一,ansible概述:
1. 几种常用运维工具比较
Puppet
—基于 Ruby 开发,采用 C/S 架构,扩展性强,基于 SSL,远程命令执行相对较弱
SaltStack
—基于 Python 开发,采用 C/S 架构,相对 puppet 更轻量级,配置语法使用 YAML,使得配置脚本更简单
Ansible
—基于 Python paramiko 开发,分布式,无需客户端,轻量级,配置语法使用YAML 及 Jinja2模板语言,更强的远程命令执行操作
2. Ansible简介
Ansible 基于Python开发,集合了众多运维工具(puppet、cfengine、chef、func、fabric)的优点,实现了批量系统配置、批量程序部署、批量运行命令等功能。ansible是基于模块工作的,本身没有批量部署的能力。真正具有批量部署的是ansible所运行的模块,ansible只是提供一种框架。
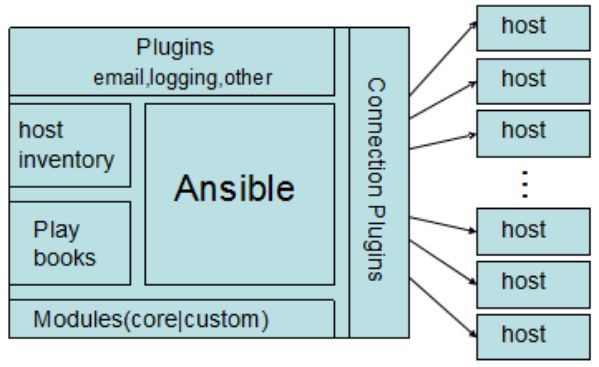

connection plugins:连接插件,负责和被监控端实现通信,有SSH,ZEROMQ等,默认使用SSH连接
host inventory:主机清单,是一个配置文件里面定义监控的主机
modules : 模块,核心模块、command模块、自定义模块等
plugins : modules功能的补充,包括连接插件,邮件插件等
playbook:编排,定义 Ansible 多任务配置文件,非必需
3. Ansible特性
1)、no agents:不需要在被管控主机上安装任何客户端,更新时,只需在操作机上进行一次更新即可
2)、no server:无服务器端,使用时直接运行命令即可
3)、modules in any languages:基于模块工作,可使用任意语言开发模块
4)、yaml,not code:使用yaml语言定制剧本playbook
5)、ssh by default:基于SSH工作
6)、strong multi-tier solution:可实现多级指挥
二,ansible安装
环境:
系统:centos7u3
主机:4台 一个控制节点 3个被控制节点
解析:本地互相解析
192.168.245.133 web1
192.168.245.4 web2
192.168.245.10 web3
192.168.245.3 ansible
配置ssh公钥认证:
控制节点需要发送ssh公钥给所有非被控制节点
安装:控制节点
1. 配置EPEL网络yum源
2. 安装ansible
# yum install ansible -y
# ansible --version
ansible 2.3.2.0
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
configured module search path = Default w/o overrides
python version = 2.7.5 (default, Aug 4 2017, 00:39:18) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-16)]
三,ansible基础
软件大 网速慢 512K 20 100M patch
yum
配置主机清单文件:
主机清单文件
定义所管理的主机组及主机,可以在主配置文件中指定清单文件位置和名称
默认位置/etc/ansible/hosts
主配置文件:
/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
主要设置一些ansible初始化的信息,比如日志存放路径、模块、插件等配置信息
#vim /etc/ansible/hosts 添加被控节点
web1
web2
web3
测试:
语法:
ansible -m -a
pattern--主机清单里定义的主机组名,主机名,IP,别名等,all表示所有的主机,支持通配符,正则
: --多个组,组名之间用冒号隔开
*web* --组名或主机名中含web的
webservers[0] - webservers组中的第一台主机
以~开头,匹配正则
-m module_name: 模块名称,默认为command
-a arguments: 传递给模块的参数
使用ping模块检查ansible节点的连通性:
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web1 -m ping
web1 | SUCCESS => {
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web1 -m ping -o
web1 | SUCCESS => {"changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
同时指定多台机器:
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web1,web2,web3 -m ping -o
web3 | SUCCESS => {"changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
web2 | SUCCESS => {"changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
web1 | SUCCESS => {"changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web* -m ping -o
web3 | SUCCESS => {"changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
web2 | SUCCESS => {"changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
web1 | SUCCESS => {"changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
[root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m ping -o
web1 | SUCCESS => {"changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
web3 | SUCCESS => {"changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
web2 | SUCCESS => {"changed": false, "ping": "pong"}
执行shell命令:
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web1 -m shell -a 'uptime'
web1 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
10:59:56 up 2 days, 15:04, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web1 -m command -a 'uptime'
web1 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
11:00:03 up 2 days, 15:04, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
因为默认模块就是command,所以上面命令可以不加-m:
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web1 -a 'uptime'
web1 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
11:01:39 up 2 days, 15:06, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web1 -a 'uptime' -u root -k
SSH password:
web1 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
11:02:56 up 2 days, 15:07, 2 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
使用ssh账户和密码:-u和-k
-u 用户 //指定ssh账户
-k //指定使用ssh密码,注意:如果设置了公钥认证,这里写什么密码都可以
注意:没有传公钥的其他账户就有用了,比如上面的root换成wing账户(前提:wing账户在被控制机器中已存在)
给节点增加用户:
[root@vm20 ~]# ansible 192.168.245.143 -a "useradd tom"
192.168.245.143 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
[root@vm20 ~]# ansible 192.168.245.143 -a "grep tom /etc/passwd"
192.168.245.143 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
tom:x:1001:1001::/home/tom:/bin/bash
重定向输出到本地文件中:
[root@vm20 ~]# ansible 192.168.245.143 -a "df -h" > /tmp/a.txt
[root@vm20 ~]# cat /tmp/a.txt
192.168.245.143 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
文件系统 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
/dev/mapper/centos-root 17G 5.5G 12G 33% /
devtmpfs 963M 0 963M 0% /dev
tmpfs 979M 0 979M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 979M 9.1M 970M 1% /run
tmpfs 979M 0 979M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 1014M 161M 854M 16% /boot
tmpfs 196M 28K 196M 1% /run/user/0
四,ansible的各种组件
1,ansible组件-inventory
