OpenShift Infrastructure安装和使用指导
1 Installation
1.1 Preparation
Note: This article will take pre-production ofSpain as an environment to show the steps.
1.1.1 Infrastructure plan
According to the OpenShift specification, see https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/3.7/install_config/install/prerequisites.html#install-config-install-prerequisites,each VM should be created with minimum flavor required by OpenShift. Ifcustomer wants to expand business scale, they could reference the same link toadd new node or scale up the node flavor.
The infrastructure will incorporate thefollowing VMs:
Load balancer: 1 VM, acts as NTP server, and HAProxyfor distributing traffic to masters.
Master: 3 VMs
Node: 2 VMs
Infra node: 1 VM, router POD, metric POD,logging POD will be created here.
DNS: 1 VM.
1.1.2 Domain name plan
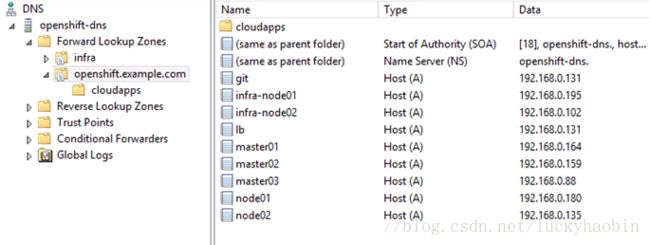
LB:(NTP, LB)
-lb.openshift.example.com 192.168.0.131
master:
-master01.openshift.example.com 192.168.0.164
-master02.openshift.example.com 192.168.0.159
-master03.openshift.example.com 192.168.0.88
node:
-node01.openshift.example.com 192.168.0.180
-node02.openshift.example.com 192.168.0.135
infra:
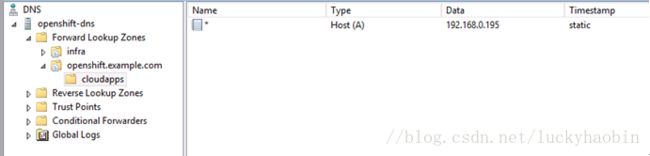
-infra-node01.openshift.example.com 192.168.0.195
1.1.3 Provision VMs
Based on the infrastructure plan, create eachVM with 8 vCPU, 16GB memory, 40GB system disk and 20GB data disk, and with OSof RHEL 7.3.
Note:currently we provision VMs using RHEL image, but in the future we will improveby creating another new image which contains some packages and configurationsbeforehand.
Meanwhile, bind LB VM and Infra node VM withelastic IP (EIP) respectively.
During the installation, all of the nodes needto access Internet to download Docker images, therefore you need to configureSNAT for the subnet. Steps:
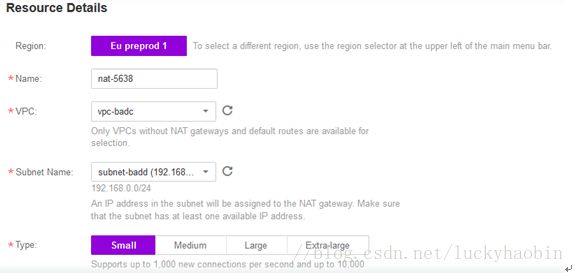
Switch to NAT Gateway on VPC console, andcreate one by:
Here, you need to choose VPC and subnet namewhich are same with your infrastructure’s network definition.
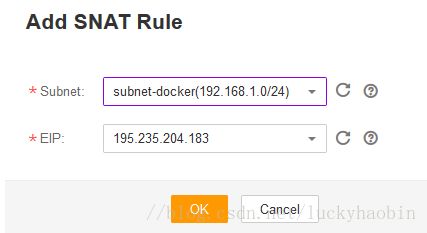
After the NAT Gateway is created, you need to add SNAT rules, like:
This will allow all the VMs in subnet-docker tovisit Internet using SNAT. In this step, you have to apply an EIP in advance.Therefore, considering LB and Infra node bund with EIP, you need 3 EIPs intotal during the installation.
1.2 Configurations before installing
1.2.1 Change host name
On each VM, change host name by command ntmui.
