Python3.7学习笔记20-内置模块
Python3.7学习笔记20-内置模块
一、os 模块
os 模块的功能主要是对系统的操作
# 使用模块之前必须先导入
import os
#获取当前工作目录(当前工作目录默认都是当前文件所在的文件夹)
os.getcwd()
#改变当前工作目录
os.chdir('/home')
#获取指定文件夹中所有内容的名称列表
os.listdir('/home')
#创建文件夹
os.mkdir('test')
#递归创建文件夹
os.makedirs('/home/a/b/c/d')
#删除空目录
os.rmdir('test')
#递归删除文件夹 必须都是空目录
os.removedirs('/home/a/b/c/d')
#文件或文件夹重命名
os.rename('/home/a/','/home/sb')
#获取文件或者文件夹的信息
os.stat('/home/dev/test.py')
# 删除文件
os.remove('home/test.py')
# 改变目录权限
os.chmod()
#执行系统命令. 涉及到删除的命令一定要小心
os.system('ls -al') #获取隐藏文件
#获取系统的环境变
os.getenv('PATH')
#将一个目录添加到环境变量中(临时增加仅对当前脚本有效)
os.putenv('PATH','/home/a')
#获取系统环境变量
os.environ['PATH']
#设置系统环境变量 putenv()
os.environ['PATH'] += ':/home/a/b'
os.system('chls')
#表示当前文件夹
os.curdir
#表示上一层文件夹 ..表示上一层文件夹 不可省略!
os.pardir
#name 获取代表操作系统的名称字符串
os.name
#sep 获取系统路径间隔符号 window ->\ linux ->/
os.sep
#extsep 获取文件名称和后缀之间的间隔符号 window & linux -> .
os.extsep
#linesep 获取操作系统的换行符号 window -> \r\n linux/unix -> \n
os.linesep
#os.path子模块函数
#abspath() 将相对路径转化为绝对路径
path = './boys'#相对
os.path.abspath(path)
#获取完整路径当中的目录部分 & basename()获取完整路径当中的主体部分
path = '/home/a/b'
os.path.dirname(path)
os.path.basename(path)
#将一个完整的路径切割成目录部分和主体部分
path = '/home/a/b'
os.path.split(path)
#join() 将2个路径合并成一个
a = '/home/m'
b = 'test.py'
os.path.join(a,b)
#将一个路径切割成文件后缀和其他两个部分,主要用于获取文件的后缀
path = '/home/a/test.py'
os.path.splitext(path)
#获取文件的大小
path = '/home/a/b.py'
os.path.getsize(path)
#检测是否是文件
path = '/home/a'
os.path.isfile(path)
#检测是否是文件夹
os.path.isdir(path)
#检测是否是链接
path = 'www'
os.path.islink(path)
#getctime() 获取文件的创建时间 get create time
#getmtime() 获取文件的修改时间 get modify time
#getatime() 获取文件的访问时间 get active time
import time
filepath = '/home/a/b'
result = os.path.getctime(filepath)
print(time.ctime(result))
result = os.path.getmtime(filepath)
print(time.ctime(result))
result = os.path.getatime(filepath)
print(time.ctime(result))
#检测某个路径是否真实存在
filepath = '/home/a'
os.path.exists(filepath)
#检测一个路径是否是绝对路径
path = '/boys'
os.path.isabs(path)
#检测2个路径是否是同一个文件
path1 = '/home/a/b/test'
path2 = '../../../b/test'
os.path.samefile(path1,path2)
二、sys 模块
sys 常用函数如下。使用前也需要导入。import sys
- sys.argv 命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径
- sys.modules.keys() 返回所有已经导入的模块列表
- sys.exc_info() 获取当前正在处理的异常类,exc_type、exc_value、exc_traceback当前处理的异常详细信息
- sys.exit(n) 退出程序,正常退出时exit(0)
- sys.hexversion 获取Python解释程序的版本值,16进制格式如:0x020403F0
- sys.version 获取Python解释程序的版本信息
- sys.maxint 最大的Int值
- sys.maxunicode 最大的Unicode值
- sys.modules 返回系统导入的模块字段,key是模块名,value是模块
- sys.path 返回模块的搜索路径,初始化时使用PYTHONPATH环境变量的值
- sys.platform 返回操作系统平台名称
- sys.stdout 标准输出
- sys.stdin 标准输入
- sys.stderr 错误输出
- sys.exc_clear() 用来清除当前线程所出现的当前的或最近的错误信息
- sys.exec_prefix 返回平台独立的python文件安装的位置
- sys.byteorder 本地字节规则的指示器,big-endian平台的值是'big',little-endian平台的值是'little'
- sys.copyright 记录python版权相关的东西
- sys.api_version 解释器的C的API版本
三、time 模块
time模块中时间表现的格式主要有三种:
- timestamp时间戳,时间戳表示的是从1970年1月1日00:00:00开始按秒计算的偏移量
- struct_time时间元组,共有九个元素组。
- format time 格式化时间,已格式化的结构使时间更具可读性。包括自定义格式和固定格式。
三种时间格式的生成函数以及互相转化函数如下
import time
# 生成时间戳
t = time.time()
print(t)
# 时间戳转化成固定格式的时间表示格式
m = time.ctime(t)
print(m)
# 时间戳转化成时间元组
n = time.localtime(t)
print(n)
# 生成时间元组
x = time.localtime()
print(x)