inventory 主机清单
http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/intro_inventory.html#
inventory文件通常用于定义要管理主机及其认证信息,例如ssh登录用户名、密码以及key相关信息。
主机清单文件配置格式
#vim /etc/ansible/hosts
web1 //单独指定主机,可以使用主机名称或IP地址
web2
web3
#-----------------------------------------------------------------
[webservers] //使用[]标签指定主机组
192.168.10.128
bar.example.com
up.example.com:5309 //指定 SSH 端口 5309
web5 ansible_ssh_host=web2 //设置主机web2的别名为 web5
web1 ansible_ssh_pass='123' //设置ssh密码,使用-k参数之后提示的密码可以不写,直接回车
www[01:50].example.com //支持通配符匹配www01,www02,...,www50
db-[a:f].example.com //通配符匹配db-a,db-b,...,db-f
#-----------------------------------------------------------------
为每个主机单独指定变量,这些变量随后可以在 playbooks 中使用:
[atlanta]
host1 http_port=80 maxRequestsPerChild=808
host2 http_port=303 maxRequestsPerChild=909
#------------------------------------------------------------------
为一个组指定变量,组内每个主机都可以使用该变量:
[atlanta]
host1
host2
[atlanta:vars]
ansible_ssh_pass='123'
ntp_server=ntp.atlanta.example.com
proxy=proxy.atlanta.example.com
-----------------------------------------------------------------
组可以包含其他组:
[atlanta]
host1
host2
[raleigh]
host3
host4
[southeast:children] //southeast包括两个子组
atlanta
raleigh
[southeast:vars]
some_server=foo.southeast.example.com
halon_system_timeout=30
1 2 3 4 5 6
1 2 3 nginx
4 5 6 tomcat
1 2 3 4 5 6 php
查看组内主机列表:
[root@ansible ~]# ansible webservers --list-hosts
hosts (3):
web1
192.168.245.135
web3
手动指定其他任意位置的主机清单:
[root@ansible ~]# cat web2.host
web2
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web2 -a 'uptime' -i web2.host
web2 | SUCCESS | rc=0 >>
13:37:24 up 1 day, 19:03, 6 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
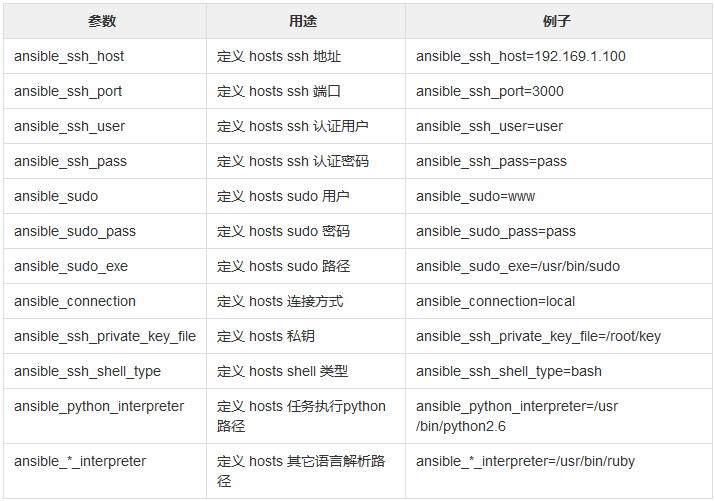
Ansible Inventory 内置参数列表:
2,ansible组件-ad-hoc
Ad-Hoc
ad hoc 临时的,在ansible中是指需要快速执行,并且不需要保存的命令。其实就是执行简单的命令——一条命令。对于复杂的命令则为 playbook。
列出ansible支持的模块:
ansible-doc命令:
获取模块列表,及模块使用格式;
-l:获取列表
-s module_name:获取指定模块的使用信息
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -l
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc yum
[root@ansible ~]# ansible-doc -s yum
执行命令
-m shell
-f 2 指定定要使用的并行进程数,默认为5个。
[root@ansible ~]# grep forks /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
#forks = 5
[root@ansible ~]# ansible all -m shell -a 'hostname' -o -f 3
192.168.245.135 | SUCCESS | rc=0 | (stdout) galera4
web1 | SUCCESS | rc=0 | (stdout) web1
web2 | SUCCESS | rc=0 | (stdout) web2
web3 | SUCCESS | rc=0 | (stdout) web3
复制文件
-m copy
# ansible all -m copy -a 'src=/etc/hosts dest=/etc/hosts owner=root group=root mode=644 backup=yes' -o
backup=yes
被控制节点上如果有文件,则会先备份再拷贝:
[root@web1 ~]# cat /etc/hosts.25856.2018-02-04@14\:15\:43~
src=/etc/hosts //指定的是ansible机器上的文件
用户管理
-m user
添加用户:
[root@ansible ~]# echo '123' | openssl passwd -1 -stdin
$1$hXe3alXf$4VGhWAbRGA6tm4NMJznSf1
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web1 -m user -a 'name=liudehua password="$1$hXe3alXf$4VGhWAbRGA6tm4NMJznSf1"' -o
使用变量需要用双引:
[root@ansible ~]# pass=`echo '1' | openssl passwd -1 -stdin`
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web1 -m user -a "name=liudehua password=$pass" -o
使用命令替换需要用双引:
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web1 -m user -a "name=liudehua password=`echo '1234' | openssl passwd -1 -stdin`" -o
删除用户:
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web1 -m user -a "name=liudehua state=absent" -o
软件包管理
-m yum
删除软件:
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web1 -m yum -a 'name=httpd state=removed'
安装软件:
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web1 -m yum -a 'name=httpd state=latest'
服务管理
-m service
[root@ansible ~]# ansible webservers -m service -a 'name=httpd state=started enabled=yes' -f 3 -o
3,ansible组件-facts
facts
facts组件是Ansible用于采集被管理主机信息的一个功能,可以使用setup模块查看主机的有的facts信息。
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web1 -m setup
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web1 -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_all_ipv4_addresses'
web1 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"ansible_all_ipv4_addresses": [
"192.168.245.133"
]
},
"changed": false
}
将所有主机的信息输入到/tmp/facts目录下:
每台主机的信息输入到主机名文件中(/etc/ansible/hosts里的主机名)
[root@ansible ansible]# ansible all -m setup --tree /tmp/facts
查看主机内存信息
[root@ansible ansible]# ansible web1 -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_*_mb'
查看地接口为eth0-2的网卡信息
[root@ansible ansible]# ansible 10.212.52.252 -m setup -a 'filter=ansible_eth[0-2]'
4,ansible组件-playbook
PlayBook
playbook介绍
playbook是由一个或多个”play”组成的列表。play的主要功能在于将事先归为一组的主机装扮成事先通过ansible中的task定义好的角色。从根本上来将,所谓的task无法是调用ansible的一个module。将多个play组织在一个playbook中,即可以让他们联通起来按事先编排的机制同唱一台大戏。
playbook-->play-->task-->module
role
Playbook是Ansible的配置,部署,编排语言。他们可以被描述为一个需要希望远程主机执行命令的方案,或者一组IT程序运行的命令集合。
