从servlet到springboot(17) springboot处理请求的过程
前面我们分析了springboot的启动,tomcat的源码,这一篇,我们将从tomcat的Acceptor开始,分析一个请求进入servlet的处理过程
首先定位到NioEndpoint中的内部类Acceptor的run方法中的
socket = NioEndpoint.this.serverSock.accept();这句话通过socket监听获取请求
然后找到AbstractProtocal中的ConnectionHandler#process。
这里面会把接收到的socket转化成request
找到state = processor.process(wrapper, status);这句话,通过调用procesor的process方法。在process方法中会调用
CoyoteAdapter#service方法进行适配这里会对Request和Response进行一些封装和转换
然后找到这句话
this.connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);this.connector.getService()获取的是StandardService,从这个service中获取的Container,根据我们在15中介绍的Container体系,在Adapter中获取到的是顶层Container:StandardEngine。从StandardEngine中获取到Pipeline,再从Pipeline中获取到第一个Valve,这边就是StandardEngineValve.调用它的invoke方法
我们看StandardEngineValve的invoke方法
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
Host host = request.getHost();
if (host == null) {
response.sendError(400, sm.getString("standardEngine.noHost", new Object[]{request.getServerName()}));
} else {
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(host.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
host.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
}
}这里会从request中获取到Host类型的Container。这里的Host就是StandardHost,然后与上面一样的方式,调用StandardHostValve的invoke方法
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
Context context = request.getContext();
if (context == null) {
response.sendError(500, sm.getString("standardHost.noContext"));
} else {
if (request.isAsyncSupported()) {
request.setAsyncSupported(context.getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());
}
boolean asyncAtStart = request.isAsync();
boolean asyncDispatching = request.isAsyncDispatching();
try {
context.bind(Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED, MY_CLASSLOADER);
if (asyncAtStart || context.fireRequestInitEvent(request.getRequest())) {
try {
if (asyncAtStart && !asyncDispatching) {
if (!response.isErrorReportRequired()) {
throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("standardHost.asyncStateError"));
}
} else {
context.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);。。。。。。。
这里面有异步处理请求相关的东西。关于这部分内容可以参考这篇文章
https://www.cnblogs.com/davenkin/p/async-servlet.html
同样还是context.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
最后我们进入StandardContextValve的invoke方法
直接看到一句类似的话
wrapper.getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);最终我们进入StandardWrapperValve的invoke方法
public final void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
。。。。。
StandardWrapper wrapper = (StandardWrapper)this.getContainer();
。。。。。。
ApplicationFilterChain filterChain = ApplicationFilterFactory.createFilterChain(request, wrapper, servlet);
filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());
。。。。
我们忽略一些废话,直接看关键性语句,首先获取到StandardWrapper,然后获取到Filter,然后调用filter拦截器链,关于filterChain.doFilter这个方法的调用,有点类似于我们在解析aop原理那一篇所提及的链式调用,通过filter中的doFilter方法,而在doFilter方法中又调用filterChina.doFilter,通过累加索引数字,最终调用到WSFitler的doFilter方法
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
if (this.sc.areEndpointsRegistered() && UpgradeUtil.isWebSocketUpgradeRequest(request, response)) {
HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest)request;
HttpServletResponse resp = (HttpServletResponse)response;
String pathInfo = req.getPathInfo();
String path;
if (pathInfo == null) {
path = req.getServletPath();
} else {
path = req.getServletPath() + pathInfo;
}
WsMappingResult mappingResult = this.sc.findMapping(path);
if (mappingResult == null) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} else {
UpgradeUtil.doUpgrade(this.sc, req, resp, mappingResult.getConfig(), mappingResult.getPathParams());
}
} else {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}这边会先走chain.doFilter(request, response);逻辑
而这段代码最终还是会重新走到ApplicationFilterChain#internalDoFilter,
private void internalDoFilter(ServletRequest request,
ServletResponse response)
throws IOException, ServletException {
// Call the next filter if there is one
if (pos < n) {
ApplicationFilterConfig filterConfig = filters[pos++];
try {
Filter filter = filterConfig.getFilter();
if (request.isAsyncSupported() && "false".equalsIgnoreCase(
filterConfig.getFilterDef().getAsyncSupported())) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR, Boolean.FALSE);
}
if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
Principal principal =
((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal();
Object[] args = new Object[]{req, res, this};
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege ("doFilter", filter, classType, args, principal);
} else {
filter.doFilter(request, response, this);
}
} catch (IOException | ServletException | RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Throwable e) {
e = ExceptionUtils.unwrapInvocationTargetException(e);
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);
throw new ServletException(sm.getString("filterChain.filter"), e);
}
return;
}
// We fell off the end of the chain -- call the servlet instance
try {
if (ApplicationDispatcher.WRAP_SAME_OBJECT) {
lastServicedRequest.set(request);
lastServicedResponse.set(response);
}
if (request.isAsyncSupported() && !servletSupportsAsync) {
request.setAttribute(Globals.ASYNC_SUPPORTED_ATTR,
Boolean.FALSE);
}
// Use potentially wrapped request from this point
if ((request instanceof HttpServletRequest) &&
(response instanceof HttpServletResponse) &&
Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED ) {
final ServletRequest req = request;
final ServletResponse res = response;
Principal principal =
((HttpServletRequest) req).getUserPrincipal();
Object[] args = new Object[]{req, res};
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege("service",
servlet,
classTypeUsedInService,
args,
principal);
} else {
servlet.service(request, response);
}
由于此时pos=n。所以直接走else逻辑,servlet.service.