# 时间元组转化成固定格式的时间表示格式
y = time.asctime(x)
print(y)
# 时间元组转化成字符串格式
z = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %X',x)
print(z)
# 时间元组转化成时间戳格式
c = time.mktime(x)
print(c)
# 生成固定格式的时间
a = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %X')
print(a)
# 固定格式的时间转化成时间元组
b = time.strptime(a,'%Y-%m-%d %X')
四、datetime 模块
datetime 模块重新封装了time模块 新增了很多方法。主要有几个类:date,time,datetime,timedelta,tzinfo
- date类
import datetime
# date 类常用的属性和方法
date_obj = datetime.date
print(date_obj.max) # 对象所能表示的最大日期
print(date_obj.min) # 对象所能表示的最小日期
print(date_obj.resolution) # 对象表示日期的最小单位,这里是天
print(date_obj.today()) # 返回一个表示当前本地日期的
print(date_obj.fromtimestamp(212131231231)) # 根据给定的时间戮,返回一个日期
print(date_obj(2020,5,1).strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')) # 返回自定义格式时间字符串
print(date_obj.weekday(datetime.date.today())) # 返回给定时间的星期几。星期一返回0。星期二返回1(哈哈哈)
print(date_obj.isocalendar(datetime.date.today())) # 返回一个元组。年 周 周的第几天
print(date_obj.timetuple(datetime.date.today())) # 返回一个时间元组
print(date_obj.isocalendar(datetime.date.today())) # 返回一个时间元组- time类
import datetime
# time 类常用的属性和方法
date_obj = datetime.time
print(date_obj.max) # 对象所能表示的最大时间
print(date_obj.min) # 对象所能表示的最小时间
print(date_obj.resolution) # 对象表示日期的最小单位,这里是秒
print(date_obj(16,20,30).hour) # 时
print(date_obj(16,20,30).minute) # 分
print(date_obj(16,20,30).second) # 秒
print(date_obj(16,20,30).tzinfo) # 时区信息
print(date_obj(16,20,30).isoformat()) # 返回字符串格式时间- datetime类
from datetime import datetime
print(datetime.today()) # 返回一个表示当前本地时间的datetime对象;
print(datetime.now()) # 返回一个表示当前本地时间的datetime对象,如果提供了参数tz,则获取tz参数所指时区的本地时间;
print(datetime.utcnow()) # 返回一个当前utc时间的datetime对象;#格林威治时间
print(datetime.fromtimestamp(21321312312)) # 根据时间戮创建一个datetime对象,参数tz指定时区信息;
print(datetime.combine(datetime.today(), datetime.time(datetime.today()))) # 参数是datetime.datetime类的对象、datetime.date对象、datetime.time对象,得到一个datetime.datetime对象
print(datetime.utcfromtimestamp(213123123)) # 根据时间戮创建一个datetime对象;
print(datetime.strptime('2020-5-5 10:10:10','%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')) # 返回自定义的格式时间字符串。参数format是自定义的时间格式
根据平时写的项目。重写了一些常用的时间函数如下
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2020-03-02 11:48
# @Author : zhonglinglong
# @File : new_time.py
"""
重写time,主要功能如下
1、返回当前 年月日 时分秒 在当下 未来 过去的数据
2、时间戳和日期的转化
"""
import datetime
import time
class NewTime:
def now_time_year(self, add_year=0):
"""
返回年份
:param add_year: 当前年份可加可减
:return:
"""
assert type(add_year) == int
return str(int(str(time.strftime('%Y', time.localtime(time.time())))) + int(add_year))
def now_time_month(self, add_month=0):
"""
返回年月
:param add_month: 当前月份可加可减
:return:
"""
assert type(add_month) == int
year_month = str(time.strftime('%Y-%m', time.localtime(time.time())))
month_total = int(add_month) + int(year_month[5:7])
# 过去且不是去年
if month_total <= -12:
multiple = abs(month_total // 12)
year = int(year_month[0:4]) - multiple
if multiple == 0:
year = int(year_month[0:4]) - 1
month = abs(month_total % 12)
if month == 0:
month = '-12'
else:
month = self._format_processing(month,1)
return str(year) + month
# 在去年年份内
elif -11 <= month_total <= 0:
month_total = month_total + 12
year = int(year_month[0:4]) - 1
return str(year) + self._format_processing(month_total,1)
