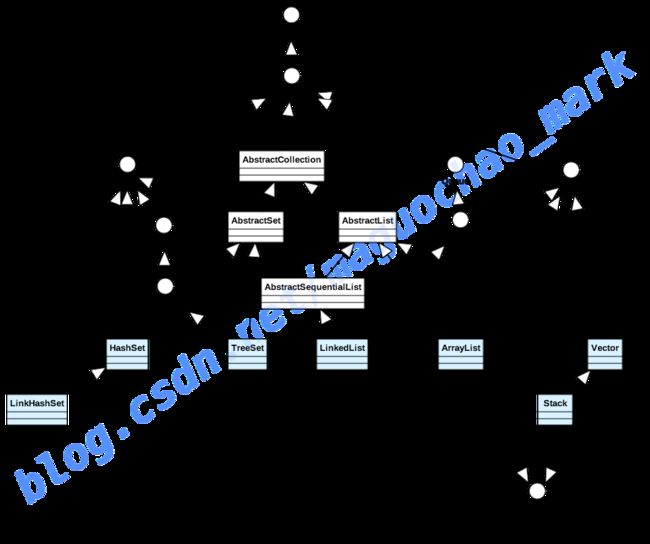
【JAVA】四 JAVA集合 Collection ArrayList LinkedList
【JAVA】四 JAVA集合 Collection ArrayList LinkedList
Collection
Collection 已知子集
BeanContext, BeanContextServices, BlockingDeque<E>, BlockingQueue<E>, Deque<E>,
List<E>,NavigableSet<E>, Queue<E>, Set<E>, SortedSet<E>, TransferQueue<E>List
ArrayList
是实现了基于动态数组的数据结构 .
ArrayList的内部实现是基于基础的对象数组 . 通过源码可以看到是Object[] 数组
ArrayList实现java.util.RandomAccess 接口 .
对于随机访问get和set,ArrayList觉得优于LinkedList, 因为LinkedList要移动指针。
ArrayList私有属性
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
/**
*默认容量
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* 共享空数组实例用于空实例.
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* ArrayList的元素的数组缓冲区存储。
* ArrayList的容量是这个数组的长度缓冲区。任何
* 空ArrayList elementData = = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA将扩大到
* DEFAULT_CAPACITY当第一个元素被添加。
*/
private transient Object[] elementData;
/**
* ArrayList的大小(它所包含的元素数量).
*
* @serial
*/
private int size;
}ArrayList构造方法
/**
* 构造一个与指定初始容量的空列表。
* @param initialCapacity列表的初始容量如果指定初始容量
* @throws IllegalArgumentException 负容量异常
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
}
/**
* 构造一个空列表的初始容量10.
*/
public ArrayList() {
super();
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* 构造一个包含指定的元素列表收集,它们的顺序返回的集合迭代器。
* @param c元素的集合被放置到这个列表中如果指定集合为空
* @throws NullPointerException
*/
public ArrayList(Collection c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
size = elementData.length;
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
}
| 构造方法 | |
|---|---|
| ArrayList() | 指定EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA,也就是一个空的ArrayList |
| ArrayList(int initialCapacity) | 指定ArrayList 的初始化大小 |
| ArrayList(Collection c) | 接受一个Collection子集,并将这个子集转为ArrayList类型 |
ArrayList添加值
/**
* 检查给定的指标范围。如果不是有效的范围,抛出一个运行时异常。
* 这个方法不检查负参数,总是立即使用数组访问之前,
* 抛出ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException如果指数是负的。
*
* PS:当用负数去访问一个数组下标时,数组就后throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException
*/
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* 替换元素在这个列表中指定的位置指定的元素。
* @param指数指数的元素来代替
* @param元素元素存储在指定的位置
* @return元素之前指定的位置
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException { @inheritDoc }
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
/**
* 将指定的元素添加到列表尾部。
* @param e 元素附加到这个列表
* @return 成功返回true { @linkCollection add方法})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
/**
* 通过添加和addAll rangeCheck版本使用。
*
* PS:在这里验证了index是否为负数
*/
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* 在指定位置插入指定的元素列表。
* 变化的元素目前位置(如果有的话)
* 任何后续元素向右(添加一个索引)。PS:要注意这句,这也是为什么相效于LinkedList插入对象时效率低的原因.
* @param指数的指数是插入指定元素
* @param要插入元素的元素
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException { @inheritDoc }
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
/**
* 附加的所有元素在指定集合的末尾
* 这个列表的顺序返回的指定集合的迭代器。
* 这个操作的行为未定义的操作时,如果指定的集合被修改在进步。
* (这意味着这个调用的行为定义如果这个列表指定的集合,这列表非空的。)
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return true if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
/**
*
* 从指定的位置将指定集合中的所有元素插入列表。
* 变化的元素目前这个位置(如果有的话)和任何后续的元素
* 正确的(增加他们的下标)。新元素就会出现的顺序在列表中返回的
* 指定集合的迭代器。
* @param index index at which to insert the first element from the
* specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return true if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
int numMoved = size - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}关于上面的代码验证index
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0) // PS:在这里验证了index是否为负数
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size) // PS:当用负数去访问一个数组下标时,数组就后throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
这里有验证index思想没有统一,估计是两个人写的两个方法,在看看ArrayList的作者
@author Josh Bloch
@author Neal Gafter
这里纯属猜测 .ArrayList 取值
/**
* 返回此列表的元素在指定的位置.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
LinkedList
基于链表的数据结构。
LinkedList中的get方法是按照顺序从列表的一端开始检查,直到另结尾 .
