CentOS7下Apache kylin2.5.0安装与配置(一篇就够)
系统:CentOS7
所需环境版本三台CentOS7虚拟机,并确认能互相ping通且支持ssh免密登录,确保防火墙关闭且开机不启动状态,请提前配置。
三台都需要设置
我的三台ip分别为
master 192.168.0.180
slave1 192.168.0.181
slave2 192.168.0.182
以下软件均为64位版本
1:JDK1.8.0_161
2:Hadoop2.7.6
3:zookeeper3.4.10
4:kafka_2.11-0.11.0.2(不需要可跳过,不影响后续正常运行)
5:Hbase1.2.6
6:hive1.2.2
7:kylin2.5.0
以上软件下载地址------->>>>>>>
https://blog.csdn.net/kuaikuai_945/article/details/97923878
准备好以上安装包,开始安装和配置
一、安装配置jdk
根目录下创建 public 文件夹
将jdk-8u161-linux-x64.tar.gz拷贝到public目录下,实行解压命令
tar -vzxf jdk-8u161-linux-x64.tar.gz根目录下 /usr/下创建java目录,然后将解压后的文件拷贝到java目录下并改名
mv /public/jdk1.8.0_161 /usr/java设置Java 环境
vim /etc/profile在文件的最后一行添加以下
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk1.8.0_161
export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
export CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar输入以下命令,确保环境变量生效
source /etc/profile输入 java -version查看java版本配置是否正确
以上操作,在三台虚拟机中都需要配置。
二、Hadoop安装
将hadoop-2.7.6.tar.gz拷贝到public目录下,实行解压命令
tar -vzxf hadoop-2.7.6.tar.gz将解压后的文件拷贝到opt目录下并改名
mv public/hadoop-2.7.6 /opt/hadoop设置 环境
vim /etc/profile在文件的最后一行添加以下
export HADOOP_HOME=/opt/hadoop
export PATH=$PATH:$HADOOP_HOME/bin输入以下命令,确保环境变量生效
source /etc/profile输入 hadoop version查看hadoop版本配置是否正确
在/opt/hadoop的路径下创建这四个文件夹
- hadoop/hdfs
- hadoop/hdfs/tmp
- hadoop/hdfs/name
- hadoop/hdfs/data
进入到/opt/hadoop/etc/hadoop/路径下
最后一行添加JAVA_HOME环境到hadoop-env.sh和yarn-env.sh
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk1.8.0_161配置以下文件
core-site.xml
fs.default.name
hdfs://master:9000
hadoop.tmp.dir
file:/opt/hadoop/hdfs/tmp
io.file.buffer.size
131702
hdfs-site.xml
dfs.replication
2
dfs.namenode.name.dir
file:/opt/hadoop/hdfs/name
true
dfs.datanode.data.dir
file:/opt/hadoop/hdfs/data
true
dfs.namenode.secondary.http-address
192.168.0.180:9001
dfs.webhdfs.enabled
true
dfs.namenode.http.address
192.168.0.180:50070
mapred-site.xml
mapreduce.framework.name
yarn
mapreduce.jobhistory.address
192.168.0.180:10020
mapreduce.jobhistory.webapp.address
192.168.0.180:19888
yarn-site.xml
yarn.nodemanager.aux-services
mapreduce_shuffle
yarn.nodemanager.aux-services.mapreduce.shuffle.class
org.apache.hadoop.mapred.ShuffleHandler
yarn.resourcemanager.address
master:8032
yarn.resourcemanager.scheduler.address
master:8030
yarn.resourcemanager.resource-tracker.address
master:8031
yarn.resourcemanager.admin.address
master:8033
yarn.resourcemanager.webapp.address
master:8088
编辑slaves文件:
清空slaves,再加入从节点的名字
master
slave1
slave2
root用户下,将hadoop分发到各个节点
scp -r /opt/hadoop slave1:/opt/hadoop
scp -r /opt/hadoop slave2:/opt/hadoop只需在master服务器启动hadoop,从节点会自动启动,进入/opt/hadoop目录
(1)初始化,输入命令
bin/hdfs namenode -format (2)全部启动
sbin/start-all.sh(3)启动jobhistoryserver
sbin/mr-jobhistory-daemon.sh start historyserver(4)终止服务器