If you provision the VMs with the exact name of domain name in plan, you dont have to change host name. If not, you have to change it.1.2.2 Disable firewalld
systemctl disable firewalld
systemctl stop firewalld
Finally check if all the firewall ruleshave been removed:
iptables -S
Normally, it should be:
-P INPUT ACCEPT
-P FORWARD ACCEPT
-P OUTPUT ACCEPT1.2.3 Allow root to access
On each VM, edit /etc/ssh/sshd_config to allow root to login using password, mainly options about:
PasswordAuthenticationyes
PermitRootLoginyes
Then restart sshd by:
systemctlrestart sshd
Check if you can login by root account with ssh.1.2.4 Configure NTP
On LB VM, install NTP by:
yum install ntp
Edit /etc/ntp.conf and add thefollowing configuration to allow the other client in the same subnet tosynchronize time:
restrict 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0 nomodifynotrap
Enable NTP service and start it:
systemctl enable ntpd
systemctl restart ntpd
Check if NTP server synchronizes time withother servers in Internet: ntpstat
On the rest VMs, install NTP with the samecommand:
yum install ntp
But edit /etc/ntp.conf and set the upperlevel NTP server to be LB VM’s internal address:
# Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project.
# Please consider joining the pool(http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html).
server 192.168.0.131
And enable the NTP service and start it:
systemctl enable ntpd
systemctl restartntpd
1.2.5 Configure DNS
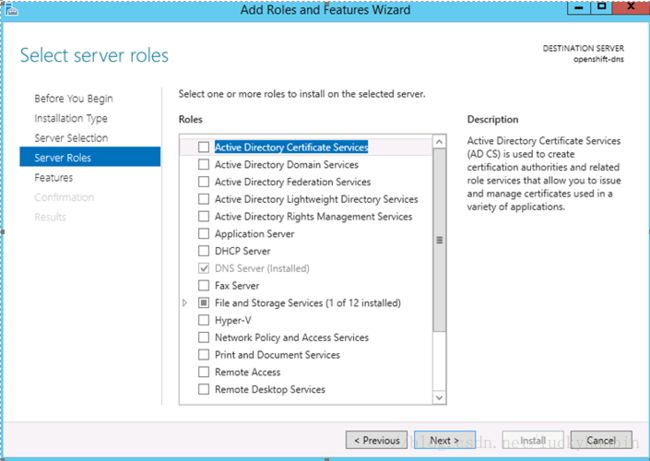
Create a VM with OS of Windows Server 2012 R2 DC.
Install DNS Server in the VM, with Add Roles and Features Wizard:
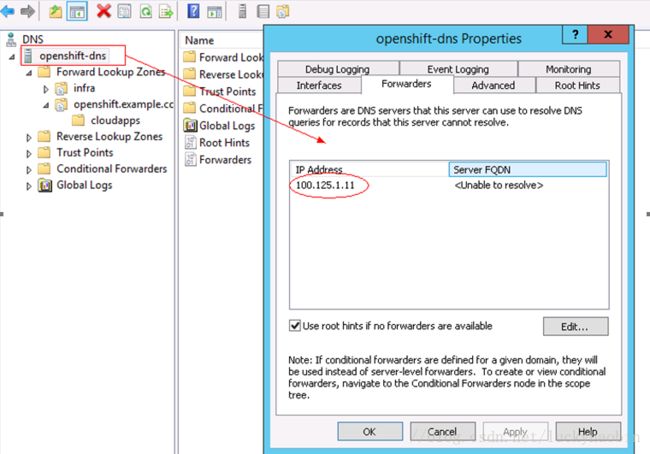
After DNS service installed, open the Properties for openshift-dns, and configure the Forwarders to be “100.125.1.11”, which is the default and internal DNS server when you create a new subnet.
Meanwhile add the DNS records in the DNS server, like:
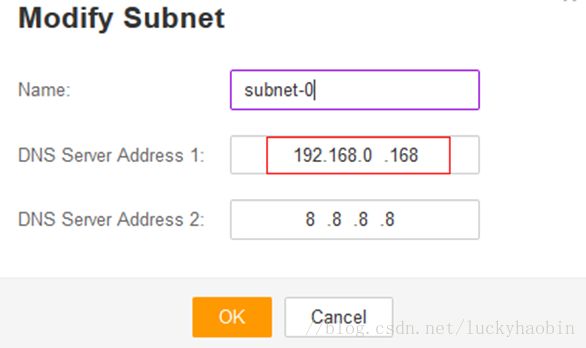
Finally modify the DNS server address for the subnet:
Here, 192.168.0.168 is the internal address of the new DNS server, and subnet-0 is the subnet in which to deploy OpenShift infrastructure.