LinkedList类是双向列表,列表中的每个节点都包含了对前一个和后一个元素的引用.
LinkedList实现Deque ,间接实现Queue .
对于新增和删除操作add和remove,LinedList比较占优势,因为ArrayList要移动数据。
LinkedList 私有属性
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node next;
Node prev;
Node(Node prev, E element, Node next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
transient int size = 0;
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node last;
}
相较于ArrayList , LinkedList要有趣的多,它的first 与 last 两个节点属性是Node的静态内部类,这也证明了LinkedArrayList 是一个双向链表的数据结构 .
transient 关键字使属性在序列化时被忽略 .
LinkedList构造方法
/**
* Constructs an empty list.
*/
public LinkedList() {
}
/**
* 构造一个包含指定的元素列表Collection,它们的顺序返回的Collection迭代器.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public LinkedList(Collection c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
| 构造方法 | |
|---|---|
| LinkedList() | 也就是一个空的LinkedList 有 first 与 last 两个属性 |
| LinkedList(Collection c) | 接受一个Collection子集,并将这个子集转为LinkedList类型 |
关于Collection子集上面简单的介绍过了.
LinkedList添加值
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the beginning of this list.
* 添加一个指定的对象到头
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
* 添加一个指定的对象到尾
* This method is equivalent to {@link #add}.
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node l = last;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
* 添加一个指定的对象到尾
* This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* 附加的所有元素在指定集合的末尾
* 这个列表的顺序指定返回的集合的迭代器。
* 这个操作的行为是未定义的指定的集合操作时被修改进步。
* (注意,这将发生如果指定的集合这个列表,非空的)。
*
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
/**
* 从指定的位置将指定集合中的所有元素插入列表。
* 变化的元素目前这个位置(如果有的话)和任何后续的元素正确的(增加他们的指标)。
* 新元素就会出现的顺序在列表中返回的指定集合的迭代器。
*
* @param index index at which to insert the first element
* from the specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
/**
* 替换的元素在这个列表的指定位置指定元素。
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
checkElementIndex(index);
Node x = node(index);
E oldVal = x.item;
x.item = element;
return oldVal;
}
/**
* 在指定位置插入指定元素在这个列表中。
* 转变当前元素(如果有的话)和任何位置
* 后续元素向右(添加一个索引)。
*
* PS : 相效于ArrayList 要移动index后所有的元素 LinkedList 要高效很多.
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
/**
* 之前插入元素e succ非空节点。.
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node pred = succ.prev;
final Node newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
/**
* 添加一个元素到头.
*
* This method is equivalent to {@link #addFirst}.
*
* @param e the element to push
* @since 1.6
*/
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
LinkedList 取值
/**
* 返回头元素.
*
* @return the first element in this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E getFirst() {
final Node f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
/**
* 返回尾元素.
*
* @return the last element in this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E getLast() {
final Node l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
/**
* 通过下标得到元素.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
/**
* node方法通过下标得到元素
*
* PS : 第一次进入方法用到一个二分,之后就是for,其实可以改为二分查找 .
*/
Node node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
/**
* 返回头元素.
*
* @return the head of this list, or {@code null} if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E peek() {
final Node f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
/**
* 返回头元素.
*
* @return the head of this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
/**
* 取得头元素, 并将头元素删除 , 将第二个元素作为头元素
* @return the head of this list, or {@code null} if this list is empty
* @since 1.5
*/
public E poll() {
final Node f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
/**
*
* 取得头元素
*
* PS : 此方法与 1.5 peek方法内容一至
*
* @return the first element of this list, or {@code null}
* if this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E peekFirst() {
final Node f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : f.item;
}
/**
* 取得尾元素 .
*
* @return the last element of this list, or {@code null}
* if this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E peekLast() {
final Node l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : l.item;
}
/**
* 取头,删除头,第二个元素做为头元素.
*
* @return the first element of this list, or {@code null} if
* this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E pollFirst() {
final Node f = first;
return (f == null) ? null : unlinkFirst(f);
}
/**
* 取尾,删除尾,倒数第二个元素做为尾元素..
*
* @return the last element of this list, or {@code null} if
* this list is empty
* @since 1.6
*/
public E pollLast() {
final Node l = last;
return (l == null) ? null : unlinkLast(l);
}
ArrayList LinkedList 性能比较
package com.cn.mark.java.util;
import java.util.*;
/**
* Created by mark on 5/22/16.