当执行一些简单的改动时ansible命令是非常有用的,然而它真的作用在于它的脚本能力。当对一台机器做环境初始化的时候往往需要不止做一件事情,这时使用playbook会更加适合。通过playbook你可以一次在多台机器执行多个指令。通过这种预先设计的配置保持了机器的配置统一,并很简单的执行日常任务。
Playbook还开创了很多特性,它可以允许你传输某个命令的状态到后面的指令,如你可以从一台机器的文件中抓取内容并附为变量,然后在另一台机器中使用,这使得你可以实现一些复杂的部署机制,这是ansible命令无法实现的。
在如右的连接中: https://github.com/ansible/ansible-examples,有一些整套的playbooks,它们阐明了上述的这些技巧。
YAML介绍
Ansible使用标准的YAML解析器,使用YAML文件语法即可书写playbook。
YAML是一个可读性高的用来表达资料序列的格式,YAML参考了其他多种语言,包括:XML、C语言、Python、Perl以及电子邮件格式RFC2822等。Clark Evans在2001首次发表了这种语言。
YAML Ain’t Makup Language,即YAML不是XML。不过,在开发这种语言时,YAML的意思是:Yet Another Makrup Language(仍是一种标记语言),其特性:YAML的可读性好、YAML和脚本的交互性好、YAML有一个一致的信息模型、YAML易于实现、 YAML可以基于流来处理、YAML表达能力强,扩展性好。更多的内容及规范参见www.yaml.org。
GNU GNU IS NOT UNIX
LINUX linus's mix
核心元素:
Playbooks
Variables #变量元素,可传递给Tasks/Templates使用;
Tasks #任务元素,由模块定义的操作的列表,即调用模块完成任务;
Templates #模板元素,使用了模板语法的文本文件,可根据变量动态生成配置文件;
Handlers #处理器元素,通常指在某事件满足时触发的操作;
Roles #角色元素
playbook的基础组件:
name
定义playbook或者task的名称
hosts
playbook中的每一个paly的目的都是为了让某个或某些以某个指定用户的身份执行任务。hosts用于指定要执行指定任务的主机,其可以是一个或多个由冒号分割主机组。与命令模式下的ansible匹配规则一样
user
remote_user则用于指定远程主机上的执行任务的用户,也可以使用user
tasks
任务列表
play的主体部分是task list. task list中的各任务按次序逐个在hosts中指定的所有主机上执行,即在所有主机上完成第一个任务后再开始第二个。
vars
定义变量
vars_files
定义变量文件
notify
任务执行结果如果是发生更改了的则触发定义在handler的任务执行
handlers
用于当前关注的资源发生变化时采取一定指定的操作
include
能包含的包括task,handler和playbook
可以在include的时候传递变量
示例1:简单playbook
文档以---开头,没有也可以
[root@master ~]# cd /etc/ansible/
[root@master ansible]# vim test.yml //固定后缀为yml
---
- hosts: all //特别注意-后面的空格 指定执行本play的主机组
user: root //指定运行本play的远程主机用户
tasks:
- name: playbook_test //任务描述
shell: touch /tmp/playbook.txt //shell是ansible模块
tags: suibian //这是一个任务标记,可用来单独执行此任务
参数解释:
hosts参数指定了对哪些主机进行操作;
user参数指定了使用什么用户登录远程主机操作;
tasks指定了一个任务,其下面的name参数同样是对任务的描述,在执行过程中会打印出来。
tags:给指定的任务定义一个调用标识,形式如下
- name: NAME
module: arguments
tags: TAG_ID
语法检测:
[root@ansible ansible]# ansible-playbook --syntax-check test.yml
playbook: test.yml
测试运行
[root@master ansible]#ansible-playbook -C /path/to/playbook.yaml
可以使用如下参数:
--list-hosts
--list-tasks
--list-tags
运行Playbook:
[root@master ansible]# ansible-playbook test.yml
只运行指定标记的任务:-t tags
[root@ansible ansible]# ansible-playbook -t 标记名称 test.yml
跳过某一个被标记的任务:--skip-tags=SKIP_TAGS
[root@ansible ansible]# ansible-playbook --skip-tags=标记名称 test.yml
从某一个任务开始往下运行:--start-at-task 任务名称
[root@ansible ansible]# ansible-playbook --start-at-task "start httpd service" test.yml
示例2.每个playbook可以有多个play
[root@ansible ansible]# cat test.yml
- hosts: all //play1
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install a group
group: name=mygrp system=true
- name: install a user
user: name=user1 group=mygrp system=true
- hosts: webservers //play2
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install httpd package
yum: name=httpd
- name: start httpd service
service: name=httpd state=started
示例3:使用变量
[root@ansible ansible]# cat create_user.yml
- name: create_user //剧本描述信息
hosts: web1
user: root
gather_facts: false
vars:
- user: "msiyuetian"
tasks:
- name: create user
user: name="{{ user }}"
参数解释:
name参数
对该playbook实现的功能做一个概述,后面执行过程中,会打印 name变量的值 ,可以省略;
gather_facts参数
指定了在以下任务部分执行前,是否先执行setup模块获取主机相关信息,这在后面的task会使用
到setup获取的信息时用到;
默认值为true,改成false之后在执行过程中就看不到以下信息:
TASK [Gathering Facts]
*********************************************************
ok: [web1]
ok: [web3]
ok: [web2]
ok: [192.168.245.135]
vars参数
指定了变量,这里指字一个user变量,其值为test ,需要注意的是,变量值一定要用引号引住;
user
指定了调用user模块,name是user模块里的一个参数,而增加的用户名字调用了上面user变量的值。
运行playbook:
[root@master ansible]# ansible-playbook create_user.yml
示例4:条件执行
[root@master ansible]# vim when.yml
- hosts: web1
user: root
gather_facts: True
tasks:
- name: use when
shell: touch /tmp/when.txt
when: ansible_hostname == "web1"
[root@ansible ansible]# cat when.yml
- hosts: web1
user: root
gather_facts: True
tasks:
- name: use when
shell: touch /tmp/when.txt
when: ansible_all_ipv4_addresses[0] == "192.168.245.133"
只有当参数ansible_all_ipv4_addresses[0]为 192.168.245.133 时才在该机器上新建指定文件;意思就是只对 testhost 组中特定的主机进行操作,忽略组内其他的主机。可以通过setup模块查看各个参数的值
setup模块变量获取:
上面的变量:ansible_hostname和ansible_all_ipv4_addresses[0] 是从setup模块中获取
注意看
是:
"ansible_hostname": "web1"
还是:
"ansible_all_ipv4_addresses": [
"192.168.245.133"
]
如果变量值是用[]括起来的需要用[0]方式切片获取
[root@master ansible]# ansible-playbook when.yml
示例5:handlers:由特定条件触发的Tasks
调用及定义方式:
tasks:
- name: TASK_NAME
module: arguments
notify: HANDLER_NAME
handlers:
- name: HANDLER_NAME
module: arguments
handlers示例1
[root@ansible ansible]# cat handlers.yml
- name: handlers test
hosts: web1
user: root
tasks:
- name: test copy
copy: src=/etc/passwd dest=/tmp/handlers.txt
notify: test handlers
handlers:
- name: test handlers
shell: echo "www.qianfeng.com" >> /tmp/handlers.txt
说明:只有 copy 模块真正执行后,才会去调用下面的 handlers 相关的操作,追加内容。所以这种比较适合配置文件发生更改后,需要重启服务的操作。
[root@master ansible]# ansible-playbook handlers.yml
handlers示例2:
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install httpd package
