FastJSON 转换保存null值
缺省情况下FastJSON不输入为值Null的字段,可以使用SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue使其输出。
例10:
![]()
1 Map map = new HashMap();
2
3 String b = null;
4 Integer i = 1;
5
6 map.put("a", b);
7 map.put("b", i);
8
9 String listJson = JSON.toJSONString(map, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue); ![]()
输出结果:
{"a":null,"b":1}
JSONObject data1 = JSONObject.parseObject(json);
String string = JSON.toJSONString(data1, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue);
System.out.println(string);
Fastjson的SerializerFeature序列化属性
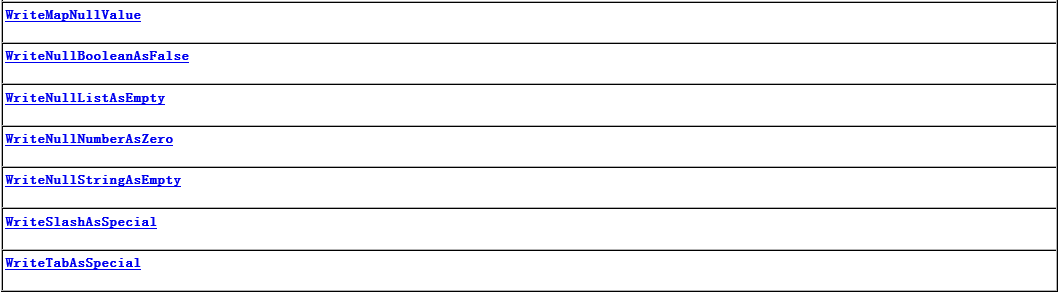
QuoteFieldNames———-输出key时是否使用双引号,默认为true
WriteMapNullValue——–是否输出值为null的字段,默认为false
WriteNullNumberAsZero—-数值字段如果为null,输出为0,而非null
WriteNullListAsEmpty—–List字段如果为null,输出为[],而非null
WriteNullStringAsEmpty—字符类型字段如果为null,输出为”“,而非null
WriteNullBooleanAsFalse–Boolean字段如果为null,输出为false,而非null
FastJSON是一个Java语言编写的高性能,功能完善,完全支持http://json.org的标准的JSON库。多了不说了,百度一下一大把。
在此,简单的总结一下自己用过,测试过的方法。
如果使用Maven,在pom.xml文件加入以下依赖。
1
2 com.alibaba
3 fastjson
4 1.1.23
5
序列化
序列化就是指 把JavaBean对象转成JSON格式的字符串。
com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON提供了许多方法(多态)实现序列化。
1.基本的序列化
String objJson = JSON.toJSONString(Object object);传入一个对象,将对象转成JSON字符串。
例1:将Map转成JSON
1 Map map = new HashMap();
2 map.put("key1", "One");
3 map.put("key2", "Two");
4
5 String mapJson = JSON.toJSONString(map);
输出结果:
{"key1":"One","key2":"Two"}例2:将List
![]()
1 List> list = new ArrayList>();
2
3 Map map1 = new HashMap();
4 map1.put("key1", "One");
5 map1.put("key2", "Two");
6
7 Map map2 = new HashMap();
8 map2.put("key1", "Three");
9 map2.put("key2", "Four");
10
11 list.add(map1);
12 list.add(map2);
13
14 String listJson = JSON.toJSONString(list); ![]()
输出结果:
[{"key1":"One","key2":"Two"},{"key3":"Three","key4":"Four"}]例3:自定义JavaBean User转成JSON。
1 User user = new User();
2 user.setUserName("李四");
3 user.setAge(24);
4
5 String userJson = JSON.toJSONString(user);输出结果:
{"age":24,"userName":"李四"}可以输出格式化后的 JSON 字符串。
String objJson = JSON.toJSONString(Object object, boolean prettyFormat);传入一个对象和一个布尔类型(是否格式化),将对象转成格式化后的JSON字符串。
例4:以例2代码为例。
String listJson = JSON.toJSONString(list, true);输出结果为:
![]()
1 [
2 {
3 "key1":"One",
4 "key2":"Two"
5 },
6 {
7 "key3":"Three",
8 "key4":"Four"
9 }
10 ]![]()
FastJSON提供了许多特性支持。
String objJson = JSON.toJSONString(Object object, SerializerFeature... features) 传入一个对象和SerializerFeature类型的可变变量。SerializerFeature是一个枚举。
com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature
你可以根据自己的情况使用这些特性。
简单说下几个常用的特性:
1.日期格式化:
FastJSON可以直接对日期类型格式化,在缺省的情况下,FastJSON会将Date转成long。
例5:FastJSON将java.util.Date转成long。
1 String dateJson = JSON.toJSONString(new Date());
2
3 System.out.println(dateJson);输出结果:
1401370199040例6:使用SerializerFeature特性格式化日期。
1 String dateJson = JSON.toJSONString(new Date(), SerializerFeature.WriteDateUseDateFormat);
2
3 System.out.println(dateJson);输出结果:
