Step to UEFI (137) 通过 BGRT 取得当前系统的 LOGO
对于BIOS来说,用户能够看到的是非常重要的事情。开机Logo就是这样。自从 Win8.1开始,Windows在进入桌面的时候可以显示用户自定义的Logo,而不是Microsoft自定义的图片,这是很有意思的事情。
最近看了一篇介绍的文章,恍然大悟,原来是BIOS解压自己的Logo在内存中,然后通过ACPI Table将这个Logo传递给Windows,于是开机Logo比以前显示的时间更长更持久。
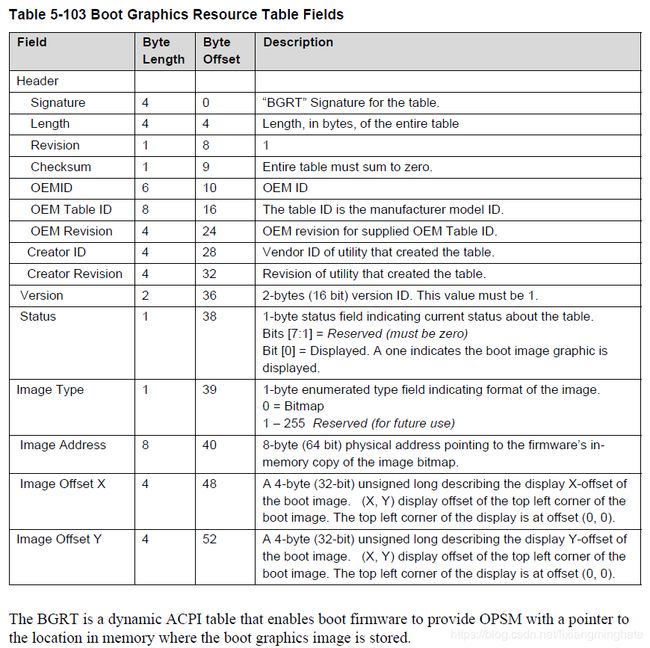
具体的Table就是 Boot Graphics Resource Table。在 ACPI 6.1的5.2.22有专门的介绍。
根据上面的原理,我们可以编写一个UEFI Application,将内存存放的 Logo Dump出来。具体操作:
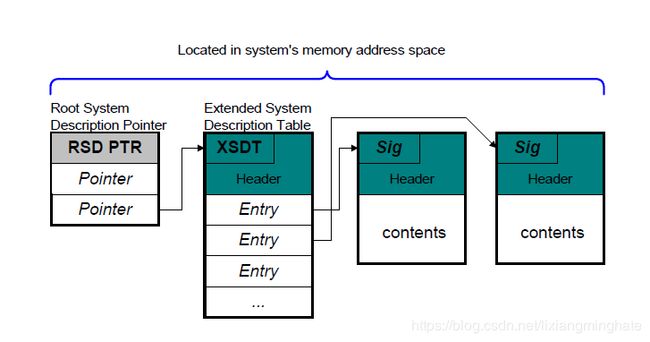
1. 找到RSDP,找到 XSDT
2. 在XSDT中检查每一个Entry,根据 Signature 找到BGRT
3. 解析 BGRT ,得到Logo 图像的地址,这个 Logo一定是 BMP格式的
4. 根据BMP格式能够解析出文件大小,直接Memory Dump即可得到结果
完整的代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "acpi.h"
#include "acpi61.h"
extern EFI_BOOT_SERVICES *gBS;
extern EFI_RUNTIME_SERVICES *gRT;
extern EFI_SYSTEM_TABLE *gST;
#pragma pack(push, 1)
/** BGRT structure */
typedef struct {
EFI_ACPI_DESCRIPTION_HEADER header;
UINT16 version;
UINT8 status;
UINT8 image_type;
UINT64 image_address;
UINT32 image_offset_x;
UINT32 image_offset_y;
} ACPI_BGRT;
/** Bitmap file header */
typedef struct {
UINT8 magic_BM[2];
UINT32 file_size;
UINT8 unused_0x06[4];
UINT32 pixel_data_offset;
UINT32 dib_header_size;
UINT32 width;
UINT32 height;
UINT16 planes;
UINT16 bpp;
} BMP;
#pragma pack(pop)
EFI_GUID gEfiAcpi20TableGuid = { 0x8868E871, 0xE4F1, 0x11D3,
{ 0xBC, 0x22, 0x00, 0x80, 0xC7, 0x3C, 0x88, 0x81 }};
EFI_GUID gEfiSimpleFileSystemProtocolGuid ={ 0x964E5B22, 0x6459, 0x11D2,
{ 0x8E, 0x39, 0x00, 0xA0, 0xC9, 0x69, 0x72, 0x3B }};
EFI_STATUS
SaveToFile(
IN UINT8 *FileData,
IN UINTN FileDataLength)
{
EFI_STATUS Status;
EFI_FILE_PROTOCOL *FileHandle;
UINTN BufferSize;
EFI_FILE_PROTOCOL *Root;
EFI_SIMPLE_FILE_SYSTEM_PROTOCOL *SimpleFileSystem;
Status = gBS->LocateProtocol(
&gEfiSimpleFileSystemProtocolGuid,
NULL,
(VOID **)&SimpleFileSystem);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(L"Cannot find EFI_SIMPLE_FILE_SYSTEM_PROTOCOL \r\n");
return Status;
}
Status = SimpleFileSystem->OpenVolume(SimpleFileSystem, &Root);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(L"OpenVolume error \r\n");
return Status;
}
Status = Root->Open(
Root,
&FileHandle,
L"BIOSLogo.bmp",
EFI_FILE_MODE_READ |
EFI_FILE_MODE_WRITE |
EFI_FILE_MODE_CREATE,
0);
if (EFI_ERROR(Status)){
Print(L"Error Open NULL [%r]\n",Status);
return Status;
}
BufferSize = FileDataLength;
Status = FileHandle->Write(FileHandle, &BufferSize, FileData);
FileHandle->Close(FileHandle);
return Status;
}
/***
Demonstrates basic workings of the main() function by displaying a
welcoming message.