yum: name=httpd state=latest
- name: install conf file
copy: src=/root/httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: restart httpd service
- name: start httpd service
service: name=httpd state=started
handlers:
- name: restart httpd service
service: name=httpd state=restarted
示例6:include参数
- name: create_user
hosts: web1
user: root
gather_facts: false
vars:
- user: "msiyuetian"
tasks:
- name: create user
user: name="{{ user }}"
- include: handlers.yml //已经用下面的import_playbook代替
- import_playbook: handlers.yml
示例7:pause暂停
在playbook执行的过程中暂停一定时间或者提示用户进行某些操作
常用参数:
minutes:暂停多少分钟
seconds:暂停多少秒
prompt:打印一串信息提示用户操作
[root@ansible ansible]# cat wait.yml
---
- name: wait
hosts: web1
tasks:
- name: wait on user input
pause: prompt="Warning! Detected slight issue. ENTER to continue CTRL-C a to quit"
- name: timed wait
pause: seconds=30
ansible变量
Variables:
类型:
内建变量
自定义变量
变量调用:
{{ var_name }}
内建变量
由facts组件提供,可以使用setup模块查询
[root@ansible ansible]# ansible web1 -m setup
自定义变量
1.用命令行传递参数
为了使Playbook更灵活、通用性更强,允许用户在执行的时候传入变量的值,这个时候就需要用到“额外变量”。
定义命令行变量
在release.yml文件里,hosts和user都定义为变量,需要从命令行传递变量值。
---
- hosts: '{{ hosts }}'
remote_user: '{{ user }}'
tasks:
- ...
使用命令行变量
在命令行里面传值的方法:
#ansible-playbook e33_var_in_command.yml --extra-vars "hosts=web user=root"
还可以用json格式传递参数:
ansible-playbook e33_var_in_command.yml --extra-vars "{'hosts':'vm-rhel7-1', 'user':'root'}"
还可以将参数放在文件里面:
ansible-playbook e33_var_in_command.yml --extra-vars "@vars.json"
2.在hosts Inventory中为每个主机定义专用变量值
向不同的主机传递不同的变量:
IP/HOSTNAME variable_name=value
向组内的所有主机传递相同的变量:
[groupname:vars]
variable_name=value
3.在playbook中定义
vars:
- var_name: value
- var_name: value
通过vars_files关键字引入变量文件:
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
vars:
favcolor: blue
vars_files:
- /vars/external_vars.yml
- /vars/nginx_vars.yml
示例文件:
# vim /vars/nginx_vars.yml
http_port: 80
server_name: localhost
cert_file: /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt
key_file: /etc/nginx/ssh/nginx.key
conf_file: /etc/nginx/conf/default.conf
注意:变量文件不一定以.yml结尾,变量冒号后面必须有空格
4.Inventory使用参数:
用于定义ansible远程连接目标主机时使用的属性,而非传递给playbook的变量;
ansible_ssh_host
ansible_ssh_port
ansible_ssh_user
ansible_ssh_pass
ansible_sudo_pass
…
5.在角色调用时传递
roles:
- { role: ROLE_NAME, var: value, …}
6.set_fact自定义facts变量:
set_fact模块可以自定义facts,这些自定义的facts可以通过template或者变量的方式在playbook中使用。如果你想要获取一个进程使用的内存的百分比,则必须通过set_fact来进行计算之后得出其值,并将其值在playbook中引用。
下面是一个配置mysql innodb buffer size的示例:
- name: Configure MySQL
hosts: mysqlservers
tasks:
- name: install MySql
yum: name=mysql-server state=installed
- name: Calculate InnoDB buffer pool size
set_fact: innodb_buffer_pool_size_mb="{{ ansible_memtotal_mb / 2 }}"
- name: Configure MySQL
template: src=templates/my.cnf dest=/etc/my.cnf owner=root group=root mode=0644
notify: restart mysql
- name: Start MySQL
service: name=mysqld state=started enabled=yes
handlers:
- name: restart mysql
service: name=mysqld state=restarted
my.cnf的配置示例:
# {{ ansible_managed }}
[mysqld]
datadir=/var/lib/mysql
socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
# Disabling symbolic-links is recommended to prevent assorted
security risks
symbolic-links=0
# Configure the buffer pool
innodb_buffer_pool_size = {{ innodb_buffer_pool_size_mb|int }}M
[mysqld_safe]
log-error=/var/log/mysqld.log
pid-file=/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
所有变量都可以在playbook或者jinja2模板中通过{{ varname }}中使用。另外,当变量和jinja2的管道配合起来的时候能提供各种灵活的条件判断和变量处理。具体看下边两个例子。
如果第一个任务执行失败了才会执行第二个任务,可以这么写:
[root@ansible ansible]# cat wait.yml
---
- name: test
hosts: web1
tasks:
- shell: /usr/bin/ls
register: result
ignore_errors: True
- debug: msg="it failed"
when: result|failed
变量的优先级
• -e 命令行指定的最高
• inventory文件定义的变量次之,其实inventory文件也分全局,group级别的和hosts级别的变量定义
• fact变量次之
• 角色的default变量优先级最低
ansible组件-role
role 角色
在ansible中,roles是playbooks的一部分。
playbooks模块化之后,成为roles的组织结构,易读,代码可重用,层次清晰。
以特定的层级目录结构进行组织的tasks、variables、handlers、templates、files等;
role_name/
files/:存储由copy或script等模块调用的文件;
tasks/:
此目录中至少应该有一个名为main.yml的文件,用于定义各task;其它的文件需要由main.yml进行“包含”调用;
handlers/:
此目录中至少应该有一个名为main.yml的文件,用于定义各handler;其它的文件需要由main.yml进行“包含”调用;
vars/:
此目录中至少应该有一个名为main.yml的文件,用于定义各variable;其它的文件需要由main.yml进行“包含”调用;
templates/:
存储由template模块调用的模板文本;
meta/:
此目录中至少应该有一个名为main.yml的文件,定义当前角色的特殊设定及其依赖关系;其它的文件需要由main.yml进行“包含”调用;
default/:
此目录中至少应该有一个名为main.yml的文件,用于设定默认变量;
在playbook中调用角色的方法:
- hosts: HOSTS
remote_user: USERNAME
roles:
- ROLE1
- ROLE2
- { role: ROLE3, VARIABLE: VALUE, ...}
- { role: ROLE4, when: CONDITION }
role目录结构:
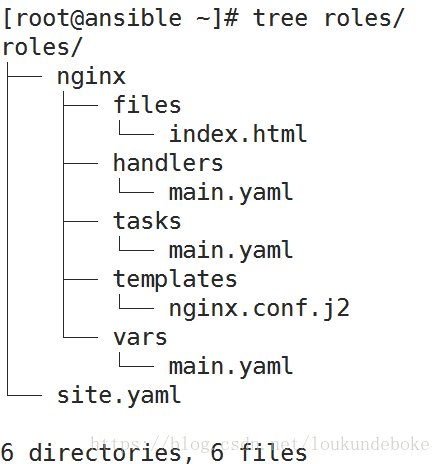
tasks:

handlers:
vars:

jinja template:

ansible-playbook
ansible模板
Templates:模板
Jinja2 is a template engine written in pure Python. It provides a Django inspired non-XML syntax but supports inline expressions and an optional sandboxed environment.
