脏”是一个时间驱动的仿
- 多线程编程之理财
周凡杨
java多线程生产者消费者理财
现实生活中,我们一边工作,一边消费,正常情况下会把多余的钱存起来,比如存到余额宝,还可以多挣点钱,现在就有这个情况:我每月可以发工资20000万元 (暂定每月的1号),每月消费5000(租房+生活费)元(暂定每月的1号),其中租金是大头占90%,交房租的方式可以选择(一月一交,两月一交、三月一交),理财:1万元存余额宝一天可以赚1元钱,
- [Zookeeper学习笔记之三]Zookeeper会话超时机制
bit1129
zookeeper
首先,会话超时是由Zookeeper服务端通知客户端会话已经超时,客户端不能自行决定会话已经超时,不过客户端可以通过调用Zookeeper.close()主动的发起会话结束请求,如下的代码输出内容
Created /zoo-739160015
CONNECTEDCONNECTED
.............CONNECTEDCONNECTED
CONNECTEDCLOSEDCLOSED
- SecureCRT快捷键
daizj
secureCRT快捷键
ctrl + a : 移动光标到行首ctrl + e :移动光标到行尾crtl + b: 光标前移1个字符crtl + f: 光标后移1个字符crtl + h : 删除光标之前的一个字符ctrl + d :删除光标之后的一个字符crtl + k :删除光标到行尾所有字符crtl + u : 删除光标至行首所有字符crtl + w: 删除光标至行首
- Java 子类与父类这间的转换
周凡杨
java 父类与子类的转换
最近同事调的一个服务报错,查看后是日期之间转换出的问题。代码里是把 java.sql.Date 类型的对象 强制转换为 java.sql.Timestamp 类型的对象。报java.lang.ClassCastException。
代码:
- 可视化swing界面编辑
朱辉辉33
eclipseswing
今天发现了一个WindowBuilder插件,功能好强大,啊哈哈,从此告别手动编辑swing界面代码,直接像VB那样编辑界面,代码会自动生成。
首先在Eclipse中点击help,选择Install New Software,然后在Work with中输入WindowBui
- web报表工具FineReport常用函数的用法总结(文本函数)
老A不折腾
finereportweb报表工具报表软件java报表
文本函数
CHAR
CHAR(number):根据指定数字返回对应的字符。CHAR函数可将计算机其他类型的数字代码转换为字符。
Number:用于指定字符的数字,介于1Number:用于指定字符的数字,介于165535之间(包括1和65535)。
示例:
CHAR(88)等于“X”。
CHAR(45)等于“-”。
CODE
CODE(text):计算文本串中第一个字
- mysql安装出错
林鹤霄
mysql安装
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -ivh MySQL-server-5.5.24-1.linux2.6.x86_64.rpm Preparing... #####################
- linux下编译libuv
aigo
libuv
下载最新版本的libuv源码,解压后执行:
./autogen.sh
这时会提醒找不到automake命令,通过一下命令执行安装(redhat系用yum,Debian系用apt-get):
# yum -y install automake
# yum -y install libtool
如果提示错误:make: *** No targe
- 中国行政区数据及三级联动菜单
alxw4616
近期做项目需要三级联动菜单,上网查了半天竟然没有发现一个能直接用的!
呵呵,都要自己填数据....我了个去这东西麻烦就麻烦的数据上.
哎,自己没办法动手写吧.
现将这些数据共享出了,以方便大家.嗯,代码也可以直接使用
文件说明
lib\area.sql -- 县及县以上行政区划分代码(截止2013年8月31日)来源:国家统计局 发布时间:2014-01-17 15:0
- 哈夫曼加密文件
百合不是茶
哈夫曼压缩哈夫曼加密二叉树
在上一篇介绍过哈夫曼编码的基础知识,下面就直接介绍使用哈夫曼编码怎么来做文件加密或者压缩与解压的软件,对于新手来是有点难度的,主要还是要理清楚步骤;
加密步骤:
1,统计文件中字节出现的次数,作为权值
2,创建节点和哈夫曼树
3,得到每个子节点01串
4,使用哈夫曼编码表示每个字节
- JDK1.5 Cyclicbarrier实例
bijian1013
javathreadjava多线程Cyclicbarrier
CyclicBarrier类
一个同步辅助类,它允许一组线程互相等待,直到到达某个公共屏障点 (common barrier point)。在涉及一组固定大小的线程的程序中,这些线程必须不时地互相等待,此时 CyclicBarrier 很有用。因为该 barrier 在释放等待线程后可以重用,所以称它为循环的 barrier。
CyclicBarrier支持一个可选的 Runnable 命令,
- 九项重要的职业规划
bijian1013
工作学习
一. 学习的步伐不停止 古人说,活到老,学到老。终身学习应该是您的座右铭。 世界在不断变化,每个人都在寻找各自的事业途径。 您只有保证了足够的技能储
- 【Java范型四】范型方法
bit1129
java
范型参数不仅仅可以用于类型的声明上,例如
package com.tom.lang.generics;
import java.util.List;
public class Generics<T> {
private T value;
public Generics(T value) {
this.value =
- 【Hadoop十三】HDFS Java API基本操作
bit1129
hadoop
package com.examples.hadoop;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileStatus;
import org.apache.hadoo
- ua实现split字符串分隔
ronin47
lua split
LUA并不象其它许多"大而全"的语言那样,包括很多功能,比如网络通讯、图形界面等。但是LUA可以很容易地被扩展:由宿主语言(通常是C或 C++)提供这些功能,LUA可以使用它们,就像是本来就内置的功能一样。LUA只包括一个精简的核心和最基本的库。这使得LUA体积小、启动速度快,从 而适合嵌入在别的程序里。因此在lua中并没有其他语言那样多的系统函数。习惯了其他语言的字符串分割函
- java-从先序遍历和中序遍历重建二叉树
bylijinnan
java
public class BuildTreePreOrderInOrder {
/**
* Build Binary Tree from PreOrder and InOrder
* _______7______
/ \
__10__ ___2
/ \ /
4