sbin/stop-all.sh (5)查看hadoop启动状态
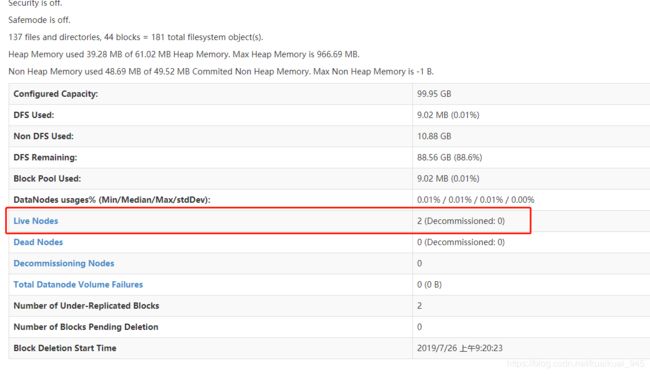
http://192.168.0.180:8088/
http://192.168.0.180:50070/
三、zookeeper安装
将zookeeper-3.4.10.tar.gz拷贝到public目录下,实行解压命令
tar -vzxf zookeeper-3.4.10.tar.gz将解压后的文件拷贝到opt/hadoop/目录下并改名
mv public/zookeeper-3.4.10 /opt/hadoop/zookeeper建立数据目录
mkdir /opt/hadoop/zookeeper/data
chown -R hadoop:hadoop /opt/hadoop/zookeeper/datazookeeper/conf/目录下复制zoo文件并配置
cp zoo_sample.cfg zoo.cfgzoo.cfg
# The number of milliseconds of each tick
tickTime=2000
# The number of ticks that the initial
# synchronization phase can take
initLimit=10
# The number of ticks that can pass between
# sending a request and getting an acknowledgement
syncLimit=5
# the directory where the snapshot is stored.
# do not use /tmp for storage, /tmp here is just
# example sakes.
dataDir=/opt/hadoop/zookeeper/data
# the port at which the clients will connect
clientPort=2181
# the maximum number of client connections.
# increase this if you need to handle more clients
#maxClientCnxns=60
#
# Be sure to read the maintenance section of the
# administrator guide before turning on autopurge.
#
# http://zookeeper.apache.org/doc/current/zookeeperAdmin.html#sc_maintenance
#
# The number of snapshots to retain in dataDir
#autopurge.snapRetainCount=3
# Purge task interval in hours
# Set to "0" to disable auto purge feature
#autopurge.purgeInterval=1
server.1=master:2888:3888
server.2=slave1:2888:3888
server.3=slave2:2888:3888在zookeeper/data目录中新建myid文件,文件内容为server.id中的id号
echo 1 > myidroot用户下,将zookeeper分发到各个节点
scp -r /opt/hadoop/zookeeper slave1:/opt/hadoop/zookeeper
scp -r /opt/hadoop/zookeeper slave2:/opt/hadoop/zookeeperslave1虚拟机中将myid的值改为2,slave2虚拟机中将myid的值改为3
三台虚拟机均进行以下环境变量配置
vim /etc/profile
export ZOOKEEPER_HOME=/opt/hadoop/zookeeper
export PATH=$PATH:$ZOOKEEPER_HOME/bin
source /etc/profile启动zookeeper
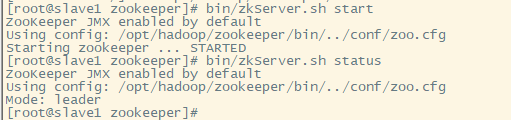
分别在master/slave1/slave2服务器的/opt/hadoop/zookeeper/ 目录下输入:bin/zkServer.sh start
三台虚拟机启动完成后检查启动状态,输入:bin/zkServer.sh status
三个虚拟机中,一个是leader,其它两个是follower,证明zookeeper正常启动
四、Kafka安装(不需要可直接跳过)
将kafka_2.11-1.0.0.tgz拷贝到public目录下,实行解压命令
tar -vzxf kafka_2.11-1.0.0.tgz将解压后的文件拷贝到opt/目录下并改名
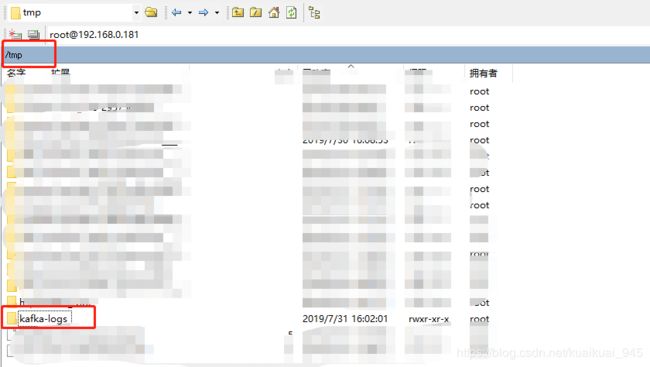
mv public/kafka_2.11-0.11.0.2 /opt/kafka三台虚拟机中,在CentOS根目录下的tmp/目录下,创建kafka-logs目录。
编辑config/目录下的server.properties,并保存修改
server.properties
# Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
# contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
# this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
# The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
# (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
# the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# see kafka.server.KafkaConfig for additional details and defaults