# 在当前年份内
elif 1 <= month_total <= 12:
return year_month[0:4] + self._format_processing(month_total,1)
# 未来且不是今年
elif month_total > 12:
multiple = month_total // 12
year = int(year_month[0:4]) + multiple
month = month_total % 12
if month == 0:
year = int(year_month[0:4]) + multiple - 1
month = '-12'
else:
month = self._format_processing(month,1)
return str(year) + month
def now_time_day(self, add_day=0):
"""
返回年月日
:param add_day: 日可加可减
:return:
"""
assert type(add_day) == int
year_month_day = str(datetime.date.today() + datetime.timedelta(days=add_day))
return year_month_day
def now_time_hour(self, add_hour):
"""
返回年月日时
:param add_hour: 小时可加可减
:return:
"""
assert type(add_hour) == int
year_month_day_hour = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H', time.localtime(time.time()))
hour = year_month_day_hour[11:13]
hour_total = add_hour + int(hour)
multiple = hour_total // 24
# 要返回的时间属于过去到至前一天
if hour_total < -24:
year_month_day = self.now_time_day(multiple)
hour = self._format_processing(abs(hour_total % 24))
return year_month_day + hour
# 要返回的时间属于过去的一天
elif -24 <= hour_total <= 0:
if hour_total == 0:
year_month_day = self.now_time_day(0)
hour = ' 00'
else:
year_month_day = self.now_time_day(-1)
hour = self._format_processing(str(hour_total + 24))
return year_month_day + hour
# 要返回的时间属于当天
elif 0 < hour_total <= 24:
if hour_total == 24:
return self.now_time_day(1) + ' 00'
return year_month_day_hour[0:10] + self._format_processing(hour_total)
# 要返回的时间属于明天至未来
elif 24 < hour_total:
year_month_day = self.now_time_day(multiple)
hour = self._format_processing(hour_total % 24)
return year_month_day + hour
def now_time_minute(self,add_minute=0):
"""
返回年月日 时分
:param add_minute: 分钟可加可减
:return:
"""
assert type(add_minute) == int
year_month_day_hour_minute = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M', time.localtime(time.time()))
minute = year_month_day_hour_minute[14:16]
minute_total = add_minute + int(minute)
multiple = minute_total // 60
# 要返回的时间属于 过去至最近1小时
if minute_total < -60:
year_month_day_hour = self.now_time_hour(multiple)
minute = self._format_processing(abs(minute_total % 60),val=2)
return year_month_day_hour + minute
# 要返回的时间属于最近过去的1小时
elif -60 <= minute_total <= 0:
if minute_total == 0:
year_month_day_hour = self.now_time_hour(0)
minute = ':00'
else:
year_month_day_hour = self.now_time_hour(-1)
minute = self._format_processing(str(minute_total + 60),val=2)
return year_month_day_hour + minute
# 要返回的时间属于当前1小时
elif 0 < minute_total <= 60:
if minute_total == 60:
return self.now_time_hour(1) + ':00'
else:
return year_month_day_hour_minute[0:13] + self._format_processing(minute_total,val=2)
# 要返回的时间属于未来1小时以后
elif 60 < minute_total:
year_month_day = self.now_time_hour(multiple)
minute = self._format_processing(minute_total % 60,val=2)
return year_month_day + minute
def now_time_second(self,add_second=0):
"""
返回年月日 时分秒
:param add_second: 秒可加可减
:return:
"""
assert type(add_second) == int
year_month_day_hour_minute_second = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.localtime(time.time()))
second = year_month_day_hour_minute_second[14:16]
second_total = add_second + int(second)
multiple = second_total // 60