"2014-05-29 21:36:24"也可以指定输出日期格式。
例7:指定输出日期格式。
1 String dateJson = JSON.toJSONStringWithDateFormat(new Date(), "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS");
2
3 System.out.println(dateJson);输出结果:
"2014-05-29 21:47:00.154"2.使用单引号。
例8:以例2为例。
String listJson = JSON.toJSONString(list, SerializerFeature.UseSingleQuotes);输出结果:
[{'key1':'One','key2':'Two'},{'key3':'Three','key4':'Four'}]3.JSON格式化。
例9:
String listJson = JSON.toJSONString(list, SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat);输出结果:与例4结果一致。
4.输出Null字段。
缺省情况下FastJSON不输入为值Null的字段,可以使用SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue使其输出。
例10:
![]()
1 Map map = new HashMap();
2
3 String b = null;
4 Integer i = 1;
5
6 map.put("a", b);
7 map.put("b", i);
8
9 String listJson = JSON.toJSONString(map, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue); ![]()
输出结果:
{"a":null,"b":1}5.序列化是写入类型信息。
例11:
1 User user = new User();
2
3 user.setAge(18);
4 user.setUserName("李四");
5
6 String listJson = JSON.toJSONString(user, SerializerFeature.WriteClassName);输出结果:
{"@type":"User","age":18,"userName":"李四"}由于序列化带了类型信息,使得反序列化时能够自动进行类型识别。
例12:将例11反序列化。
1 User user1 = (User) JSON.parse(listJson);
2
3 System.out.println(user1.getAge());输出结果:
18如果User序列化是没有加入类型信息(SerializerFeature.WriteClassName),按照例12的做法就会报错(java.lang.ClassCastException)。
反序列化
反序列化就是把JSON格式的字符串转化为Java Bean对象。
com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON提供了许多方法(多态)实现反序列化。
简单举几个例子。
指定Class信息反序列化。
例13:将例3反序列化。
1 User user1 = JSON.parseObject(userJson, User.class);
2 System.out.println(user1.getUserName());输出结果:
李四集合反序列化。
例14:将例2反序列化。
1 List输出结果:
1 One
2 Two
3 Three
4 Four泛型的反序列化(使用TypeReference传入类型信息)。
例15:将例1反序列化。
1 Map map1 = JSON.parseObject(mapJson, new TypeReference>(){});
2 System.out.println(map1.get("key1"));
3 System.out.println(map1.get("key2")); 输出结果:
1 One
2 Two
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
JSONObject,JSONArray是JSON的两个子类。
JSONObject相当于Map
JSONArray相当于List
简单方法示例:
例16:将Map转成JSONObject,然后添加元素,输出。
![]()
1 Map map = new HashMap();
2 map.put("key1", "One");
3 map.put("key2", "Two");
4
5 JSONObject j = new JSONObject(map);
6
7 j.put("key3", "Three");
8
9 System.out.println(j.get("key1"));
10 System.out.println(j.get("key2"));
11 System.out.println(j.get("key3")); ![]()
输出结果:
1 One
2 Two
3 Three
例17:将List对象转成JSONArray,然后输出。
![]()
1 List> list = new ArrayList>();
2
3 Map map = new HashMap();
4 map.put("key1", "One");
5 map.put("key2", "Two");
6
7 Map map2 = new HashMap();
8 map2.put("key1", "Three");
9 map2.put("key2", "Four");
10
11 list.add(map);
12 list.add(map2);
13
14 JSONArray j = JSONArray.parseArray(JSON.toJSONString(list));
15
16 for(int i=0; i ![]()
输出结果:
1 {"key1":"One","key2":"Two"}
2 {"key1":"Three","key2":"Four"}更多方法使用请参考API(没有注释的API,让我很头疼啊)。
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Jie-Jack/p/3758046.html