############################# Server Basics #############################
# The id of the broker. This must be set to a unique integer for each broker.
# broker.id=0
# Switch to enable topic deletion or not, default value is false
#delete.topic.enable=true
############################# Socket Server Settings #############################
# The address the socket server listens on. It will get the value returned from
# java.net.InetAddress.getCanonicalHostName() if not configured.
# FORMAT:
# listeners = listener_name://host_name:port
# EXAMPLE:
# listeners = PLAINTEXT://your.host.name:9092
#listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9092
# Hostname and port the broker will advertise to producers and consumers. If not set,
# it uses the value for "listeners" if configured. Otherwise, it will use the value
# returned from java.net.InetAddress.getCanonicalHostName().
#advertised.listeners=PLAINTEXT://your.host.name:9092
# Maps listener names to security protocols, the default is for them to be the same. See the config documentation for more details
#listener.security.protocol.map=PLAINTEXT:PLAINTEXT,SSL:SSL,SASL_PLAINTEXT:SASL_PLAINTEXT,SASL_SSL:SASL_SSL
# The number of threads that the server uses for receiving requests from the network and sending responses to the network
num.network.threads=3
# The number of threads that the server uses for processing requests, which may include disk I/O
num.io.threads=8
# The send buffer (SO_SNDBUF) used by the socket server
socket.send.buffer.bytes=102400
# The receive buffer (SO_RCVBUF) used by the socket server
socket.receive.buffer.bytes=102400
# The maximum size of a request that the socket server will accept (protection against OOM)
socket.request.max.bytes=104857600
############################# Log Basics #############################
# A comma seperated list of directories under which to store log files
# log.dirs=/tmp/kafka-logs
# The default number of log partitions per topic. More partitions allow greater
# parallelism for consumption, but this will also result in more files across
# the brokers.
num.partitions=1
# The number of threads per data directory to be used for log recovery at startup and flushing at shutdown.
# This value is recommended to be increased for installations with data dirs located in RAID array.
num.recovery.threads.per.data.dir=1
############################# Internal Topic Settings #############################
# The replication factor for the group metadata internal topics "__consumer_offsets" and "__transaction_state"
# For anything other than development testing, a value greater than 1 is recommended for to ensure availability such as 3.
offsets.topic.replication.factor=1
transaction.state.log.replication.factor=1
transaction.state.log.min.isr=1
############################# Log Flush Policy #############################
# Messages are immediately written to the filesystem but by default we only fsync() to sync
# the OS cache lazily. The following configurations control the flush of data to disk.
# There are a few important trade-offs here:
# 1. Durability: Unflushed data may be lost if you are not using replication.
# 2. Latency: Very large flush intervals may lead to latency spikes when the flush does occur as there will be a lot of data to flush.
# 3. Throughput: The flush is generally the most expensive operation, and a small flush interval may lead to exceessive seeks.
# The settings below allow one to configure the flush policy to flush data after a period of time or
# every N messages (or both). This can be done globally and overridden on a per-topic basis.
# The number of messages to accept before forcing a flush of data to disk
#log.flush.interval.messages=10000
# The maximum amount of time a message can sit in a log before we force a flush
#log.flush.interval.ms=1000
############################# Log Retention Policy #############################
# The following configurations control the disposal of log segments. The policy can
# be set to delete segments after a period of time, or after a given size has accumulated.
# A segment will be deleted whenever *either* of these criteria are met. Deletion always happens
# from the end of the log.
# The minimum age of a log file to be eligible for deletion due to age
log.retention.hours=168
# A size-based retention policy for logs. Segments are pruned from the log as long as the remaining
# segments don't drop below log.retention.bytes. Functions independently of log.retention.hours.
#log.retention.bytes=1073741824
# The maximum size of a log segment file. When this size is reached a new log segment will be created.
log.segment.bytes=1073741824
# The interval at which log segments are checked to see if they can be deleted according
# to the retention policies
log.retention.check.interval.ms=300000
############################# Zookeeper #############################
# Zookeeper connection string (see zookeeper docs for details).
# This is a comma separated host:port pairs, each corresponding to a zk
# server. e.g. "127.0.0.1:3000,127.0.0.1:3001,127.0.0.1:3002".
# You can also append an optional chroot string to the urls to specify the
# root directory for all kafka znodes.
# zookeeper.connect=localhost:2181
# Timeout in ms for connecting to zookeeper
zookeeper.connection.timeout.ms=6000
############################# Group Coordinator Settings #############################
# The following configuration specifies the time, in milliseconds, that the GroupCoordinator will delay the initial consumer rebalance.