最简示例:
[root@ansible ansible]# cat wait.yml
- name: user
hosts: web1
user: root
vars:
- user: "wing"
- say: "wingfile"
tasks:
- name: task {{ user }}
template: src=/root/testfile dest=/root/{{ say }}
[root@ansible ansible]# cat /root/testfile
hello
i love {{ user }}
[root@ansible ansible]# ansible-playbook wait.yml
模板文件语法:
字面量:
字符串:使用单引号或双引号;
数字:整数、浮点数;
列表:[item1, item2, …]
元组:(item1, item2, …)
字典:{key1:value1, key2:value2, …}
布尔型:true/false
算术运算:
+, -, , /, //, %, *
比较操作:
==, !=, >, <, >=, <=
逻辑运算:
and, or, not
执行模板文件中的脚本,并生成结果数据流,需要使用template模块;
在实际应用中,我们的配置文件有些地方可能会根据远程主机的配置的不同而有稍许的不同,template可以使用变量来接收远程主机上setup收集到的facts信息,针对不同配置的主机,定制配置文件。用法大致与copy模块相同。
常用参数:
backup:如果原目标文件存在,则先备份目标文件
dest:目标文件路径
force:是否强制覆盖,默认为yes
group:目标文件属组
mode:目标文件的权限
owner:目标文件属主
src:源模板文件路径
validate:在复制之前通过命令验证目标文件,如果验证通过则复制
注意:此模板不能在命令行使用,而只能用于playbook;
示例:
- hosts: ngxsrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install nginx package
yum: name=nginx state=latest
- name: install conf file
template: src=/root/nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
tags: ngxconf
notify: reload nginx service
- name: start nginx service
service: name=nginx state=started enabled=true
handlers:
- name: reload nginx service
shell: /usr/sbin/nginx -s reload
条件测试:
when语句:在tasks中使用,Jinja2的语法格式;
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install nginx package
yum: name=nginx state=latest
- name: start nginx service on CentOS6
shell: service nginx start
when: ansible_distribution == "CentOS" and ansible_distribution_major_version == "6"
- name: start nginx service
shell: systemctl start nginx.service
when: ansible_distribution == "CentOS" and ansible_distribution_major_version == "7"
循环:
当有需要重复性执行的任务时,可以使用迭代机制。
其使用格式为:
将需要迭代的内容定义为item变量引用,并通过with_items语句来指明迭代的元素列表即可。
注意:变量名"item"是固定的
元素列表有两种:字符串和字典
基于字符串列表给出元素示例:
- hosts: websrvs
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install packages
yum: name={{ item }} state=latest
with_items:
- httpd
- php
- php-mysql
- php-mbstring
- php-gd
基于字典列表给出元素示例:
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: create groups
group: name={{ item }} state=present
with_items:
- groupx1
- groupx2
- groupx3
- name: create users
user: name={{ item.name }} group={{ item.group }} state=present
with_items:
- {name: 'userx1', group: 'groupx1'}
- {name: 'userx2', group: 'groupx2'}
- {name: 'userx3', group: 'groupx3'}
文件通配符循环
用with_fileglob可以获取本地文件列表。示例如下:
[root@ansible ansible]# cat filelist.yml
---
- name: test
hosts: web1
tasks:
- copy: src={{ item }} dest=/tmp/ owner=root mode=600
with_fileglob:
- /etc/yum.repos.d/*
官方简单示例:
- template: src=/mytemplates/foo.j2 dest=/etc/file.conf owner=bin group=wheel mode=0644
- template: src=/mytemplates/foo.j2 dest=/etc/file.conf owner=bin group=wheel mode="u=rw,g=r,o=r"
- template: src=/mine/sudoers dest=/etc/sudoers validate='visudo -cf %s'named.conf
配置文件的jinja2模板示例:
options {
listen-on port 53 {
127.0.0.1;
{% for ip in ansible_all_ipv4_addresses %}
{{ ip }};
{% endfor %}
};
listen-on-v6 port 53 { ::1; };
directory "/var/named";
dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db";
statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt";
memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt";
};
zone "." IN {
type hint;
file "named.ca";
};
include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones";
include "/etc/named.root.key";
{# Variables for zone config #}
{% if 'authorativenames' in group_names %}
{% set zone_type = 'master' %}
{% set zone_dir = 'data' %}
{% else %}
{% set zone_type = 'slave' %}
{% set zone_dir = 'slaves' %}
{% endif %}
zone "internal.example.com" IN {
type {{ zone_type }};
file "{{ zone_dir }}/internal.example.com";
{% if 'authorativenames' not in group_names %}
masters { 192.168.2.2; };
{% endif %}
};
注:
group_names 是魔法变量,表示当前host所在的group的组名列表,包括其父组
要使这个模板文件生效,需要建立一个authorative nameserver,在设备清单文件中创建一个叫authorative nameserver的组,并添加一些主机(远程受管主机)
playbook的引用该模板配置文件的方法示例:
- name: Setup BIND
host: allnames
tasks:
- name: configure BIND
template: src=templates/named.conf.j2 dest=/etc/named.conf owner=root group=named mode=0640
nginx.conf.j2配置
[root@ansible ansible]# cat roles/nginx/templates/nginx.conf.j2
#user nobody;
worker_processes {{ ansible_processor_cores }};
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections {{ worker_connections }};
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
实验过程(给其他机器安装nginx)
实验准备:首先在/下面建一个文件夹roles,然后在roles里面建一个文件夹nginx和一个文件site.yaml,在nginx文件夹里面建vars,handlers,templates,tasts,files五个文件夹。
1.在site.yaml里面写入
- hosts: tomcat
user: root
roles:
- nginx
2.在vars文件夹里面建文件main.yaml并写入
worker_connections: 10000
3.在handlers文件夹里面建文件main.yaml并写入
- name: restart nginx
service: name=nginx state=restarted
4.在templates文件夹里面建文件main.yaml并写入(其实就是nginx.conf文件改了下面红色部分)
# For more information on configuration, see:
# * Official English Documentation: http://nginx.org/en/docs/
# * Official Russian Documentation: http://nginx.org/ru/docs/
user nginx;
worker_processes {{ ansible_processor_cores }};
