2018有赞校招笔试题
昨天晚上参加了有赞校招Java类笔试,题目总体难度适中,这里我给大家分享一下这次笔试的三个编程题。
2.思路
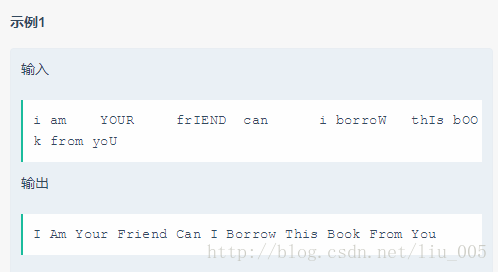
我对这个题目的基本思路是用空格分隔字符串得到字符串数组,该字符串数组元素可能是空,也可能是包含单词和空格的字符串。然后将数组转换成List,对List的每个元素处理成开头大写、之后小写的形式再输出。
3.实现
以下代码是我的实现:
package com.liu.date20171017;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 2018有赞笔试编程题第一题:字符串转换
* Created by Herry on 2017/10/17.
*/
public class TransferString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String input = scanner.nextLine();
transfer(input);
//transferList(input);
}
//方法一:普通迭代器实现(笔试时100%通过测试用例)
public static void transfer(String input) {
List numList = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(input.split(" ")));
ArrayList result = new ArrayList();
Iterator it = numList.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
String item = it.next();
if(item.equals("")) {
it.remove();
continue;
}
item = item.toUpperCase().charAt(0) + item.substring(1).toLowerCase();
result.add(item);
}
//JDK1.8中不需要循环输出。因为笔试时牛客网只提供JDK 1.7,不能使用String类的jion()来拼接字符串,所以这里通过循环输出
for(int i = 0; i < result.size() -1; i ++) {
System.out.print(result.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.print(result.get(result.size() -1));
//JDK 1.8输出方式。不需要循环输出,换用下面的输出即可
//System.out.print(String.join(" ", result));
}
//方法二:List专用迭代器实现(未经过测试用例测试)
public static void transferList(String input) {
List numList = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(input.split(" ")));
ListIterator it = numList.listIterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
String item = it.next();
if(item.equals("")) {
it.remove();
continue;
}
it.set(item.toUpperCase().charAt(0) + item.substring(1).toLowerCase());
}
System.out.print(String.join(" ", numList));
}
}
需要说明的是,实现中使用了两种方式,第一种是采用普通迭代器实现的,普通迭代器不能在元素遍历的时候对元素进行修改,所以只能用另外一个List来接收处理后的元素,输出时也有JDK版本的区分。第二种是采用List专用迭代器实现的,这种迭代器支持在元素遍历的时候对元素进行修改,所以不用额外用List接收处理后的元素。
2.思路
我一开始是采用最原始的穷举法来做的,就是从较小的数开始一个一个往下测试是否满足同时整除给定的两个数,这种思路不满足题目对于性能的要求。后来参考了网上的思路,采用辗转相除的方式来实现。
3.实现
以下代码是我的实现:
package com.liu.date20171017;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 2018有赞笔试编程题第二题:求两个数的最大公约数
* Created by Herry on 2017/10/17.
*/
public class GreatestCommonDivisor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
long num1 = scanner.nextLong();
long num2 = scanner.nextLong();
System.out.print(getGCD(num1, num2));
}
//方法一:该方法由于复杂度比较大,只能部分通过测试用例
public static long getGreatestCommonDivisor(long num1, long num2) {
long d = num1 < num2 ? num1 : num2; //约数
while (d >= 1) {
if (num1 % d == 0 && num2 % d == 0) {
break;
}
d--;
}
return d;
}
//方法二:100%通过测试用例
public static long getGCD(long num1, long num2) // 循环实现
{
long k = 0, y = 0;
if(num1 < num2)
{
k = num1;
num1 = num2;
num2 = k;
}
while(num1 % num2 != 0)
{
y = num1 % num2;
num1 = num2;
num2 = y;
}
return num2;
}
}我在网上还看到一种相减的方法可以求得两个数的最大公约数,有兴趣的朋友可以自行搜索学习。
第三题
2.思路
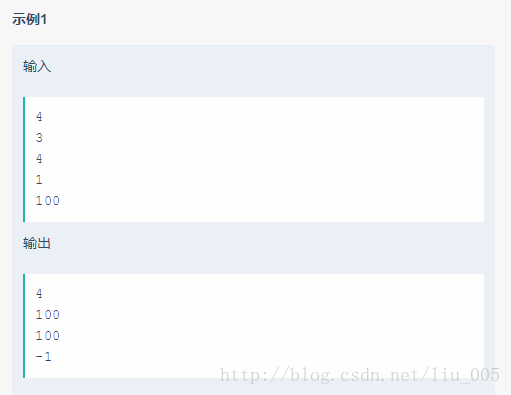
我的思路还是比较原始,就是对于数组的每个元素,从该元素的下一个元素开始遍历整个数组,找到第一个比它大的元素就返回,如果没有找到即返回-1。但是这种方式的复杂度不满足题设要求,只通过了10%,还请做出了这道题的大神指点。
3.实现
package com.liu.date20171017;
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* 2018有赞笔试编程题第三题:打印每个数组元素的NGE(NGE为元素右边第一个比它大的元素)
* <已实现算法不完善,只通过10%>
* Created by Herry on 2017/10/17.
*/
public class PrintNGE {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
long[] nums = new long[n];
// 获取输入
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
nums[i] = scanner.nextLong();
}
//测试用例通过率为10%
for(int j = 0; j < n -1; j ++) {
int flag = 0;
for (int k = j + 1; k < n; k ++) {
if(nums[j] < nums[k]) {
System.out.println(nums[k]);
flag = 1;
break;
}
}
if(flag == 0) {
System.out.println("-1");
}
}
System.out.println("-1");
}
}
总结:总体来说,这几道题的难度都不是很大,重在平时多练习,多注重对性能的追求。以上内容中,一些算法没有完全通过测试用例,还有些是考完之后我补充的实现方式,所以未用完善的测试用例测试,所以可能存在错误之处,要是发现了的话,还望指正。同时,对于以上未完全通过测试的题目,还望大神指点。如有大神有更好的实现方式,也望不吝赐教,不胜感激!