Mybatis运行原理及源码解析
Mybatis源码解析
一、前言
本文旨在mybatis源码解析,将整个mybatis运行原理讲解清楚,本文代码地址:
https://github.com/lchpersonal/mybatis-learn
本文使用的mybatis版本:3.2.8,
jdk版本:1.8
数据库版本:mysql 5.6,数据库脚本如下,此外在源文件为:resources/mybatis.sql
-- 导出 mybatis 的数据库结构
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS `mybatis` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
USE `mybatis`;
-- 导出 表 mybatis.user 结构
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`age` int(11) NOT NULL,
`sex` int(11) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=MyISAM AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- 正在导出表 mybatis.user 的数据:3 rows
DELETE FROM `user`;
INSERT INTO `user` (`id`, `name`, `age`, `sex`) VALUES
(1, '张三', 42, 0),
(2, '李四', 15, 0),
(3, '王五', 45, 0),
(4, '赵六', 47, 0),
(5, '孙艳', 26, 1);
本文主要是探究mybatis运行原理,所以示例项目非常简单,目录结构如下:
mybatis主配置文件mybatis-config.xml内容如下:
<configuration>
<properties resource="dbconfig.properties">properties>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
dataSource>
environment>
environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="UserMapper.xml"/>
mappers>
configuration>
UserMapper.xml的内容如下:
<mapper namespace="com.cl.mybatis.learn.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="selectById" resultType="com.cl.mybatis.learn.user.User">
select * from user where id = #{id}
select>
mapper>
UserMapper.java内容如下:
package com.cl.mybatis.learn.mapper;
import com.cl.mybatis.learn.user.User;
/**
* @Author: chengli
* @Date: 2018/11/24 12:08
*/
public interface UserMapper {
User selectById(int id);
}
Mybatis001.java 主函数内容如下:
package com.cl.mybatis.learn;
/**
* @Author: chengli
* @Date: 2018/11/24 12:00
*/
public class Mybatis001 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
System.out.println(mapper.selectById(1));
} finally {
session.close();
}
}
}
其他内容过于简单,详情请移步github下载源代码查看。
从main函数的运行步骤,本文将主要通过四个部分探讨mybatis的原理:
- SqlSessionFactory的创建
- SqlSession的创建
- UserMapper代理的生成
- 数据库查询操作执行流程
二、SqlSessionFactory的创建
2.1 整体介绍
SqlSessionFactory的创建是SqlSessionFactoryBuilder通过mybatis主配置文件构建出的:
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
SqlSessionFactory var5;
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
/**主要逻辑在下面这行代码*/
var5 = this.build(parser.parse());
}
……
……
return var5;
}
parser.parse()到底做了什么呢?看如下代码:
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
/**解析配置文件中的各种属性*/
this.propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
/**解析别名配置*/
this.typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
/**解析插件配置*/
this.pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
/**解析对象工厂元素*/
this.objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
this.objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
/**解析mybatis的全局设置信息*/
this.settingsElement(root.evalNode("settings"));
/**解析mybatis的环境配置*/
this.environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
this.databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
/**解析类型处理器配置信息*/
this.typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
/**解析mapper配置信息*/
this.mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception var3) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + var3, var3);
}
}
实际上就是解析主配置文件中的各个节点,然后保存在Configuration当中,然后使用Configuration创建出一个DefaultSqlsessionFactory对象,至此过程结束:
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
此处,我们可以重点关注如下两个地方,看看具体在做了什么动作:
this.pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins")); this.mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
以上两个点分别是插件注册,和mapper的扫描注册。
2.2 插件的注册
首先我们先看一下源代码:
private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
Iterator i$ = parent.getChildren().iterator();
while(i$.hasNext()) {
XNode child = (XNode)i$.next();
String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute("interceptor");
Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties();
/**实例化拦截器类*/
Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor)this.resolveClass(interceptor).newInstance();
interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties);
/**将实例化的拦截器类放到configuration中的interceptorChain中*/
this.configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance);
}
}
}
实际上就是通过interceptor标签,解析出拦截器类,然后将其实例化并保存到Configuration类中的InterceptorChain中,以备后用。
public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) {
this.interceptorChain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
2.3 mappers的扫描与解析
this.mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
通过代码我们可以知道,这里主要是解析mappers标签的。我们先来看一下mappers标签里面是什么:
<mappers>
<mapper resource="UserMapper.xml"/>
mappers>
所以他会去解析UserMapper.xml中的内容:
<mapper namespace="com.cl.mybatis.learn.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="selectById" resultType="com.cl.mybatis.learn.user.User">
select * from user where id = #{id}
select>
mapper>
我们看一下源代码:
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
/**如果子节点是配置的package,那么进行包自动扫描处理*/
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
/**如果子节点配置的是resource、url、mapperClass,本文我们使用的是resource*/
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
/**解析resource引入的另外一个xml文件*/
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
下面我们具体看一下他是如何解析另一个xml文件的:
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
/**解析sql语句*/
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
/**解析名称空间,实际上就是对应绑定的接口类*/
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingChacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
下面我们来看一下 configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"))到底做了什么:
public void parseStatementNode() {
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) return;
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: and were parsed and removed)
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? new Jdbc3KeyGenerator() : new NoKeyGenerator();
}
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(
String id,
SqlSource sqlSource,
StatementType statementType,
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType,
Integer fetchSize,
Integer timeout,
String parameterMap,
Class<?> parameterType,
String resultMap,
Class<?> resultType,
ResultSetType resultSetType,
boolean flushCache,
boolean useCache,
boolean resultOrdered,
KeyGenerator keyGenerator,
String keyProperty,
String keyColumn,
String databaseId,
LanguageDriver lang,
String resultSets) {
if (unresolvedCacheRef) throw new IncompleteElementException("Cache-ref not yet resolved");
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlSource, sqlCommandType);
statementBuilder.resource(resource);
statementBuilder.fetchSize(fetchSize);
statementBuilder.statementType(statementType);
statementBuilder.keyGenerator(keyGenerator);
statementBuilder.keyProperty(keyProperty);
statementBuilder.keyColumn(keyColumn);
statementBuilder.databaseId(databaseId);
statementBuilder.lang(lang);
statementBuilder.resultOrdered(resultOrdered);
statementBuilder.resulSets(resultSets);
setStatementTimeout(timeout, statementBuilder);
setStatementParameterMap(parameterMap, parameterType, statementBuilder);
setStatementResultMap(resultMap, resultType, resultSetType, statementBuilder);
setStatementCache(isSelect, flushCache, useCache, currentCache, statementBuilder);
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
}
通过解析一个个的标签,最终将sql语句的所有信息封装成MappedStatement对象,然后存储在configuration对象中。
那么bindMapperForNamespace();又做了什么呢?
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
if (namespace != null) {
Class<?> boundType = null;
try {
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
//ignore, bound type is not required
}
if (boundType != null) {