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
# Load dynamic modules. See /usr/share/nginx/README.dynamic.
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections {{ worker_connections }};
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
# Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory.
# See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include
# for more information.
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
server_name _;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
location / {
}
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /40x.html {
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
}
# Settings for a TLS enabled server.
#
# server {
# listen 443 ssl http2 default_server;
# listen [::]:443 ssl http2 default_server;
# server_name _;
# root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#
# ssl_certificate "/etc/pki/nginx/server.crt";
# ssl_certificate_key "/etc/pki/nginx/private/server.key";
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 10m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
#
# # Load configuration files for the default server block.
# include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
#
# location / {
# }
#
# error_page 404 /404.html;
# location = /40x.html {
# }
#
# error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
# location = /50x.html {
# }
# }
}
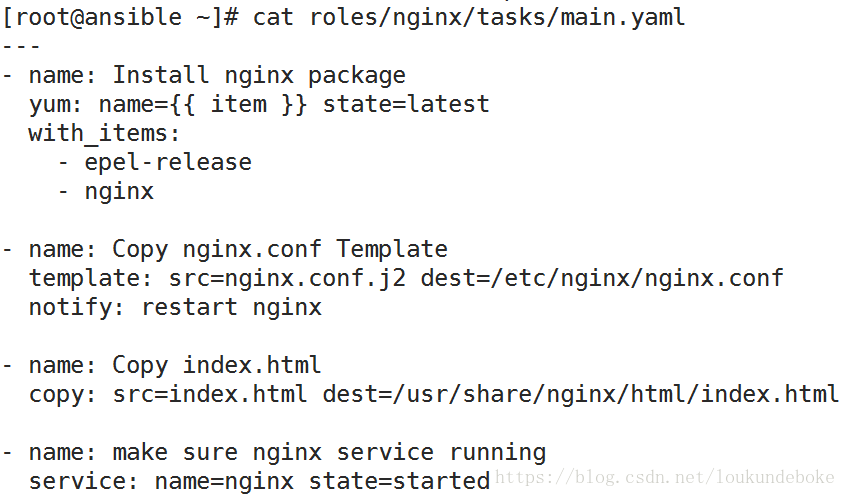
5.在tasts文件夹里面建文件main.yaml并写入
- name: Install nginx package
yum: name={{ item }} state=latest
with_items:
- epel-release
- nginx
- name: Copy nginx.conf Template
template: src=nginx.conf.j2 dest=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify: restart nginx
- name: Copy index.html
copy: src=index.html dest=/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
- name: make sure nginx service running
service: name=nginx state=started
6.在files文件夹里面建文件index.html并写入(其实就是nginx的主页 /usr/local/nginx/html/index.html 直接拷贝到这里来)
http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml11/DTD/xhtml11.dtd">
Test Page for the Nginx HTTP Server on Fedora Welcome to nginx on Fedora!
This page is used to test the proper operation of the
nginx HTTP server after it has been
installed. If you can read this page, it means that the
web server installed at this site is working
properly.
Website Administrator
This is the default index.html page that
is distributed with nginx on
Fedora. It is located in
/usr/share/nginx/html.
You should now put your content in a location of
your choice and edit the root configuration
directive in the nginx
configuration file
/etc/nginx/nginx.conf.
常见问题
问题1:
如果ssh的known_hosts文件被删除,远程登陆的时候会出现提示yes/no,ansible不能自动处理则报错如下:
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web2 -a 'uptime'
web2 | FAILED | rc=-1 >>
Using a SSH password instead of a key is not possible because Host Key checking is enabled and sshpass does not support this. Please add this host's fingerprint to your known_hosts file to manage this host.
解决:扫描远程主机信息添加到known_hosts文件
[root@ansible ~]# ssh-keyscan web2 >> /root/.ssh/known_hosts
常见模块
1. setup: 查看远程主机的基本信息
2. ping: 测试远程主机的运行状态
3. file: 设置文件属性
相关选项如下:
force:需要在两种情况下强制创建软链接,一种是源文件不存在,但之后会建立的情况下;另一种是目标软链接已存在,需要先取消之前的软链,然后创建新的软链,有两个选项:yes|no
group:定义文件/目录的属组
mode:定义文件/目录的权限
owner:定义文件/目录的属主
path:必选项,定义文件/目录的路径
recurse:递归设置文件的属性,只对目录有效,有两个选项:yes|no
src:被链接的源文件路径,只应用于state=link的情况
dest:被链接到的路径,只应用于state=link的情况
state:
directory:如果目录不存在,就创建目录
file:即使文件不存在,也不会被创建
link:创建软链接
hard:创建硬链接
touch:如果文件不存在,则会创建一个新的文件,如果文件或目录已存在,则更新其最后修改时间
absent:删除目录、文件或者取消链接文件
使用示例:
ansible test -m file -a "src=/etc/fstab dest=/tmp/fstab state=link"
ansible test -m file -a "path=/tmp/fstab state=absent"
ansible test -m file -a "path=/tmp/test state=touch"
4. copy: 把主控端的文件复制到远程主机
相关选项如下:
backup:在覆盖之前,将源文件备份,备份文件包含时间信息。有两个选项:yes|no
content:用于替代“src”,可以直接设定指定文件的值
dest:必选项。要将源文件复制到的远程主机的绝对路径,如果源文件是一个目录,那么该路径也必须是个目录
directory_mode:递归设定目录的权限,默认为系统默认权限
force:如果目标主机包含该文件,但内容不同,如果设置为yes,则强制覆盖,如果为no,则只有当目标主机的目标位置不存在该文件时,才复制。默认为yes
others:所有的file模块里的选项都可以在这里使用
src:被复制到远程主机的本地文件,可以是绝对路径,也可以是相对路径。如果路径是一个目录,它将递归复制。在这种情况下,如果路径使用“/”来结尾,则只复制目录里的内容,如果没有使用“/”来结尾,则包含目录在内的整个内容全部复制,类似于rsync
示例如下:
ansible test -m copy -a "src=/srv/myfiles/foo.conf dest=/etc/foo.conf owner=foo group=foo mode=0644"
ansible test -m copy -a "src=/mine/ntp.conf dest=/etc/ntp.conf owner=root group=root mode=644 backup=yes"