*/
public class ListTest {
private static int N = 50000;
private static List values;
private static int list_size ;
static Random r = new Random();
//add
static long test_ArrayList_add_first(ArrayList list){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
list.add(0, i);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
static long test_LinkedList_add_first(LinkedList list){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
list.addFirst(i);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
static long test_ArrayList_add_last(ArrayList list){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
list.add(i);//ArrayList 默认加在尾
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
static long test_LinkedList_add_last(LinkedList list){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
list.addLast(i);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
static long test_ArrayList_add_random(ArrayList list){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
list.add(r.nextInt(N), 1);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
static long test_LinkedList_add_random(LinkedList list){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
list.add(r.nextInt(N), 1);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
//del
static long test_ArrayList_del_first(ArrayList list){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
list.remove(0);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
static long test_LinkedList_del_first(LinkedList list){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
list.remove();// 默认删除头
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
static long test_ArrayList_del_last(ArrayList list){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
list.remove(list.size()-1);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
static long test_LinkedList_del_last(LinkedList list){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
list.removeLast();
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
static long test_ArrayList_del_random(ArrayList list){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
list_size = list.size();
for (int i = 0; i < list_size; i++){
list_size = list.size();
list.remove(r.nextInt(list_size - 1));
}
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
static long test_LinkedList_del_random(LinkedList list){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
list_size = list.size();
for (int i = 0; i < list_size; i++){
list_size = list.size();
list.remove(r.nextInt(list_size - 1));
}
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
//modifier
static long test_ArrayList_set_random(ArrayList list){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
list.set(r.nextInt(N), 1);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
static long test_LinkedList_set_random(LinkedList list){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
list.set(r.nextInt(N), 1);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
//query
static long test_ArrayList_get_first(ArrayList list) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
list.get(i);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
static long test_LinkedList_get_first(LinkedList list) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
list.poll();
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
static long test_ArrayList_get_last(ArrayList list) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = N-1; i >0; i--)
list.get(i);
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
static long test_LinkedList_get_last(LinkedList list) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
list.pollLast();
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
static long test_ArrayList_get_random(ArrayList list) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
list.get(r.nextInt(N));
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
static long test_LinkedList_get_random(LinkedList list) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
list.get(r.nextInt(N));
return System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Long vals[] = new Long[N];
Random r = new Random();
for (int i = 0, currval = 0; i < N; i++) {
vals[i] = new Long(currval);
currval += r.nextInt(100) + 1;
}
values = Arrays.asList(vals);
// add
System.out.println("test_ArrayList_add_first \t" + test_ArrayList_add_first(new ArrayList(values)));
System.out.println("test_LinkedList_add_first \t" + test_LinkedList_add_first(new LinkedList(values)));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("test_ArrayList_add_last \t" + test_ArrayList_add_last(new ArrayList(values)));
System.out.println("test_LinkedList_add_last \t" + test_LinkedList_add_last(new LinkedList(values)));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("test_ArrayList_add_random \t" + test_ArrayList_add_random(new ArrayList(values)));
System.out.println("test_LinkedList_add_random \t" + test_LinkedList_add_random(new LinkedList(values)));
System.out.println();
//del
System.out.println("test_ArrayList_del_first \t" + test_ArrayList_del_first(new ArrayList(values)));
System.out.println("test_LinkedList_del_first \t" + test_LinkedList_del_first(new LinkedList(values)));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("test_ArrayList_del_last \t" + test_ArrayList_del_last(new ArrayList(values)));
System.out.println("test_LinkedList_del_last \t" + test_LinkedList_del_last(new LinkedList(values)));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("test_ArrayList_del_random \t" + test_ArrayList_del_random(new ArrayList(values)));
System.out.println("test_LinkedList_del_random \t" + test_LinkedList_del_random(new LinkedList(values)));
System.out.println();
//modifier
System.out.println("test_ArrayList_set_random \t" + test_ArrayList_set_random(new ArrayList(values)));
System.out.println("test_LinkedList_set_random \t" + test_LinkedList_set_random(new LinkedList(values)));
System.out.println();
//query
System.out.println("test_ArrayList_get_first \t" + test_ArrayList_get_first(new ArrayList(values)));
System.out.println("test_LinkedList_get_first \t" + test_LinkedList_get_first(new LinkedList(values)));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("test_ArrayList_get_last \t" + test_ArrayList_get_last(new ArrayList(values)));
System.out.println("test_LinkedList_get_last \t" + test_LinkedList_get_last(new LinkedList(values)));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("test_ArrayList_get_random \t" + test_ArrayList_get_random(new ArrayList(values)));
System.out.println("test_LinkedList_get_random \t" + test_LinkedList_get_random(new LinkedList(values)));
}
}
运行结果
test_ArrayList_add_first 833
test_LinkedList_add_first 8
test_ArrayList_add_last 7
test_LinkedList_add_last 10
test_ArrayList_add_random 455
test_LinkedList_add_random 7905
test_ArrayList_del_first 223
test_LinkedList_del_first 5
test_ArrayList_del_last 3
test_LinkedList_del_last 4
test_ArrayList_del_random 69
test_LinkedList_del_random 713
test_ArrayList_set_random 4
test_LinkedList_set_random 1303
test_ArrayList_get_first 2
test_LinkedList_get_first 2
test_ArrayList_get_last 2
test_LinkedList_get_last 3
test_ArrayList_get_random 3
test_LinkedList_get_random 1299
Process finished with exit code 0