Nginx + FastCGI架构部署指导
本文主要介绍使用 Nginx + FastCGI 技术,搭建一个简单的 Web Server 的方法。关于 Nignx 的相关知识,请点击此处。关于 FastCGI 的相关知识,请点击此处。
1. 概述
Nginx 不能像 Apache 那样直接执行外部的可执行程序,但是 Nginx 可以作为代理服务器,将Web请求转发给后端(服务器中的)应用程序,这是 Nginx 的主要作用之一。
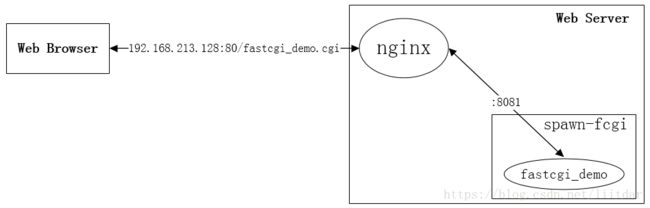
在本文中,我们使用 Nginx 接收Web客户端的请求,然后 Nginx 将该Web请求转发给后端的FastCGI进程, Nginx + FastCGI 模式的架构图如下:
2. 编写FastCGI应用程序
本文使用FastCGI软件开发套件“fcgi”编写FastCGI应用程序。
2.1 安装fcgi
使用 yum 命令安装 fcgi :
yum install fcgi-devel2.2 编写FastCGI应用程序代码
FastCGI应用程序代码(fastcgi_demo.cpp)如下:
#include "fcgi_stdio.h"
#include
int main(void)
{
int count = 0;
while (FCGI_Accept() >= 0)
{
printf("Content-type: text/html\r\n"
"\r\n"
"Hello World "
"Hello World from FastCGI!
"
"Request number is: %d\n",
++count);
}
return 0;
} 上面的FastCGI程序会将接收到的请求的次数打印出来,因为FastCGI程序是“常驻”的,所以其打印出来的请求次数会一直增加。
2.3 编译生成FastCGI应用程序
运行如下命令编译生成FastCGI应用程序:
g++ -o fastcgi_demo fastcgi_demo.cpp -lfcgi3. FastCGI进程管理器
由于FastCGI进程是由FastCGI进程管理器管理的(而不是 Nginx ),所以我们需要一个FastCGI进程管理器,来管理我们编写FastCGI应用程序(本文中为 fastcgi_demo )。
本文使用 spawn-fcgi 作为FastCGI进程管理器。
spawn-fcgi 是一个通用的FastCGI进程管理器,简单小巧,原先是属于 lighttpd 的一部分,后来由于使用比较广泛,所以就迁移出来作为独立项目了。 spawn-fcgi 使用 pre-fork 模式,主要功能是打开监听端口、绑定地址,然后 fork-and-exec 执行我们编写的FastCGI应用程序,之后 spawn-fcgi 进程退出(即 spawn-fcgi 非常驻进程)。在这个过程中,FastCGI应用程序首先进行初始化,然后进入死循环,监听(来自 Nginx 的)socket的连接请求。
3.1 安装FastCGI进程管理器
使用 yum 命令安装 spawn-fcgi ,如下:
yum install spawn-fcgi3.2 启动FastCGI应用程序
通过FastCGI进程管理器 spawn-fcgi 启动本文前面编写FastCGI程序,命令如下:
spawn-fcgi -a 192.168.213.128 -p 8081 -f /opt/liitdar/mydemos/simples/fastcgi_demo查看FastCGI程序是否已经开始监听8081端口了,命令如下:
[root@node1 /opt/liitdar/mydemos/simples]# netstat -anpot |grep 8081
tcp 0 0 192.168.213.128:8081 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3766/fastcgi_demo off (0.00/0/0)
[root@node1 /opt/liitdar/mydemos/simples]# 从上述查询结果能够看到,FastCGI程序 fastcgi_demo 已经在监听8081端口了。
查看FastCGI进程管理器 spawn-fcgi 的运行状态:
[root@node1 /opt/liitdar/mydemos/simples]# ps -ef|grep spawn-fcgi
root 3843 2661 0 16:46 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto spawn-fcgi
[root@node1 /opt/liitdar/mydemos/simples]# 从上述查询结果能够看到, spawn-fcgi 进程没有在运行了,这说明 spawn-fcgi 完成对FastCGI程序 fastcgi_demo 的拉起操作后就结束自己的运行状态了。
4. Nginx的相关配置
4.1 关联FastCGI程序
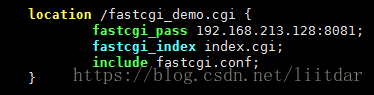
为了让 Nginx 使用FastCGI程序, 我们需要在 Nginx 配置文件(/etc/nginx/nginx.conf)中新增如下内容:
说明:
- 上述新增内容,需要根据实际情况进行配置;
- 关于 Nginx 配置文件的的其他配置项,点击此处。
4.2 启动Nginx
修改完配置文件后,启动 Nginx ,如下:
[root@node1 /opt/liitdar/mydemos/simples]# nginx查看 Nginx 的运行状态:
[root@node1 /opt/liitdar/mydemos/simples]# ps -ef|grep nginx
root 3734 1 0 15:09 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process nginx
nginx 3735 3734 0 15:09 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
root 3851 2661 0 16:57 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
[root@node1 /opt/liitdar/mydemos/simples]#
5. 测试
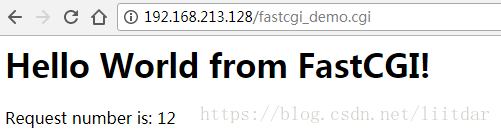
在Web浏览器中,打开Nginx配置的FastCGI应用程序链接,测试 Nginx + FastCGI 模式是否搭建成功,如下:
上图显示我们的 Nginx + FastCGI 模式已搭建成功了,其中数字“12”对应着12次的Web浏览器请求,如果再点击一次刷新,则该数字会变为13。
在这个例子中, Nginx 通过 http://192.168.213.128/fastcgi_demo.cgi 收到来自Web浏览器的请求时,会匹配到配置文件中的“location /fastcgi_demo.cgi”块,所以会将该Web请求传到后端的FastCGI应用程序 fastcgi_demo 进行处理。