LZW编解码原理与C++实现
一、LZW编解码原理及算法
1.1 树的结构
| 尾缀字符(suffix) |
|---|
| 母节点(parent) |
| 第一个孩子节点(firstchild) |
| 下一个兄弟节点(nextsibling) |
1.2 LZW编码原理和实现算法
LZW的编码思想是不断地从字符流中提取新的字符串,通俗地理解为新“词条”,然后用“代号”也就是码字表示这个“词条”。这样一来,对字符流的编码就变成了用码字去替换字符流,生成码字流,从而达到压缩数据的目的。LZW编码是围绕称为词典的转换表来完成的。LZW编码器通过管理这个词典完成输入与输出之间的转换。LZW编码器的输入是字符流,字符流可以是用8位ASCII字符组成的字符串,而输出是用n位(例如12位)表示的码字流。
LZW编码算法的步骤如下:
步骤1:将词典初始化为包含所有可能的单字符,当前前缀P初始化为空。
步骤2:当前字符C=字符流中的下一个字符。
步骤3:判断P+C是否在词典中
(1)如果“是”,则用C扩展P,即让P=P+C,返回到步骤2。
(2)如果“否”,则
输出与当前前缀P相对应的码字W;
将P+C添加到词典中;
令P=C,并返回到步骤2
1.3 LZW解码原理和实现算法
LZW解码算法开始时,译码词典和编码词典相同,包含所有可能的前缀根。具体解码算法如下:
步骤1:在开始译码时词典包含所有可能的前缀根。
步骤2:令CW:=码字流中的第一个码字。
步骤3:输出当前缀-符串string.CW到码字流。
步骤4:先前码字PW:=当前码字CW。
步骤5:当前码字CW:=码字流的下一个码字。
步骤6:判断当前缀-符串string.CW 是否在词典中。
(1)如果”是”,则把当前缀-符串string.CW输出到字符流。
当前前缀P:=先前缀-符串string.PW。
当前字符C:=当前前缀-符串string.CW的第一个字符。
把缀-符串P+C添加到词典。
(2)如果”否”,则当前前缀P:=先前缀-符串string.PW。
当前字符C:=当前缀-符串string.CW的第一个字符。
输出缀-符串P+C到字符流,然后把它添加到词典中。
步骤7:判断码字流中是否还有码字要译。
(1)如果”是”,就返回步骤4。
(2)如果”否”,结束。
二、关键语句分析
2.1 main()函数分析
以下语句表示如果调试属性中输入的参数个数不足3个,
则会输出相应的提示信息并退出程序。
if (4 > argc) {
fprintf(stdout, "usage: \n%s \n" , argv[0]);
fprintf(stdout, "\t: E or D reffers encode or decode\n" );
fprintf(stdout, "\t: input file name\n" );
fprintf(stdout, "\t: output file name\n" );
return -1;
}
如果调试属性中第一个参数为E, 则代表编码
if (ch == 'E') { // 编码 文件1—>文件2
errno_t err = 0;
err = fopen_s(&fp, FileName1, "rb");//打开输出文件
bf = OpenBitFileOutput(FileName2);//打开输入的二进制文件(结果文件)
if (err == 0 && NULL != bf) {
LZWEncode(fp, bf); //编码操作
//关闭文件
fclose(fp);
CloseBitFileOutput(bf);
fprintf(stdout, "encoding done\n");
}
}
如果调试属性中第一个参数为D, 则代表解码
else if (ch=='D') { // 解码 文件1—>文件2
errno_t err = 0;
err = fopen_s(&fp, FileName2, "wb");
bf = OpenBitFileInput(FileName1);//打开需要解码的文件
if (NULL != fp && NULL != bf) {
LZWDecode(bf, fp);//解码操作
//关闭文件
fclose(fp);
CloseBitFileInput(bf);
fprintf(stdout, "decoding done\n");
}
}
2.2 LZWEncode()函数分析
/*编码
1.字典初始化 包含256个单字符,当前前缀串p为空
2.当前字符c=数据流中的下一字符
3.判断p+c是否在字典中 直到字符流结束
Y:令p=p+c
N:1.输出1.输出与p对应的码字string_code(cw
2.令P+c入词典
3.令p=c
*/
fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_END);//指针定位到文件尾
file_length = ftell(fp);//文件长度
fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_SET);//指针重新指回文件开头
BitsOutput(bf, file_length, 4 * 8);//写文件长度 将需要编码的文件的长度写入输出文件中 (32bit)
InitDictionary();//初始化字典树 字典中有256个字符
string_code = -1;//string_code字符串符号 表示前缀的编码 -1表示前缀为空
//流程图部分
while (EOF != (character = fgetc(fp))) {
index = InDictionary(character, string_code);//判断是否在字典中
if (0 <= index) {// string+character in dictionary string+character在字典中