if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we set a flag
// to prevent loading again this resource from the mapper interface
// look at MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResource
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
}
实际上就是解析该sql对应的class,并把该class放到configuration中的mapperRegistry中。实际上mybatis的所有配置信息以及运行时的配置参数全部都保存在configuration对象中。
所以整个流程可以用如下的时序图表示:
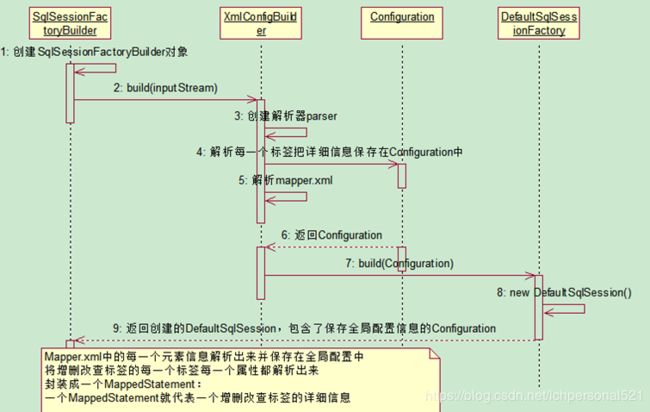
三、SqlSession的创建
我们知道,SqlSessionFactory创建的时候实际上返回的是一个DefaultSqlSessionFactory对象。
当执行openSession()操作的时候,实际上执行的代码如下:
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
/**根据execType创建Executor对象*/
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
从代码可以知道,openSession操作会创建Mybatis四大对象之一的Executor对象,创建过程如下:
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
/**如果开启了二级缓存,executor会被CachingExecutor包装一次*/
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
/**尝试将executor使用interceptorChain中的每个interceptor包装一次(根据配置),这里是对Mybatis强大的插件开发功能做支持*/
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
默认情况下会返回一个SimpleExecutor对象。然后SimpleExecutor被封装到DefaultSqlSession。这里我们需要注意一下,在Executor创建完毕之后,会根据配置是否开启了二级缓存,来决定是否使用CachingExecutor包装一次Executor。最后尝试将executor使用interceptorChain中的每个interceptor包装一次(根据配置),这里是对Mybatis强大的插件开发功能做支持。
四、Mapper代理的生成
当我们使用如下代码:
UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
来获取UserMapper的时候,实际上是从configuration当中的MapperRegistry当中获取UserMapper的代理对象:
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null)
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
knownMappers属性里面的值,实际上就是我们在mappers扫描与解析的时候放进去的。
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
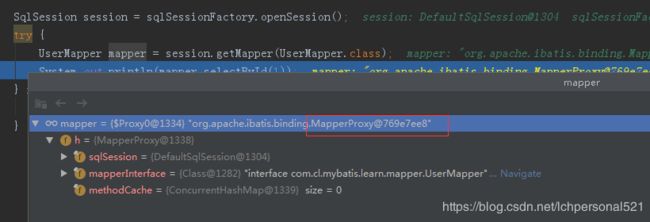
并且MapperProxy实现了InvocationHandler接口,从以上代码可以看出,实际上使用的就是jdk的动态代理,给UserMapper接口生成一个代理对象。实际上就是MapperProxy的一个对象,如下图调试信息所示:
所以整个代理对象生成过程可以用如下时序图表示:
五、执行查询语句
我们知道,我们获取到的UserMapper实际上是代理对象MapperProxy,所以我们执行查询语句的时候实际上执行的是MapperProxy的invoke方法:
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
/**如果调用的是Object原生的方法,则直接放行*/
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
我们再来看看cachedMapperMethod方法:
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
可以看到,先根据方法签名,从方法缓存中获取方法,如果为空,则生成一个MapperMethod放入缓存并返回。
所以最终执行查询的是MapperMethod的execute方法:
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
if (SqlCommandType.INSERT == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.UPDATE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.DELETE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
/**select查询语句*/
} else if (SqlCommandType.SELECT == command.getType()) {
/**档返回类型为空*/
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
/**当返回many的时候*/
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
/**当返回值类型为Map时*/
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else {
/**除去以上情况,执行这里的步骤*/
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
} else {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
我们示例中执行的分支语句是:
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
这里有一个查询参数的解析过程:
public Object convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(Object[] args) {
final int paramCount = params.size();
if (args == null || paramCount == 0) {
return null;
/**参数没有标注@Param注解,并且参数个数为一个*/
} else if (!hasNamedParameters && paramCount == 1) {
return args[params.keySet().iterator().next()];
/**否则执行这个分支*/
} else {
final Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap<Object>();
int i = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : params.entrySet()) {
param.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey()]);
// issue #71, add param names as param1, param2...but ensure backward compatibility
final String genericParamName = "param" + String.valueOf(i + 1);
if (!param.containsKey(genericParamName)) {