这里的servlet就是DispatcherServlet,也就是意味着请求正式进入Servlet中,所以我们接下去将分析request在servlet中的走向。
---------------------------------------------------------------
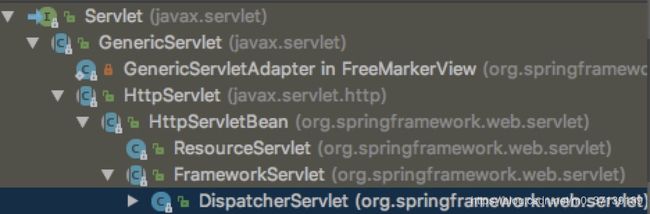
先看下Servlet的结构
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException;
public ServletConfig getServletConfig();
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)
throws ServletException, IOException;
public String getServletInfo();
public void destroy();
其中init方法是在初始化的时候调用的,service是处理request请求的方法, getServletConfig()是获取servlet配置信息的方法
在springboot中,第一次发起请求调用首先会初始化DispatcherServlet,初始化首先会调用init方法,init方法的实现类在HttpServletBean中
首先这句话花会将servletConfig中的配置设置到PropertyValues中
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this); ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext()); bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment())); initBeanWrapper(bw); bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
是一个赋值方法,关于BeanWrapper的用法可以参考https://blog.csdn.net/lz710117239/article/details/79502902
initServletBean是一个模板方法,在子类中实现,我们看FrameworkSevlet#initServletBean
这个方法的核心就是两句话
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); initFrameworkServlet();
第一步初始化了一个WebApplicationContext
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}
这一大串代码主要做了三件事:
1.获取到rootContext
2.调用onRefresh方法
3.把webApplicationContext设置到ServletContext中
onRefresh也是一个模板方法,我们看在DispatherServlet中的实现
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
可以发现这里是初始化了SpringMVC中的九大组件,这个后面再说
initFrameworkServlet();方法也是一个模板方法,但是什么都没做
我们回到Framework的service方法
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());
if (HttpMethod.PATCH == httpMethod || httpMethod == null) {
processRequest(request, response);
}
else {
super.service(request, response);
}
}
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());首先获取到当前request的类型,然后直接调用HttpServlet中的service方法
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String method = req.getMethod();
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
// servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason
// to go through further expensive logic
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince;
try {
ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) {
// Invalid date header - proceed as if none was set
ifModifiedSince = -1;
}
if (ifModifiedSince < (lastModified / 1000 * 1000)) {
// If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet()
// Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare
// A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
doOptions(req,resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
doTrace(req,resp);
} else {
//
// Note that this means NO servlet supports whatever
// method was requested, anywhere on this server.
//
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}
这个方法其实就是根据请求的不同类型来实现不同的路由方法
我们假定是get方法,直接调用frameworkServlet的doGet方法
*/
@Override
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
进入processRequest方法
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (failureCause != null) {
this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", failureCause);
}
else {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing");
}
else {
this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request");
}
}
}
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
这段代码主要做了四件事情
1.设置LocaleContext和RequestAt't'ributes
2.实际处理请求doService
3.在finally语句块中恢复LocaleContext和RequestAt't'ributes
4.发布请求处理完成事件
我们主要看doService这个核心方法
DispatcherServlet#doService
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : "";
logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed +
" processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]");
}
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap();
Enumeration attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
这个方法中主要做了两件事情,
1.给request设置一些属性
2.执行核心方法doDispatcher
前面一些组件设置我们会在后续章节中介绍,这里我们主要说一个东西FlashMap
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response); if (inputFlashMap != null) { request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap)); } request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap()); request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
这串话都是和这个组件息息相关的
这个组件主要用于Redirect的转发时传递参数。比如为了避免重复提交表单,可以在post请求后附加一个get请求。但是如果提交表单之后Redirect也需要前面post请求的参数,由于Redirect本身不能携带参数,只能放在url中,如果我们不想透露一些参数信息,那么就可以把参数放在FlashMap中。具体我们会在以后的springMVC组件系列文章中说明,这里我们简要说明下:inputFlashMap用于保存上次请求中转发过来的属性,outputFlashMap用于保存本次请求需要转发的属性,FlashMapManager用于管理它们。
这一篇已经比较长了,下一篇我们将分析doDispatcher方法