Note that the UEFI command line is composed of 16-bit UCS2 wide characters.
The easiest way to access the command line parameters is to cast Argv as:
wchar_t **wArgv = (wchar_t **)Argv;
@param[in] Argc Number of argument tokens pointed to by Argv.
@param[in] Argv Array of Argc pointers to command line tokens.
@retval 0 The application exited normally.
@retval Other An error occurred.
***/
INTN
EFIAPI
ShellAppMain (
IN UINTN Argc,
IN CHAR16 **Argv
)
{
EFI_STATUS Status;
EFI_ACPI_DESCRIPTION_HEADER *XSDT;
EFI_ACPI_6_1_ROOT_SYSTEM_DESCRIPTION_POINTER *RSDP;
UINT8 *p;
UINTN Index;
UINT64 *Entry;
ACPI_BGRT *pBGRT;
BMP *pBMP;
//1. Find RSDP
Status=EfiGetSystemConfigurationTable(&gEfiAcpi20TableGuid,(VOID**)&RSDP);
if(EFI_ERROR(Status)) {
Print(L"Can't find Acpi Table\n");
return 0;
}
//2. Find XSDT
Print(L"RSDP address [%X]\n",RSDP);
Print(L"XSDT address [%X]\n",RSDP->XsdtAddress);
XSDT=(EFI_ACPI_DESCRIPTION_HEADER*)RSDP->XsdtAddress;
Print(L"XSDT information\n");
p=(UINT8*)XSDT;
//Show some DSDT information
Print(L" Signature [%c%c%c%c]\n",*p,*(p+1),*(p+2),*(p+3));
//3.Find entries
Entry=(UINT64*)&XSDT[1];
Print(L" Entry 0 @[0x%x]\n",Entry);
for (Index=0;Index<(XSDT->Length-sizeof(EFI_ACPI_DESCRIPTION_HEADER))/8;Index++) {
//Print(L" Entry [0x%x]",Index);
p=(UINT8*)(*Entry);
//You can show every signature here
//Print(L" [%x][%c%c%c%c]\n",*Entry,*p,*(p+1),*(p+2),*(p+3));
if ((*p=='B')&&(*(p+1)=='G')&&(*(p+2)=='R')&&(*(p+3)=='T')) {
pBGRT=(ACPI_BGRT*)p;
Print(L" Found BGRT @[0x%X]\n",*Entry);
Print(L" Image address @[0x%X]\n",pBGRT->image_address);
//Get BMP address
pBMP=(BMP*)(pBGRT->image_address);
Print(L" [0x%X]\n",pBMP);
Print(L" Image size [0x%X]\n",pBMP->file_size);
Print(L" Data offset [0x%X]\n",pBMP->pixel_data_offset);
Print(L" Header size [0x%X]\n",pBMP->dib_header_size);
Print(L" Width [0x%X]\n",pBMP->width);
Print(L" Height[0x%X]\n",pBMP->height);
Print(L" Planes[0x%X]\n",pBMP->planes);
Print(L" BPP [0x%X]\n",pBMP->bpp);
SaveToFile((UINT8*)pBMP,pBMP->file_size);
Print(L"BIOS logo has been saved to 'BIOSLogo.bmp'\n");
}
Entry++;
}
return 0;
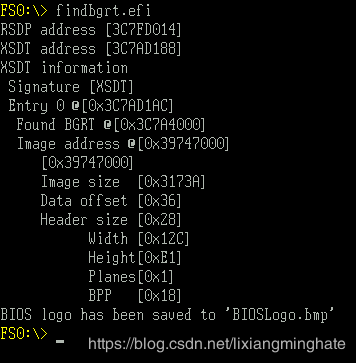
} 运行结果,测试平台为 Intel Kabylake-R HDK,使用的是 Byo BIOS
(不知道为啥,他家的 Shell分辨率很高, 字体极小,看起来简直要瞎) 取得的 BIOSLogo.bmp 结果如下
完整的代码下载:FindBGRT
特别鸣谢sssky307在之前的文章中给出了EfiGetSystemConfigurationTable函数使得代码能够能够大幅度化简。