param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]);
}
i++;
}
return param;
}
}
这里的代码看起来可能逻辑不太好懂,我这里解释一下结论就好,这里参数解析如果判断参数一个只有一个(一个单一参数或者是一个集合参数),并且没有标注@Param注解,那么直接返回这个参数的值,否则会被封装为一个Map,然后再返回。
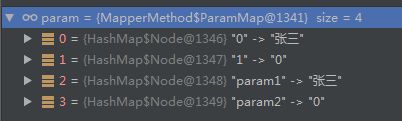
封装的样式如下用几个示例解释:
例1:
/**接口为*/
User selectByNameSex(String name, int sex);
/**我们用如下格式调用*/
userMapper.selectByNameSex("张三",0);
/**参数会被封装为如下格式:*/
0 ---> 张三
1 ---> 0
param1 ---> 张三
param2 ---> 0
如下图所示:
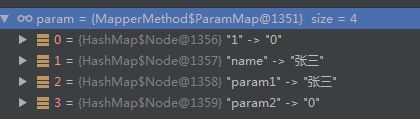
例2:
/**接口为*/
User selectByNameSex(@Param("name") String name, int sex);
/**我们用如下格式调用*/
userMapper.selectByNameSex("张三",0);
/**参数会被封装为如下格式:*/
name ---> 张三
1 ---> 0
param1 ---> 张三
param2 ---> 0
如下图所示:
参数处理完接下来就是调用执行过程,最终调用执行的是DefaultSqlSession中的selectList方法:
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
List<E> result = executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
这里调用SimpleExecutor的query方法执行查询操作,接着调用doQuery方法:
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
/**这里出现了Mybatis四大对象中的StatementHandler*/
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler)
/**创建StatementHandler并应用到插件支持*/
interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
在创建StatementHandler的同时,应用插件功能,同时创建了Mybatis四大对象中的另外两个对象:
protected BaseStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
……
……
……
/**Mybatis四大对象中的ParameterHandler*/
this.parameterHandler = configuration.newParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
/**Mybatis四大对象中的ResultSetHandler*/
this.resultSetHandler = configuration.newResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, rowBounds, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql);
}
同时在创建的时候,也运用到了插件增强功能:
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
……
……
……
interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
……
……
……
interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
接下来就是执行正常的JDB C查询功能了,参数设置由ParameterHandler操作,结果集处理由ResultSetHandler处理。至此,整个查询流程结束。
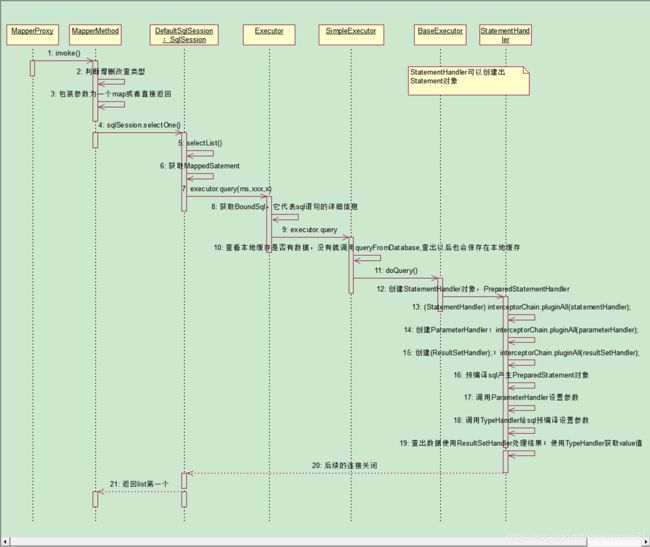
整个查询阶段的时序图可以用如下图表示:
整个查询流程,可以总结如下图:
六、Mybatis插件开发
6.1 四大对象
Mybatis四大对象指的是:Executor、StatementHandler、ParamaterHandler、ResultSetHandler。Mybatis允许我们在四大对象执行的过程中对其指定方法进行拦截,这样就可以很方便了进行功能的增强,这个功能跟Spring的切面编程非常类似。上文我们都有提到过,在四大对象创建的时候,都进行了插件增强,下面我们就来讲解一下其实现原理。
例如我们希望在sql语句之前前后进行时间打印,计算出sql执行的时间。此功能我们就可以拦截StatementHandler。这里我们需要时间Mybatis提供的Intercaptor接口。
package com.cl.mybatis.learn.intercaptor;
/**
* @Author: chengli
* @Date: 2018/11/24 17:37
*/
/**该注解签名告诉此拦截器拦截四大对象中的哪个对象的哪个方法,以及方法的签名信息*/
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = "query", args = {Statement.class, ResultHandler.class})
})
public class SqlLogPlugin implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
return invocation.proceed();
} finally {
long time = System.currentTimeMillis() - begin;
System.out.println("sql 运行了 :" + time + " ms");
}
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
}
}
接下来我们需要在mybatis-config.xml配置该拦截器:
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.cl.mybatis.learn.intercaptor.SqlLogPlugin">
<property name="参数1" value="root"/>
<property name="参数2" value="123456"/>
plugin>
plugins>
此时,拦截器的配置就完成了,运行结果如下:
DEBUG 11-24 17:51:34,877 ==> Preparing: select * from user where id = ? (BaseJdbcLogger.java:139)
DEBUG 11-24 17:51:34,940 ==> Parameters: 1(Integer) (BaseJdbcLogger.java:139)
DEBUG 11-24 17:51:34,990 <== Total: 1 (BaseJdbcLogger.java:139)
sql 运行了 :51 ms
User{id=1, name='张三', age=42, sex=0}
6.2 插件原理探究
从代码我们可以看出:
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
该代码是对目标对象的包装,实际运行的时候,是使用的包装之后的类,运行的时候执行的是intercept方法。那么现在我们来看下它是怎么进行包装的:
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap));
}
return target;
}
而Plugin类实现了InvocationHanlder接口:
public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler {
……
}
显然这里使用的就是JDK的动态代理,对目标对象包装了一层。
假如一个对象被多个拦截器进行了多次包装,那么后包装的在最外层会先执行。