1.2.6 Install depended packages
On each VM:
yum -y install wget git net-tools bind-utilsiptables-services bridge-utils bash-completion kexec-tools sos psacct
yum -y update
yum -y install atomic-openshift-utils
yum -y install atomic-openshift-excluder atomic-openshift-docker-excluder
atomic-openshift-excluder unexclude
1.2.7 Install and configure Docker
On the nodes except for LB VM, install Docker by:
yum install docker-1.12.6
Check if it's installed correctly:
docker version
In Chapter 1.1.3, we introduced the VM being provisioned with one 20GB data disk. This disk is used to be Docker's backend storage. According to OpenShift's proposal, in production environment, it should be at least 100GB, and 300GB as suggested.
Edit /etc/sysconfig/docker-storage-setup,and set it to be:
CONTAINER_THINPOOL=docker-pool
DEVS=/dev/xvdb
VG=docker-vg
Note: /dev/xvdb is the data volume, and you can get your path by“fdisk -l”.
Configure it using command:
docker-storage-setup
Verify your configuration. You should have a dm.thinpooldev value in the /etc/sysconfig/docker-storage file and a docker-pool logical volume:
DOCKER_STORAGE_OPTIONS="--storage-driverdevicemapper --storage-opt dm.fs=xfs --storage-opt dm.thinpooldev=/dev/mapper/docker--vg-docker--pool--storage-opt dm.use_deferred_removal=true --storage-optdm.use_deferred_deletion=true "
Check if docker is running:
systemctl status docker
If it's not running, enable it and start it:
systemctl enable docker
systemctl start docker
If Docker is already running, re-initialize Docker:
systemctl stop docker
rm -rf /var/lib/docker/*
systemctl restart docker1.2.8 Enable ssh trusty
During the installation, such as executing the command on the LB VM with root, the root user needs to access the other VMs without password.
On the LB VM, generate an ssh key, without any password:
ssh-keygen
Then distribute the ssh key to all the other VMs:
for host in lb.openshift.example.com \
master01.openshift.example.com \
master02.openshift.example.com \
master03.openshift.example.com\
node01.openshift.example.com\
node02.openshift.example.com\
infra-node01.openshift.example.com\
do ssh-copy-id $host; \
done
Check if root on LB VM could access other VM without password:
sshmaster01.openshift.example.com1.2.9 Deploy NFS on LB VM
Starting with OpenShift Container Platform3.7, the OpenShift Ansible broker (OAB) is enabled by default. The OAB deploys its own etcd instance separate from the etcd used by the rest of the OpenShift Container Platform cluster. The OAB’s etcd instance requires separate storage using persistent volumes (PVs) to function. If no PV is available, etcd will wait until the PV can be satisfied. The OAB application will enter a CrashLoop state until its etcd instance is available.
Therefore you could deploy NFS service on LB VM and provide the PV by NFS path.
First check if NFS service related RPM package has been installed:
rpm -qa | grep nfs
If not installed, install NFS by:
yum install nfs-utils
Create a directory used for exporting to outside, such as /nfsexports.
Edit /etc/exports, and add thefollowing content:
/nfsexports *(rw,insecure,sync,all_squash)
Enable and start NFS service:
systemctl enable nfs-server
systemctl enable rpcbind
systemctl restart rpcbind
systemctl restart nfs-server
Check if the path is exported correctly. Execute the mount command on other VM, such as mater VM:
mount -t nfs lb.openshift.example.com:/nfsexports /tmp/test
Finally unmounts it after checks withsuccess:
umount /tmp/test1.3 Install OpenShift Infrastructure
Reference Chapter 2.1 for ansible inventory file, and copy the content to /etc/ansible/hosts.