# 要返回的时间属于过去至最近的1分钟
if second_total < -60:
year_month_day_hour = self.now_time_minute(multiple)
minute = self._format_processing(abs(second_total % 60), val=2)
return year_month_day_hour + minute
# 要返回的时间属于最近过去的一分钟
elif -60 <= second_total <= 0:
if second_total == 0:
year_month_day_hour = self.now_time_minute(0)
minute = ':00'
else:
year_month_day_hour = self.now_time_minute(-1)
minute = self._format_processing(str(second_total + 60), val=2)
return year_month_day_hour + minute
# 要返回的时间属于当前这分钟
elif 0 < second_total <= 60:
if second_total == 60:
return self.now_time_minute(1) + ':00'
else:
return year_month_day_hour_minute_second[0:16] + self._format_processing(second_total, val=2)
# 要返回的时间属于1分钟以后
elif 60 < second_total:
year_month_day = self.now_time_minute(multiple)
minute = self._format_processing(second_total % 60, val=2)
return year_month_day + minute
def time_stamp(self,times=None):
"""
返回当前时间戳
:param times: time为空默认当前时间戳。也可以自己传入值
:return:
"""
if times is None:
time_data = time.strptime(self.now_time_second(), "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
else:
time_data = time.strptime(times, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S")
return int(time.mktime(time_data))
def analysis_time_stamp(self,time_stamp):
"""
解析时间戳
:param time_stamp:
:return:
"""
assert type(time_stamp) == int
data_time_stamp = time.localtime(time_stamp)
time_str = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", data_time_stamp)
return time_str
def _format_processing(self,data,val=0):
"""
处理数据 把10以内的数字加0
:param data: 被处理数据
:param val: 0;空格 1;- 2;:
:return:
"""
assert type(val) == int
assert type(data) == str or type(data) == int
data = str(data)
if val == 0:
if int(data) < 10:
return ' 0'+data
else:
return ' '+data
elif val == 1:
if int(data) < 10:
return '-0'+data
else:
return '-'+data
elif val == 2:
if int(data) < 10:
return ':0'+data
else:
return ':'+data
def current_month(self):
"""
当月
:return: 年月日 当月第一天至最后一天
"""
date = {}
time = self.now_time_day()[0:7]
date['start'] = time + '-01'
if int(time[5:7]) in [1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 10, 12]:
date['end'] = time + '-31'
elif int(time[5:7]) in [4, 6, 9, 11]:
date['end'] = time + '-30'
elif int(time[5:7]) == 2:
if int(time[5:7]) % 4 == 0:
date['end'] = time + '-29'
else:
date['end'] = time + '-28'
return date
五、configparser 模块
主要用来读取配置文件和写入配置到文件中。
- 主要是读取和写入
- config.remove_option(section,key) 删除 传入标签和key
- config.clear() 清除(慎用)
- 写入的时候。如果存在同样的section 和 key 会直接覆盖
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2020-03-04 09:25
# @Author : zhonglinglong
# @File : config.py
# 配置文件格式如下
"""
[ONEUSERONEINTNTERFACE]
project_name = 渠道API后台管理
url = http://
data = {"type": 6}
method = post
"""
"""
配置文件读取或者写入
"""
import configparser
class Config:
"""
配置文件的读取与写入
"""
def __init__(self,path_name,section,):
"""
初始化参数
:param path_name: 文件路径
:param section: 配置文件区块名称
"""
self.path_name = path_name
self.section = section
def set_conf(self, key, value):
"""
写入值到配置文件中
:param key: 写入文件中的key
:param value: 写入配置中的值
:return:
"""
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
# path = os.path.join(os.path.split(os.path.realpath(__file__))[0]) + '/conf.ini'
path = self.path_name
config.read(path)