string_code = index;//string+character在字典中,则InDictionary()返回string+character p<-p+c
}
else { // string+character not in dictionary 否则 string+character不在字典中 那么
output(bf, string_code);//1.输出与string(p)对应的码字string_code(cw)
if (MAX_CODE > next_code) { // free space in dictionary
// add string+character to dictionary
AddToDictionary(character, string_code);//2.将string+character放入字典
}
string_code = character;//3.移动string_code
}
}
2.3 LZWDecode()函数分析
/*解码步骤
1.初始化字典、
2.令cw对应码流中第一个码字
3.从字典中取出cw对应码字,放入字符流
4.cw赋给pw cw对应码流中下一个码字
5.判断cw对应字符是否在字典中 直至码流中无码可译
Y:1.从字典中取出cw对应码字,放入字符流
2.当前前缀p为pw对应码字
3.当前字符c为cw对应码字的第一个字符
4.将p+c写入词典 cw赋给pw
N:1.当前前缀p为pw对应码字
2.当前字符c为pw对应码字的第一个字符
3.将p+c写入词典,再写入字符流 cw赋给pw
*/
file_length = BitsInput(bf, 4 * 8); //读出文件长度
if (-1 == file_length) file_length = 0;
InitDictionary(); //字典初始化
last_code = -1;//初始化时好没有last_code
while (0 < file_length) {
new_code = input(bf);
if (new_code >= next_code) { // this is the case CSCSC( not in dict)cw不在词典中 则由pw 和cw第一个组成
d_stack[0] = character;//
phrase_length = DecodeString(1, last_code);
}
else {
phrase_length = DecodeString(0, new_code);//cw在词典中 则由pw和pw第一个组成
}
character = d_stack[phrase_length - 1];
while (0 < phrase_length) {
phrase_length--;
fputc(d_stack[phrase_length], fp);
file_length--;
}
if (MAX_CODE > next_code) { // add the new phrase to dictionary
AddToDictionary(character, last_code);//所有字符串写入词典
}
last_code = new_code;
}
}
2.4 其他函数
PrintDictionary()
打印词典以供参考。
FindCharacter()
重复寻找前缀 直至没有前缀 返回寻找次数count 也是码字个数 最后一次的suffix为character。
PrintCW
解码时将new_code对应的码字写入二进制文件。
InitDictionary()
初始化字典,字典初始化为包含所有的256个单字符。单个字符没有母节点。每个节点的尾缀字符是自身,兄弟节点是自己+1,最后一个节点没有下一个兄弟节点。
InDictionary()
查找字典中是否有字符串, 即p+c是否在字典中。
如果没有前缀,那么直接返回刚读入进来的字符
如果某一child的尾缀和character相同 则说明字典中有string+character(p+c)则返回sibling(string+character)
否则,child尾缀与character不相同,则查找当前child的nextsibling
int InDictionary(int character, int string_code) { //string_code:前缀串号 character:数据流中的下一个字符c
int sibling;
if (0 > string_code) return character;//如果没有前缀,那么直接返回刚读入进来的字符
sibling = dictionary[string_code].firstchild;//sibling为前缀p 前缀为string_code的first_child
while (-1 < sibling) {
if (character == dictionary[sibling].suffix) return sibling;//如果某一child的尾缀和character相同 则说明字典中有string+character(p+c)则返回sibling(string+character)
sibling = dictionary[sibling].nextsibling;//否则,child尾缀与character不相同,则查找当前child的nextsibling
}
return -1;
}
AddToDictionary()
将string+character放入字典。
若前缀string_code的树中有后缀:
查找nextsibling的下一个值,直到最后一个节点,
将nextsibing的下一个字符设为next_code;
若前缀string_code的树中无后缀:
将strin_code的first_child设为next_code。