Install command:
ansible-playbook -i /etc/ansible/hosts /usr/share/ansible/openshift-ansible/playbooks/byo/config.yml
Uninstall command:
ansible-playbook -i /etc/ansible/hosts /usr/share/ansible/openshift-ansible/playbooks/adhoc/uninstall.yml
1.4 Verification
1.4.1 Login portal and provision PODs
oc get node
It should show the following output:
NAME STATUS AGE VERSION
infra-node01.openshift.example.com Ready 38m v1.7.6+a08f5eeb62
master01.openshift.example.com Ready,SchedulingDisabled 38m v1.7.6+a08f5eeb62
master02.openshift.example.com Ready,SchedulingDisabled 38m v1.7.6+a08f5eeb62
master03.openshift.example.com Ready,SchedulingDisabled 38m v1.7.6+a08f5eeb62
node01.openshift.example.com Ready 38m v1.7.6+a08f5eeb62
node02.openshift.example.com Ready 38m v1.7.6+a08f5eeb62
Generate a new user account on each master:
htpasswd -b /etc/origin/master/htpasswd admin admin
Restart service on each master by:
systemctl restart atomic-openshift-master-api atomic-openshift-master-controllers
Add following domain name mappings in the hosts file of laptop:
195.235.204.174 lb.openshift.example.com
195.235.204.175 *.cloudapps.openshift.example.com #### should be the public IP of router infra node
Finally login console with URL: https://lb.openshift.example.com:8443/console, using credentials admin/admin.
Afterlogin with success, you need to create a project for yourself and then you can provision POD by selecting application images in the catalog.1.4.2 Create persistent volume
Edit a PV file in any one of the master, withfollowing content:
apiVersion:v1
kind:PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: pv0001
spec:
capacity:
storage: 5Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
nfs:
path: /share-7eaade1d
server:sfs-nas1.eu-preprod.telefonicaopencloud.com
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Recycle
Create PV with command:
occreate -f ./nfs-pv.yaml
You can check PV created successfully or not:
oc get pvOn the console, you can provision storage, andattach it to some pod.
Note: openshift willschedule by find a PV with capacity more than required.1.4.3 Add nodes to the cluster
Create new VMs, and install the necessary packages, and configure them properly by referencing the above steps.
Edit /etc/ansible/hosts:
[OSEv3:children]
masters
nodes
etcd
lb
nfs
...
...
[new_nodes]
node03.openshift.example.com openshift_node_labels="{'region':'primary','zone':'default'}"
node04.openshift.example.comopenshift_node_labels="{'region':'primary', 'zone':'default'}"
Add the nodes to cluster:
ansible-playbook-i /etc/ansible/hosts /usr/share/ansible/openshift-ansible/playbooks/byo/openshift-node/scaleup.yml
Finally, move any hosts you had defined in the[new_
[OSEv3:children]
masters
nodes
etcd
lb
nfs
...
...
[nodes]
master01.openshift.example.com
master02.openshift.example.com
master03.openshift.example.com
infra-node01.openshift.example.comopenshift_node_labels="{'region':'infra', 'zone':'default'}"
infra-node02.openshift.example.comopenshift_node_labels="{'region':'infra', 'zone':'default'}"
node01.openshift.example.comopenshift_node_labels="{'region':'primary', 'zone':'default'}"
node02.openshift.example.comopenshift_node_labels="{'region':'primary', 'zone':'default'}"
node03.openshift.example.comopenshift_node_labels="{'region':'primary', 'zone':'default'}"
node04.openshift.example.comopenshift_node_labels="{'region':'primary', 'zone':'default'}"
[new_nodes]
1.4.4 Dynamic persistent volume provisioning
In order to use storage class to provisionpersistent volume, we need first to configure OpenStack provider:
Reference: https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/3.7/install_config/configuring_openstack.html
Run the following command to delete all thenodes:
oc delete node master.openshift.example.com
On master node, edit /etc/origin/master/master-config.yaml, and add cloud-provider andcloud-config in apiServerArguments and controllerArguments sections:
kubernetesMasterConfig:
...
apiServerArguments:
cloud-provider:
-"openstack"
cloud-config:
-"/etc/cloud.conf"
controllerArguments:
cloud-provider:
-"openstack"
cloud-config:
-"/etc/cloud.conf"
On all the node nodes, edit /etc/origin/node/node-config.yamland add cloud-provider and cloud-config in kubeletArguments section:
nodeName:
OpenShift-node01/02
kubeletArguments:
cloud-provider:
-"openstack"
cloud-config:
-"/etc/cloud.conf"
Meanwhile on all the nodes, edit /etc/cloud.conf:
[Global]
auth-url =https://iam.eu-preprod.telefonicaopencloud.com:443/v3
username = haobinbin
password = "******"
domain-id = e80f19ea6bf4442381f01995ad5c7b9a
tenant-id = 64105d651c3948cbb7eb25e589821d49
region = eu-preprod-1
[LoadBalancer]
subnet-id = fb99d7d7-976d-4631-9935-4f7e12ae86be
[BlockStorage]
bs-version = v2
On all the master nodes, restart serviceby:
systemctl restart atomic-openshift-master-apiatomic-openshift-master-controllers
On all the node nodes, restart service by:
systemctl restart atomic-openshift-node
Notes: because certificate of pre-productionis self-signed, we need to import the ca certificate into all the nodes (seethe following commands). This operation should be performed in advance,otherwise the node service will not be able to restart.