- openfire开发指南《连接和登陆》
开窍的石头
openfire开发指南smack
第一步
官网下载smack.jar包
下载地址:http://www.igniterealtime.org/downloads/index.jsp#smack
第二步
把smack里边的jar导入你新建的java项目中
开始编写smack连接openfire代码
p
- [移动通讯]手机后盖应该按需要能够随时开启
comsci
移动
看到新的手机,很多由金属材质做的外壳,内存和闪存容量越来越大,CPU速度越来越快,对于这些改进,我们非常高兴,也非常欢迎
但是,对于手机的新设计,有几点我们也要注意
第一:手机的后盖应该能够被用户自行取下来,手机的电池的可更换性应该是必须保留的设计,
- 20款国外知名的php开源cms系统
cuiyadll
cms
内容管理系统,简称CMS,是一种简易的发布和管理新闻的程序。用户可以在后端管理系统中发布,编辑和删除文章,即使您不需要懂得HTML和其他脚本语言,这就是CMS的优点。
在这里我决定介绍20款目前国外市面上最流行的开源的PHP内容管理系统,以便没有PHP知识的读者也可以通过国外内容管理系统建立自己的网站。
1. Wordpress
WordPress的是一个功能强大且易于使用的内容管
- Java生成全局唯一标识符
darrenzhu
javauuiduniqueidentifierid
How to generate a globally unique identifier in Java
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/21536572/generate-unique-id-in-java-to-label-groups-of-related-entries-in-a-log
http://stackoverflow
- php安装模块检测是否已安装过, 使用的SQL语句
dcj3sjt126com
sql
SHOW [FULL] TABLES [FROM db_name] [LIKE 'pattern']
SHOW TABLES列举了给定数据库中的非TEMPORARY表。您也可以使用mysqlshow db_name命令得到此清单。
本命令也列举数据库中的其它视图。支持FULL修改符,这样SHOW FULL TABLES就可以显示第二个输出列。对于一个表,第二列的值为BASE T
- 5天学会一种 web 开发框架
dcj3sjt126com
Web框架framework
web framework层出不穷,特别是ruby/python,各有10+个,php/java也是一大堆 根据我自己的经验写了一个to do list,按照这个清单,一条一条的学习,事半功倍,很快就能掌握 一共25条,即便很磨蹭,2小时也能搞定一条,25*2=50。只需要50小时就能掌握任意一种web框架
各类web框架大同小异:现代web开发框架的6大元素,把握主线,就不会迷路
建议把本文
- Gson使用三(Map集合的处理,一对多处理)
eksliang
jsongsonGson mapGson 集合处理
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2175532 一、概述
Map保存的是键值对的形式,Json的格式也是键值对的,所以正常情况下,map跟json之间的转换应当是理所当然的事情。 二、Map参考实例
package com.ickes.json;
import java.lang.refl
- cordova实现“再点击一次退出”效果
gundumw100
android
基本的写法如下:
document.addEventListener("deviceready", onDeviceReady, false);
function onDeviceReady() {
//navigator.splashscreen.hide();
document.addEventListener("b
- openldap configuration leaning note
iwindyforest
configuration
hostname // to display the computer name
hostname <changed name> // to change
go to: /etc/sysconfig/network, add/modify HOSTNAME=NEWNAME to change permenately
dont forget to change /etc/hosts
- Nullability and Objective-C
啸笑天
Objective-C
https://developer.apple.com/swift/blog/?id=25
http://www.cocoachina.com/ios/20150601/11989.html
http://blog.csdn.net/zhangao0086/article/details/44409913
http://blog.sunnyxx
- jsp中实现参数隐藏的两种方法
macroli
JavaScriptjsp
在一个JSP页面有一个链接,//确定是一个链接?点击弹出一个页面,需要传给这个页面一些参数。//正常的方法是设置弹出页面的src="***.do?p1=aaa&p2=bbb&p3=ccc"//确定目标URL是Action来处理?但是这样会在页面上看到传过来的参数,可能会不安全。要求实现src="***.do",参数通过其他方法传!//////
- Bootstrap A标签关闭modal并打开新的链接解决方案
qiaolevip
每天进步一点点学习永无止境bootstrap纵观千象
Bootstrap里面的js modal控件使用起来很方便,关闭也很简单。只需添加标签 data-dismiss="modal" 即可。
可是偏偏有时候需要a标签既要关闭modal,有要打开新的链接,尝试多种方法未果。只好使用原始js来控制。
<a href="#/group-buy" class="btn bt
- 二维数组在Java和C中的区别
流淚的芥末
javac二维数组数组
Java代码:
public class test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] a = {{1},{2,3},{4,5,6}};
System.out.println(a[0][1]);
}
}
运行结果:
Exception in thread "mai
- systemctl命令用法
wmlJava
linuxsystemctl
对比表,以 apache / httpd 为例 任务 旧指令 新指令 使某服务自动启动 chkconfig --level 3 httpd on systemctl enable httpd.service 使某服务不自动启动 chkconfig --level 3 httpd off systemctl disable httpd.service 检查服务状态 service h