void AddToDictionary(int character, int string_code) {
int firstsibling, nextsibling;
if (0 > string_code) return;
dictionary[next_code].suffix = character;//尾缀字符添加为character
dictionary[next_code].parent = string_code;//前缀为string_code
dictionary[next_code].nextsibling = -1; //没有nextsibling
dictionary[next_code].firstchild = -1; //没有firstchild
firstsibling = dictionary[string_code].firstchild;
if (-1 < firstsibling) { // the parent has child
nextsibling = firstsibling;
while (-1 < dictionary[nextsibling].nextsibling)//查找nextsibling的下一个值,直到最后一个节点
nextsibling = dictionary[nextsibling].nextsibling;
dictionary[nextsibling].nextsibling = next_code;//将nextsibing的下一个字符设为next_code
}
else {// no child before, modify it to be the first//若前缀string_code的树中无后缀
dictionary[string_code].firstchild = next_code;//将strin_code的first_child设为next_code
}
next_code++;
}
三、实验结果
3.1 txt文件编解码
编写“1.txt”,对其编码,得到“1.dat”。
对“1.dat”进行解码操作,得到“2.txt”,程序运行结果如下:



3.2不同类型文件编码效率对比
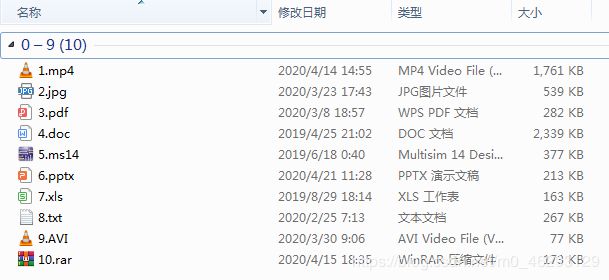
| 文件类型 | 原始大小(k) | 压缩后大小(k) | 压缩效率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| mp4 | 1761 | 2084 | -18.34% |
| jpg | 539 | 696 | -29.13% |
| 282 | 335 | -18.79% | |
| doc | 2339 | 2246 | 3.98% |
| ms14 | 377 | 453 | -20.16% |
| pptx | 213 | 268 | -25.82% |
| xls | 163 | 108 | 33.74% |
| txt | 267 | 56 | 79.03% |
| avi | 77 | 36 | 53.25% |
| rar | 173 | 233 | -34.68% |
由上表可以看出,LZW算法在xls、txt、avi等格式的文件压缩上效果较好,而用在另一些格式的文件上会“适得其反”,出现压缩后文件更大的现象。同时,文件压缩效率还与文件大小有关:以doc为例,当原始文件为2339kb,压缩效率为3.98%;而当文件大小为15993kb,压缩效率竟变成-13.59%。这可能是由于一些文件中字符重复率较高,利用字典压缩效果较好;而另一些文件中字符重复率低,字典带来的数据反而成了一种冗余。
四、代码实现
lzw_E.cpp
#include "pch.h"
#include \n" , argv[0]);
fprintf(stdout, "\t: E or D reffers encode or decode\n" );
fprintf(stdout, "\t: input file name\n" );
fprintf(stdout, "\t: output file name\n" );
return -1;
}
if ('E' == argv[1][0]) { // do encoding
errno_t err = 0;
err = fopen_s(&fp, argv[2], "rb");
//fp = fopen(argv[2], "rb");
bf = OpenBitFileOutput(argv[3]);
if (NULL != fp && NULL != bf) {
LZWEncode(fp, bf);
fclose(fp);
CloseBitFileOutput(bf);
fprintf(stdout, "encoding done\n");
}
}
else if ('D' == argv[1][0]) { // do decoding
bf = OpenBitFileInput(argv[2]);
errno_t err = 0;
err = fopen_s(&fp, argv[3], "wb");
//fp = fopen(argv[3], "wb");
if (NULL != fp && NULL != bf) {
LZWDecode(bf, fp);
fclose(fp);
CloseBitFileInput(bf);
fprintf(stdout, "decoding done\n");
}
}
else { // otherwise
fprintf(stderr, "not supported operation\n");
}
return 0;
}
bitio.cpp
#include "pch.h"
#include bitio.h
#pragma once
#ifndef __BITIO__
#define __BITIO__
#include