update-ca-trust enable
cp ca.crt /etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/
update-ca-trust extract
openssl verify ca.crt
rapidSSL-ca.crt: OK #### screen output expected
Notes: after all the nodes areup, maybe the master is schedule enabled state. We need to change them to bedisabled.
oadm manage-node master01.openshift.example.com--schedulable=false
Edit storage class yaml file cinder-storageclass.yaml:
kind: StorageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: gold
provisioner: kubernetes.io/cinder
parameters:
type:SATA
availability:eu-preprod-1a
fsType: ext4
Create storage class by:
oc create -f ./cinder-storageclass.yaml
Check if it is created successfully:
oc get storageclass
Configure the above storage class as thedefault one:
oc patch storageclass gold -p '{"metadata":{"annotations": {"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"true"}}}'
Edit PVC yaml file pvc-gold.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name:cinder-vol-binbin01
spec:
accessModes:
-ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage:10Gi
storageClassName: gold
Create PVC by:
oc create -f pvc-gold.yaml
Check if PVC is created successfully:
oc get pvc
Login OpenCloud console and check if volume iscreated:
1.4.5 (Optional) PVC provision by SFS storage
Dynamic PVC creation is only supported inKVM scenario instead of Xen. If there’s no KVM POD, end user could choose NFSstorage as PV. We take SFS service as an example to explain.
Create a new yaml file with namesfs-pv01.yaml on OpenShift Master node, and edit the content:
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name:sfs-pv0001
spec:
capacity:
storage:10Gi
accessModes:
-ReadWriteOnce
nfs:
path:/share-f7d41805
server:sfs-nas1.eu-preprod.telefonicaopencloud.com
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Recycle
Notes: the path /share-f7d41805is SFS path applied in OpenCloud, and storage is its size.
Create PV in this Master node:
oc create -f sfs-pv01.yaml
Checkif PV is created: oc get pvInitially its status is Available.
Thenend user could create persistent volume claim on the OpenShift portal, andfinally OpenShift will schedule the request on this PV, and this PV status ischanged to Bound.1.4.6 (Optional) Use PVC for docker registry
Reference: https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/3.7/install_config/registry/deploy_registry_existing_clusters.html#install-config-deploy-registry-existing-clusters
As said in the guide, a deploymentconfigs,service, and pod named with docker-registry will be created during theOpenShift infrastructure deployment. On default, the docker registry will usetemporary directory for storage of docker images. After the POD is re-created,all the images will be lost.
In order to keep the images permanently,we’d better replace the deploymentconfigs.
First we need to create PV and PVC. TakeSFS as an example, and create a SFS path in advance.
Edit sfs-pv-docker-registry.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name:sfs-pv-docker-registry
spec:
capacity:
storage:10Gi
accessModes:
-ReadWriteMany
nfs:
path:/share-152b6f67
server:sfs-nas1.eu-preprod.telefonicaopencloud.com
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Recycle
Create PV by: oc create -fsfs-pv-docker-registry.yaml
Edit sfs-pvc-docker-registry.yaml:
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name:sfs-pvc-docker-registry
spec:
accessModes:
-ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage:10Gi
Create PVC by: oc create -fsfs-pvc-docker-registry.yaml
Get the current volumes indeploymentconfigs of docker-registry:
oc volumes dc/docker-registry
deploymentconfigs/docker-registry
empty directory as registry-storage
mounted at /registry
secret/registry-certificates asregistry-certificates
mounted at /etc/secrets
Replace the current volume ofregistry-storage by:
oc volume dc/docker-registry --add--name=registry-storage -t pvc --claim-name=sfs-pvc-docker-registry--mount-path=/registry --overwrite
Finally the POD docker-registry will bere-created, and the deploymentconfigs of docker-registry will also be updated:
deploymentconfigs/docker-registry
secret/registry-certificates as registry-certificates
mountedat /etc/secrets
pvc/sfs-pvc-docker-registry (allocated 10GiB) as registry-storage
mounted at /registry
In order for test, we can access the PODand check the path:
ocrsh docker-registry-4-zrxpb1.4.7 (Optional) docker registry
oc login -u haobinbin -p ******
oc whoami -t
docker login -u haobinbin -p yFX6tpyff8kkldVGWcuTLYNkDiMbr1_7-3Q-vaf-sIcdocker-registry-default.cloudapps.openshift.example.com:443
docker pull docker.io/nginx:latest
docker tag docker.io/nginx:latestdocker-registry-default.cloudapps.openshift.example.com:443/opencloud2/nginx:latest
docker pushdocker-registry-default.cloudapps.openshift.example.com:443/opencloud2/nginx:latest
ocget is1.4.8 (Optional) Manage users
1.4.8.1 AllowAllPasswordIdentityProvider
identityProviders:
- challenge:true
login: true
mappingMethod:claim
name:my_allow_provider
provider:
apiVersion: v1
kind:AllowAllPasswordIdentityProvider
Configure the above part in all the master’sconfiguration file, and restart service on each master by:
systemctl restart atomic-openshift-master-apiatomic-openshift-master-controllers
Any user and password could login theOpenShift portal, even if the user account does not exists.