5.service模块:用于管理服务
该模块包含如下选项:
arguments:给命令行提供一些选项
enabled:是否开机启动 yes|no
name:必选项,服务名称
pattern:定义一个模式,如果通过status指令来查看服务的状态时,没有响应,就会通过ps指令在进程中根据该模式进行查找,如果匹配到,则认为该服务依然在运行
runlevel:运行级别
sleep:如果执行了restarted,在则stop和start之间沉睡几秒钟
state:对当前服务执行启动,停止、重启、重新加载等操作(started,stopped,restarted,reloaded)
使用示例:
ansible test -m service -a "name=httpd state=started enabled=yes"
asnible test -m service -a "name=foo pattern=/usr/bin/foo state=started"
ansible test -m service -a "name=network state=restarted args=eth0"
6.cron模块:用于管理计划任务
包含如下选项:
backup:对远程主机上的原任务计划内容修改之前做备份
cron_file:如果指定该选项,则用该文件替换远程主机上的cron.d目录下的用户的任务计划
day:日(1-31,*,*/2,……)
hour:小时(0-23,*,*/2,……)
minute:分钟(0-59,*,*/2,……)
month:月(1-12,*,*/2,……)
weekday:周(0-7,*,……)
job:要执行的任务,依赖于state=present
name:该任务的描述
special_time:指定什么时候执行,参数:reboot,yearly,annually,monthly,weekly,daily,hourly
state:确认该任务计划是创建还是删除
user:以哪个用户的身份执行
示例:
ansible test -m cron -a 'name="a job for reboot" special_time=reboot job="/some/job.sh"'
ansible test -m cron -a 'name="yum autoupdate" weekday="2" minute=0 hour=12 user="root
ansible test -m cron -a 'backup="True" name="test" minute="0" hour="5,2" job="ls -alh > /dev/null"'
ansilbe test -m cron -a 'cron_file=ansible_yum-autoupdate state=absent'
7.yum模块:使用yum包管理器来管理软件包
其选项有:
config_file:yum的配置文件
disable_gpg_check:关闭gpg_check
disablerepo:不启用某个源
enablerepo:启用某个源
name:要进行操作的软件包的名字,也可以传递一个url或者一个本地的rpm包的路径
state:状态(present,absent,latest)
示例如下:
ansible test -m yum -a 'name=httpd state=latest'
ansible test -m yum -a 'name="@Development tools" state=present'
ansible test -m yum -a 'name=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/6/noarch/RPMS/nginx-release-centos-6-0.el6.ngx.noarch.rpm state=present'
8.user模块与group模块
user模块是请求的是useradd, userdel, usermod三个指令,goup模块请求的是groupadd, groupdel, groupmod 三个指令。
1、user模块
home:指定用户的家目录,需要与createhome配合使用
groups:指定用户的属组
uid:指定用的uid
password:指定用户的密码
name:指定用户名
createhome:是否创建家目录 yes|no
system:是否为系统用户
remove:当state=absent时,remove=yes则表示连同家目录一起删除,等价于userdel -r
state:是创建还是删除
shell:指定用户的shell环境
使用示例:
user: name=johnd comment="John Doe" uid=1040 group=admin
user: name=james shell=/bin/bash groups=admins,developers append=yes user: name=johnd state=absent remove=yes
user: name=james18 shell=/bin/zsh groups=developers expires=1422403387
user: name=test generate_ssh_key=yes ssh_key_bits=2048 ssh_key_file=.ssh/id_rsa #生成密钥时,只会生成公钥文件和私钥文件,和直接使用ssh-keygen指令效果相同,不会生成authorized_keys文件。注:指定password参数时,不能使用明文密码,因为后面这一串密码会被直接传送到被管理主机的/etc/shadow文件中,所以需要先将密码字符串进行加密处理。然后将得到的字符串放到password中即可。
echo "123456" | openssl passwd -1 -salt $(< /dev/urandom tr -dc '[:alnum:]' | head -c 32) -stdin
$1$4P4PlFuE$ur9ObJiT5iHNrb9QnjaIB0
#使用上面的密码创建用户
ansible all -m user -a 'name=foo password="$1$4P4PlFuE$ur9ObJiT5iHNrb9QnjaIB0"'不同的发行版默认使用的加密方式可能会有区别,具体可以查看/etc/login.defs文件确认,centos 6.5版本使用的是SHA512加密算法。
2、group示例
ansible all -m group -a 'name=somegroup state=present'
9. shell: shell命令
ansible默认使用的模块是command,支持多数shell命令,但不支持shell变量及管道,如果要使用,用shell模块
主配置文件(扩展)
注意:实际上平时没有特殊情况主配置文件不需要修改,ansible默认配置已经很好了
主配置文件位置:
配置文件存在不同的位置,但只有一个可用
在下列列表中,ansible从上往下依次检查,检查到哪个可用就用哪个
• ANSIBLE_CFG 环境变量,可以定义配置文件的位置
• ansible.cfg 存在于当前工作目录
• ansible.cfg 存在与当前用户家目录
• /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
默认位置: /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
[root@vm20 share]# ansible --version
ansible 2.3.2.0
config file = /etc/ansible/ansible.cfg
configured module search path = Default w/o overrides
python version = 2.7.5 (default, Aug 4 2017, 00:39:18) [GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-16)]
wing测试:配置文件不存在也可以,会使用默认配置
ansible.cfg 配置项说明
[defaults]
| 配置 |
说明 |
| #inventory = /etc/ansible/hosts |
指定主机清单文件 |
| #library = /usr/share/my_modules/ |
指定模块地址 |
| #remote_tmp = $HOME/.ansible/tmp |
指定远程执行的路径 |
| #local_tmp = $HOME/.ansible/tmp |
ansible 管理节点得执行路径 |
| #forks = 5 |
置默认情况下Ansible最多能有多少个进程同时工作,默认设置最多5个进程并行处理 |
| #poll_interval = 15 |
轮询间隔 |
| #sudo_user = root |
sudo默认用户 |
| #ask_sudo_pass = True |
是否需要用户输入sudo密码 |
| #ask_pass = True |
是否需要用户输入连接密码 |
| #transport = smart |
|
| #remote_port = 22 |
远程链接的端口 |
| #module_lang = C |
这是默认模块和系统之间通信的计算机语言,默认为’C’语言. |
| #module_set_locale = True |
|
| #gathering = implicit |
|
| #gather_subset = all |
定义获取fact的子集,默认全部 |
| #roles_path = /etc/ansible/roles |
角色存储路径 |
| #host_key_checking = False |