# The rebalance will be further delayed by the value of group.initial.rebalance.delay.ms as new members join the group, up to a maximum of max.poll.interval.ms.
# The default value for this is 3 seconds.
# We override this to 0 here as it makes for a better out-of-the-box experience for development and testing.
# However, in production environments the default value of 3 seconds is more suitable as this will help to avoid unnecessary, and potentially expensive, rebalances during application startup.
group.initial.rebalance.delay.ms=0
broker.id=1
zookeeper.connect=192.168.0.180:2181,192.168.0.181:2181,192.168.0.182:2181
listeners=PLAINTEXT://192.168.0.180:9092将kafka分发到各个节点
scp -r /opt/kafka slave1:/opt/kafka
scp -r /opt/kafka slave2:/opt/kafkaslave1的config/server.properties做以下修改
broker.id=2
listeners=PLAINTEXT://192.168.0.181:9092slave2的config/server.properties做以下修改
broker.id=3
listeners=PLAINTEXT://192.168.0.182:9092启动Kafka
分别在master/slave1/slave2服务器的/opt/kafka/bin/ 目录下输入:
./kafka-server-start.sh -daemon /opt/kafka/config/server.properties 三台虚拟机启动完成后检查启动状态,输入jps查看是否有KaFKa进程,以此来验证启动成功
kafka使用测试
在三台虚拟机的kafka都成功启动之后
master创建topic
kafka目录下输入
bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --zookeeper 192.168.0.180:2181 --replication-factor 1 --partitions 1 --topic test
如果成功的话,会输出:Created topic "test".
查看topic
在master、slave1或者slave2,kafka目录下输入
bin/kafka-topics.sh --list --zookeeper 192.168.0.180:2181
master下创建生产消息
kafka目录下
bin/kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list 192.168.0.180:9092 --topic test
然后输入信息后按Ctrl+C退出。
创建消费
slave1或者slave2,kafka目录下
bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server 192.168.0.180:9092 --topic test --from-beginning
然后就能看到生产消息时保存的信息,按Ctrl+C退出。
到此kafka的安装与测试就完成了。
五、Hbase安装
将hbase-1.2.6-bin.tar.gz拷贝到public目录下,实行解压命令
tar -vzxf hbase-1.2.6-bin.tar.gz将解压后的文件拷贝到opt/目录下并改名
mv public/hbase-1.2.6 /opt/hbase三台虚拟机均进行以下环境变量配置
vim /etc/profile输入以下环境变量
export HBASE_HOME=/opt/hbase
export PATH=$PATH:$HBASE_HOME/bin保存环境变量生效
source /etc/profile/opt/hbase/conf目录下编辑配置以下文件
hbase-site.xml
hbase.master
master:60000
hbase.rootdir
hdfs://master:9000/hbase
hbase.cluster.distributed
true
hbase.zookeeper.quorum
master,slave1,slave2
dfs.replication
1
regionservers
master
slave1
slave2hbase-env.sh
最后一行追加
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk1.8.0_161
export HBASE_MANAGES_ZK=false将hbase分发到各个节点
scp -r /opt/hbase slave1:/opt/hbase
scp -r /opt/hbase slave2:/opt/hbase启动hbase
在master服务器的/opt/hbase/bin 目录下输入:start-hbase.sh
浏览器打开http://192.168.0.180:16010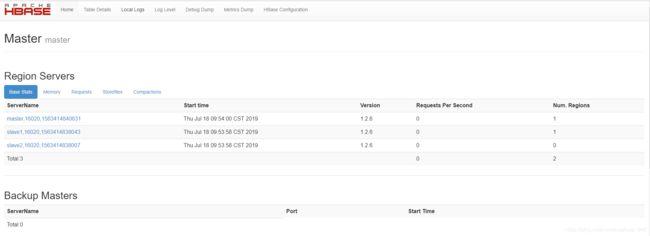
六、hive安装
预先安装mysql
wget http://repo.mysql.com/yum/mysql-5.7-community/el/7/x86_64/mysql57-community-release-el7-10.noarch.rpm将下载的文件引入repo库中
rpm -ivh mysql57-community-release-el7-10.noarch.rpm安装完成之后,启动mysql服务,然后查看端口信息
service mysqld start
netstat -a|grep mysql查询root密码