1.4.8.2 DenyAllPasswordIdentityProvider
identityProviders:
- name:my_deny_provider
challenge:true
login: true
mappingMethod: claim
provider:
apiVersion: v1
kind:DenyAllPasswordIdentityProvider
Configure the above part and restartservice by:
systemctl restart atomic-openshift-master-apiatomic-openshift-master-controllers
Notes:this identity provider does not make sense in production environment.1.4.8.3 KeystonePasswordIdentityProvider
identityProviders:
- name:my_keystone_provider
challenge:true
login: true
mappingMethod: claim
provider:
apiVersion:v1
kind:KeystonePasswordIdentityProvider
domainName: zhangchi
url:https://iam.eu-preprod.telefonicaopencloud.com:443/v3
ca:/root/ca.crt
Configure the above part and restartservice on each master by:
systemctl restart atomic-openshift-master-apiatomic-openshift-master-controllers
Notes: the OpenShift will call OpenCloudIAM API to validate username and password under domain zhangchi.
1.4.8.4 HTPasswdPasswordIdentityProvider
identityProviders:
- challenge:true
login: true
mappingMethod: claim
name:htpasswd_auth
provider:
apiVersion: v1
file:/etc/origin/master/htpasswd
kind:HTPasswdPasswordIdentityProvider
Configure the above part.
Meanwhile on each master, using thefollowing command to generate account and password:
htpasswd -b /etc/origin/master/htpasswd admin admin
Restart master service on each master by:
systemctl restart atomic-openshift-master-apiatomic-openshift-master-controllers
Notes: if htpassword cannot be run, try to install it by yum installhttpd-tools.
1.4.8.5 LDAPPasswordIdentityProvider
Reference: https://docs.openshift.com/container-platform/3.7/install_config/configuring_authentication.html#LookupMappingMethod
2 Appendix: ansible host files
2.1 multi_master_in_HA_without_persistent_storage
[OSEv3:children]
masters
nodes
etcd
lb
nfs
[OSEv3:vars]
ansible_ssh_user=root
openshift_deployment_type=openshift-enterprise
openshift_master_identity_providers=[{'name':'htpasswd_auth','login':'true', 'challenge':'true', 'kind':'HTPasswdPasswordIdentityProvider','filename':'/etc/origin/master/htpasswd'}]
openshift_master_default_subdomain=cloudapps.openshift.example.com
openshift_logging_install_logging=true
openshift_metrics_install_metrics=true
openshift_disable_check=disk_availability,memory_availability
openshift_clock_enabled=true
#### multiple master, need to add thefollowing parameters
openshift_master_cluster_method=native
openshift_master_cluster_hostname=lb.openshift.example.com
openshift_master_cluster_public_hostname=lb.openshift.example.com
openshift_template_service_broker_namespaces=['openshift','myproject']
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_kind=nfs
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_nfs_options="*(rw,root_squash,sync,no_wdelay)"
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_nfs_directory=/nfsexports
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_volume_name=
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_access_modes=["ReadWriteOnce"]
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_volume_size=20G
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_labels={'storage':'etcd'}
ansible_service_broker_local_registry_whitelist=['.*-apb$']
[masters]
master01.openshift.example.com
master02.openshift.example.com
master03.openshift.example.com
#### multiple master, need to add thefollowing etcd and lb hosts
[etcd]
master01.openshift.example.com
master02.openshift.example.com
master03.openshift.example.com
[lb]
lb.openshift.example.com
[nodes]
master01.openshift.example.com
master02.openshift.example.com
master03.openshift.example.com
infra-node01.openshift.example.comopenshift_node_labels="{'region':'infra', 'zone':'default'}"
node01.openshift.example.comopenshift_node_labels="{'region':'primary', 'zone':'default'}"
node02.openshift.example.comopenshift_node_labels="{'region':'primary', 'zone':'default'}"
[nfs]