跳过ssh 首次连接提示验证部分,False表示跳过。 |
| #stdout_callback = skippy |
|
| #callback_whitelist = timer, mail |
|
| #task_includes_static = True |
|
| #handler_includes_static = True |
|
| #sudo_exe = sudo |
sudo的执行文件名 |
| #sudo_flags = -H -S -n |
sudo的参数 |
| #timeout = 10 |
连接超时时间 |
| #remote_user = root |
指定默认的远程连接用户 |
| #log_path = /var/log/ansible.log |
指定日志文件 |
| #module_name = command |
指定ansible默认的执行模块 |
| #executable = /bin/sh |
用于执行脚本得解释器 |
| #hash_behaviour = replace |
如果变量重叠,优先级更高的一个是替换优先级低得还是合并在一起,默认为替换 |
| #private_role_vars = yes |
默认情况下,角色中的变量将在全局变量范围中可见。 为了防止这种情况,可以启用以下选项,只有tasks的任务和handlers得任务可以看到角色变量。 |
| #jinja2_extensions = jinja2.ext.do,jinja2.ext.i18n |
jinja2的扩展应用 |
| #private_key_file = /path/to/file |
指定私钥文件路径 |
| #vault_password_file = /path/to/vault_password_file |
指定vault密码文件路径 |
| #ansible_managed = Ansible managed: {file} modified on %Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S by {uid} on {host} |
定义一个Jinja2变量,可以插入到Ansible配置模版系统生成的文件中 |
| #display_skipped_hosts = True |
如果设置为False,ansible 将不会显示任何跳过任务的状态.默认选项是显示跳过任务的状态 |
| #display_args_to_stdout = False |
|
| #error_on_undefined_vars = False |
如果所引用的变量名称错误的话, 是否让ansible在执行步骤上失败 |
| #system_warnings = True |
|
| #deprecation_warnings = True |
|
| #command_warnings = False |
|
| #action_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/action |
action模块的存放路径 |
| #callback_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/callback |
callback模块的存放路径 |
| #connection_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/connection |
connection模块的存放路径 |
| #lookup_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/lookup |
lookup模块的存放路径 |
| #vars_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/vars |
vars模块的存放路径 |
| #test_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/test |
test模块的存放路径 |
| #strategy_plugins = /usr/share/ansible/plugins/strategy |
strategy模块的存放路径 |
| #bin_ansible_callbacks = False |
|
| #nocows = 1 |
|
| #cow_selection = default |
|
| #cow_selection = random |
|
| #cow_whitelist=bud-frogs,bunny,cheese,daemon,default,dragon,elephant-in-snake,elephant,eyes,\ |
|
| #nocolor = 1 |
默认ansible会为输出结果加上颜色,用来更好的区分状态信息和失败信息.如果你想关闭这一功能,可以把’nocolor’设置为‘1’: |
| #fact_caching = memory |
fact值默认存储在内存中,可以设置存储在redis中,用于持久化存储 |
| #retry_files_enabled = False |
当playbook失败得情况下,一个重试文件将会创建,默认为开启此功能 |
| #retry_files_save_path = ~/.ansible-retry |
重试文件的路径,默认为当前目录下.ansible-retry |
| #squash_actions = apk,apt,dnf,package,pacman,pkgng,yum,zypper |
Ansible可以优化在循环时使用列表参数调用模块的操作。 而不是每个with_项调用模块一次,该模块会一次调用所有项目一次。该参数记录哪些action是这样操作得。 |
| #no_log = False |
任务数据的日志记录,默认情况下关闭 |
| #no_target_syslog = False |
防止任务的日志记录,但只在目标上,数据仍然记录在主/控制器上 |
| #allow_world_readable_tmpfiles = False |
|
| #var_compression_level = 9 |
控制发送到工作进程的变量的压缩级别。 默认值为0,不使用压缩。 此值必须是从0到9的整数。 |
| #module_compression = 'ZIP_DEFLATED' |
指定压缩方法,默认使用zlib压缩,可以通过ansible_module_compression来为每个主机设置 |
| #max_diff_size = 1048576 |
控制--diff文件上的截止点(以字节为单位),设置0则为无限制(可能对内存有影响) |
[privilege_escalation]
#become=True
#become_method=sudo
#become_user=root
#become_ask_pass=False
[paramiko_connection]
#record_host_keys=False
#pty=False
[ssh_connection]
| 配置 |
说明 |
| #ssh_args = -o ControlMaster=auto -o ControlPersist=60s |
ssh连接时得参数 |
| #control_path = %(directory)s/ansible-ssh-%%h-%%p-%%r |
保存ControlPath套接字的位置 |
| #pipelining = False |
SSH pipelining 是一个加速 Ansible 执行速度的简单方法。ssh pipelining 默认是关闭,之所以默认关闭是为了兼容不同的 sudo 配置,主要是 requiretty 选项。如果不使用 sudo,建议开启。打开此选项可以减少 ansible 执行没有传输时 ssh 在被控机器上执行任务的连接数。不过,如果使用 sudo,必须关闭 requiretty 选项。 |
| #scp_if_ssh = True |
该项为True时,如果连接类型是ssh,使ansible使用scp,为False是,ansible使用sftp。默认为sftp |
| #sftp_batch_mode = False |
该项为False时,sftp不会使用批处理模式传输文件。 这可能导致一些类型的文件传输失败而不可捕获,但应该只有在您的sftp版本在批处理模式上有问题时才应禁用 |
[accelerate]
加速配置
#accelerate_port = 5099
#accelerate_timeout = 30
#accelerate_connect_timeout = 5.0
#accelerate_daemon_timeout = 30
#accelerate_multi_key = yes
[selinux]
| 配置 |
说明 |
| #special_context_filesystems=nfs,vboxsf,fuse,ramfs |
文件系统在处理安全上下文时需要特殊处理,定义复制现有上下文的文件系统 |
| #libvirt_lxc_noseclabel = yes |
将此设置为yes,以允许libvirt_lxc连接在没有SELinux的情况下工作。 |
[colors]
定义输出颜色
#highlight = white
#verbose = blue
#warn = bright purple
#error = red
#debug = dark gray
#deprecate = purple
#skip = cyan
#unreachable = red
#ok = green
#changed = yellow
#diff_add = green
#diff_remove = red
#diff_lines = cyan