grep "password" /var/log/mysqld.loglocalhost:密码(注:结尾;也属于密码的一部分)
添加mysql开机自启动
systemctl enable mysqld
systemctl daemon-reload登录root账户
mysql -u root -p输入密码,登录成功之后创建新用户用于hive 的登录,名为abc123,密码是123456
create user abc123 identified by '123456';授权为远程用户并刷新权限
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'abc123'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '123456' WITH GRANT OPTION;
flush privileges;创建 hive 数据库
create database hive;查询编码格式
show variables like 'character%';修改编码方式,编辑etc/my.cnf,追加以下变量
character-set-server=utf8
init_connect='set names utf8'修改完成后重启mysql即可
service mysqld restart通过Navicat测试远程连接访问是否成功。
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------分割线-----------------------------------------------------------------------
将apache-hive-1.2.2-bin.tar.gz拷贝到public目录下并解压
tar -zxvf apache-hive-1.2.2-bin.tar.gz
mv public/apache-hive-1.2.2-bin /opt/hivevi /etc/profile 在最后添加:
export HIVE_HOME=/opt/hive
export PATH=$PATH:$HIVE_HOME/bin使配置文件生效
source /etc/profile到hive/conf目录下,复制以下文件并改名
cp hive-env.sh.template hive-env.sh
cp hive-default.xml.template hive-site.xml
cp hive-log4j2.properties.template hive-log4j2.properties
cp hive-exec-log4j2.properties.template hive-exec-log4j2.propertieshive-site.xml
javax.jdo.option.ConnectionURL
jdbc:mysql://192.168.0.180:3306/hive?createDatabaseIfNotExist=true
JDBC connect string for a JDBC metastore
javax.jdo.option.ConnectionDriverName
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
Driver class name for a JDBC metastore
javax.jdo.option.ConnectionUserName
abc123
username to use against metastore database
javax.jdo.option.ConnectionPassword
123456
password to use against metastore database
hive-env.sh
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk1.8.0_161
export HADOOP_HOME=/opt/hadoop
export HIVE_HOME=/opt/hive
export HIVE_CONF_DIR=/opt/hive/conf下载mysql-connector-java-5.1.32.jar,放入hive/lib目录下
下载地址:https://www.kumapai.com/open/467-mysql-connector-java/5-1-32
在hive 的lib目录下找到jline-2.12.jar,将其拷贝到hadoop/share/hadoop/yarn/lib/目录下
在以上软件都正常启动下,/opt/hive/bin目录下输入hive启动程序
hive出现下图表示正常启动
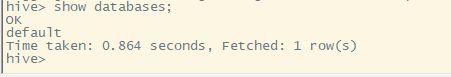
接着输入show databases;查看数据库
到这里就是hive暗转的全部内容了,剩下你可以开心的通过hive操作数据库~
七、Apache Kylin安装
将apache-kylin-2.5.0-bin-hbase1x.tar.gz拷贝到public目录下,实行解压命令
tar -vzxf apache-kylin-2.5.0-bin-hbase1x.tar.gz将解压后的文件拷贝到opt目录下并改名
mv apache-kylin-2.5.0-bin-hbase1x /opt/kylinkylin目录下新建文件夹kylin_meta
mkdir kylin_meta配置conf目录下的kylin.properties,追加以下内容,myDatabaseNeme是在hive里创建的数据库名
kylin.metadata.url=/opt/kylin//kylin_meta
kylin.rest.servers=192.168.0.180:7070
kylin.server.mode=all
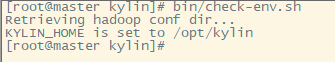
kylin.job.hive.database.for.intermediatetable=myDatabaseName检查kylin环境,bin目录下输入
check-env.sh启动kylin,bin目录下输入
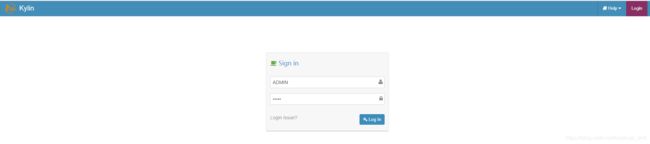
kylin.sh start打开浏览器输入http://192.168.0.1801:7070/kylin
用默认账号密码登录即可
账号:ADMIN
密码:KYLIN