config.set(self.section, str(key), str(value))
config.write(open(path, 'w'))
def get_conf(self,key, valueType=str):
"""
获取配置文件值
:param key: 配置文件对应的key
:param valueType: 默认值
:return:
"""
config = configparser.RawConfigParser()
# path = os.path.join(os.path.split(os.path.realpath(__file__))[0]) + '/conf.ini'
path = self.path_name
config.read(path)
# 根据所获取的值不同数据类型转化成正确的值
if valueType is str:
value = config.get(self.section, key)
return value
elif valueType is int:
value = config.getint(self.section, key)
return value
elif valueType is bool:
value = config.getboolean(self.section, key)
return value
elif valueType is float:
value = config.getfloat(self.section, key)
return value
else:
value = config.get(self.section, key)
return value
六、json模块
json是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。主要有如下四种方法
- dumps 把数据序列化成字符串
import json
print(json.dumps([]),type(json.dumps([]))) # 可以格式化所有数据类型为字符串
print(json.dumps(1),type(json.dumps(1)))
print(json.dumps('1'),type(json.dumps('1')))
print(json.dumps((2,3)),type(json.dumps((2,3))))
print(json.dumps({1:3}),type(json.dumps({1:3})))- dump 把数据序列化成字符串,且必须传入文件描述符,将序列化的str保存到文件中
import json
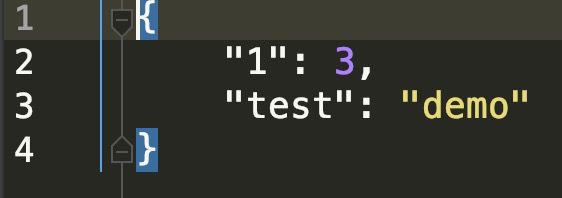
data = {1:3,'test':'demo'}
with open('test.json',"w",encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(data,f,indent=4)- loads 完成反序列化
import json
print(json.loads('{"test":"demo", "1":22}'),type(json.loads('{"test":"demo", "1":22}')))
print(json.loads('[]'),type(json.loads('[]')))
print(json.loads(json.dumps('(2,3)')),type(json.loads(json.dumps('(2,3)'))))
print(json.loads('3333'),type(json.loads('3333')))- load 只接受文件描述符 完成了读取文件和反序列化
import json
with open("test.json", "r", encoding='utf-8') as f:
data = json.loads(f.read())
print(data,type(data))七、smtplib email 模块
主要用来发邮件。之前项目中用到整理了一部分功能如下
import smtplib
from email.header import Header
from email.mime.application import MIMEApplication
from email.mime.multipart import MIMEMultipart
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
class SendEmail:
def __init__(self, username,passwold,to_addr,):
self.to_addr = to_addr.split(',')
self.username = username
self.passwold = passwold
def send(self, info,path=None):
"""
发送邮件
:param path: 附件路径 默认为空
:return:
"""
# 建立
self.msg = MIMEMultipart()
# 发送接受邮箱配置
self.msg['From'] = self.username
self.msg['To'] = ('钟玲龙<%s>' % self.to_addr[0])
# 主题
self.msg['Subject'] = Header('自动化测试报告', 'utf-8')
# 正文内容
self.info = info
self.text = MIMEText(self.info, 'plain', 'utf-8')
self.msg.attach(self.text)
# 钉钉服务器配置及登录
# self.smtpObj = smtplib.SMTP_SSL()
# self.smtpObj.connect('smtp.mxhichina.com',625)
# self.smtpObj.login(self.username, self.passwold)
self.smtpObj = smtplib.SMTP('smtp.mxhichina.com', 25)
self.smtpObj.login(self.username, self.passwold)
if path is None:
self.smtpObj.sendmail(self.username, self.to_addr[0], self.msg.as_string())
else:
self.att = MIMEApplication(open(path, 'rb').read())
self.att.add_header('Content-Disposition', 'attachment', filename='%s' % path.split('/')[-1])
self.msg.attach(self.att)
self.smtpObj.sendmail(self.username, self.to_addr[0], self.msg.as_string())
self.smtpObj.quit()
还有很多内置模块会经常用到。篇幅和时间有限。如果用到的时候可以网上查资料。
- random 生成随机数
- shutil 拷贝文件
- hashlib 加密
- logging 日志
- 。。。。。。====