lb.openshift.example.com2.2 allinone_with_persistent_storage
[OSEv3:children]
masters
nodes
etcd
nfs
[OSEv3:vars]
ansible_ssh_user=root
debug_level=4
openshift_deployment_type=openshift-enterprise
openshift_master_identity_providers=[{'name':'htpasswd_auth','login':'true', 'challenge':'true', 'kind':'HTPasswdPasswordIdentityProvider','filename':'/etc/origin/master/htpasswd'}]
openshift_master_default_subdomain=cloudapps.openshift.example.com
####install cluster logging, with persistent volume
openshift_logging_install_logging=true
openshift_logging_storage_kind=nfs
openshift_logging_storage_access_modes=['ReadWriteOnce']
openshift_logging_storage_host=sfs-nas1.eu-preprod.telefonicaopencloud.com
openshift_logging_storage_nfs_directory=/share-84a7b897
openshift_logging_storage_volume_name=
openshift_logging_storage_volume_size=20Gi
####install cluster metrics, with persistent volume
openshift_metrics_install_metrics=true
openshift_metrics_storage_kind=nfs
openshift_metrics_storage_access_modes=['ReadWriteOnce']
openshift_metrics_storage_host=sfs-nas1.eu-preprod.telefonicaopencloud.com
openshift_metrics_storage_nfs_directory=/share-7d9c5e07
openshift_metrics_storage_volume_name=
openshift_metrics_storage_volume_size=20Gi
openshift_disable_check=disk_availability,memory_availability
openshift_clock_enabled=true
openshift_template_service_broker_namespaces=['openshift','myproject']
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_kind=nfs
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_nfs_options="*(rw,root_squash,sync,no_wdelay)"
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_nfs_directory=/nfsexports
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_volume_name=
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_access_modes=["ReadWriteOnce"]
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_volume_size=20G
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_labels={'storage':'etcd'}
ansible_service_broker_local_registry_whitelist=['.*-apb$']
[masters]
master.openshift.example.comopenshift_schedulable=true
[nodes]
master.openshift.example.comopenshift_node_labels="{'region':'infra'}"openshift_node_kubelet_args="{'image-gc-high-threshold':['90'],'image-gc-low-threshold': ['80']}" openshift_schedulable=true
[etcd]
master.openshift.example.com
[nfs]
master.openshift.example.com
2.3 allinone_without_persistent_storage
[OSEv3:children]
masters
nodes
etcd
nfs
[OSEv3:vars]
ansible_ssh_user=root
debug_level=4
openshift_deployment_type=openshift-enterprise
openshift_master_identity_providers=[{'name':'htpasswd_auth','login':'true', 'challenge':'true', 'kind':'HTPasswdPasswordIdentityProvider','filename':'/etc/origin/master/htpasswd'}]
openshift_master_default_subdomain=cloudapps.openshift.example.com
####install cluster logging, without persistent volume
openshift_logging_install_logging=true
openshift_disable_check=disk_availability,memory_availability
openshift_clock_enabled=true
openshift_template_service_broker_namespaces=['openshift','myproject']
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_kind=nfs
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_nfs_options="*(rw,root_squash,sync,no_wdelay)"
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_nfs_directory=/nfsexports
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_volume_name=
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_access_modes=["ReadWriteOnce"]
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_volume_size=20G
openshift_hosted_etcd_storage_labels={'storage':'etcd'}
ansible_service_broker_local_registry_whitelist=['.*-apb$']
[masters]
master.openshift.example.comopenshift_schedulable=true
[nodes]
master.openshift.example.comopenshift_node_labels="{'region':'infra'}"openshift_node_kubelet_args="{'image-gc-high-threshold':['90'],'image-gc-low-threshold': ['80']}" openshift_schedulable=true
[etcd]
master.openshift.example.com
[nfs]
master.openshift.example.com