WebRTC VideoEngine综合应用示例(一)——视频通话的基本流程
本系列目前共三篇文章,后续还会更新
WebRTC VideoEngine综合应用示例(一)——视频通话的基本流程
WebRTC VideoEngine综合应用示例(二)——集成OPENH264编解码器
WebRTC VideoEngine综合应用示例(三)——集成X264编码和ffmpeg解码
关注下方公众号,回复“webrtc视频通话”,查看源码地址,是一个可以脱离webrtc那个大项目而独立运行的工程
关注公众号,掌握更多多媒体领域知识与资讯
![]()
文章帮到你了?可以扫描如下二维码进行打赏~,打赏多少您随意~
![]()
WebRTC技术的出现改变了传统即时通信的现状,它是一套开源的旨在建立浏览器端对端的通信标准的技术,支持浏览器平台,使用P2P架构。WebRTC所采用的技术都是当前VoIP先进的技术,如内部所采用的音频引擎是Google收购知名GIPS公司获得的核心技术:视频编解码则采用了VP8。
大家都说WebRTC好,是未来的趋势,但是不得不说这个开源项目对新手学习实在是太不友好,光是windows平台下的编译就能耗费整整一天的精力,还未必能成功,关于这个问题在我之前的文章中有所描述。编译成功之后打开一看,整个solution里面有215个项目,绝对让人当时就懵了,而且最重要的是,google方面似乎没给出什么有用的文档供人参考,网络上有关的资料也多是有关于web端开发的,和Native API开发有关的内容少之又少,于是我决定把自己这两天学习VideoEngine的成果分享出来,供大家参考,有什么问题也欢迎大家指出,一起学习一起进步。
首先需要说明的是,webrtc项目的all.sln下有一个vie_auto_test项目,里面包含了一些针对VideoEngine的测试程序,我这里的demo就是基于此修改得到的。
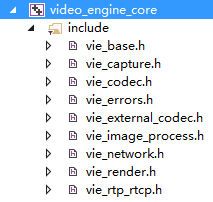
先来看一下VideoEngine的核心API,基本上就在以下几个头文件中了。
具体来说
ViEBase用于
- 创建和销毁 VideoEngine 实例
- 创建和销毁 channels
- 将 video channel 和相应的 voice channel 连接到一起并同步
- 发送和接收的开始与停止
ViECapture用于
- 分配capture devices.
- 将 capture device 与一个或多个 channels连接起来.
- 启动或停止 capture devices.
- 获得capture device 的可用性.
ViECodec用于
- 设置发送和接收的编解码器.
- 设置编解码器特性.
- Key frame signaling.
- Stream management settings.
ViEError即一些预定义的错误消息
ViEExternalCodec用于注册除VP8之外的其他编解码器
ViEImageProcess提供以下功能
- Effect filters
- 抗闪烁
- 色彩增强
ViENetwork用于
- 配置发送和接收地址.
- External transport support.
- 端口和地址过滤.
- Windows GQoS functions and ToS functions.
- Packet timeout notification.
- Dead‐or‐Alive connection observations.
ViERender用于
- 为输入视频流、capture device和文件指定渲染目标.
- 配置render streams.
ViERTP_RTCP用于
- Callbacks for RTP and RTCP events such as modified SSRC or CSRC.
- SSRC handling.
- Transmission of RTCP reports.
- Obtaining RTCP data from incoming RTCP sender reports.
- RTP and RTCP statistics (jitter, packet loss, RTT etc.).
- Forward Error Correction (FEC).
- Writing RTP and RTCP packets to binary files for off‐line analysis of the call quality.
- Inserting extra RTP packets into active audio stream.
下面将以实现一个视频通话功能为实例详细介绍VideoEngine的使用,在文末将附上相应源码的下载地址
第一步是创建一个VideoEngine实例,如下
webrtc::VideoEngine* ptrViE = NULL;
ptrViE = webrtc::VideoEngine::Create();
if (ptrViE == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in VideoEngine::Create\n");
return -1;
}然后初始化VideoEngine并创建一个Channel
webrtc::ViEBase* ptrViEBase = webrtc::ViEBase::GetInterface(ptrViE);
if (ptrViEBase == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in ViEBase::GetInterface\n");
return -1;
}
error = ptrViEBase->Init();//这里的Init其实是针对VideoEngine的初始化
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViEBase::Init\n");
return -1;
}
webrtc::ViERTP_RTCP* ptrViERtpRtcp =
webrtc::ViERTP_RTCP::GetInterface(ptrViE);
if (ptrViERtpRtcp == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in ViERTP_RTCP::GetInterface\n");
return -1;
}
int videoChannel = -1;
error = ptrViEBase->CreateChannel(videoChannel);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViEBase::CreateChannel\n");
return -1;
}列出可用的capture devices等待用户进行选择, 然后进行allocate和connect,最后start选中的capture device
webrtc::ViECapture* ptrViECapture =
webrtc::ViECapture::GetInterface(ptrViE);
if (ptrViEBase == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in ViECapture::GetInterface\n");
return -1;
}
const unsigned int KMaxDeviceNameLength = 128;
const unsigned int KMaxUniqueIdLength = 256;
char deviceName[KMaxDeviceNameLength];
memset(deviceName, 0, KMaxDeviceNameLength);
char uniqueId[KMaxUniqueIdLength];
memset(uniqueId, 0, KMaxUniqueIdLength);
printf("Available capture devices:\n");
int captureIdx = 0;
for (captureIdx = 0;
captureIdx < ptrViECapture->NumberOfCaptureDevices();
captureIdx++)
{
memset(deviceName, 0, KMaxDeviceNameLength);
memset(uniqueId, 0, KMaxUniqueIdLength);
error = ptrViECapture->GetCaptureDevice(captureIdx, deviceName,
KMaxDeviceNameLength, uniqueId,
KMaxUniqueIdLength);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViECapture::GetCaptureDevice\n");
return -1;
}
printf("\t %d. %s\n", captureIdx + 1, deviceName);
}
printf("\nChoose capture device: ");
if (scanf("%d", &captureIdx) != 1)
{
printf("Error in scanf()\n");
return -1;
}
getchar();
captureIdx = captureIdx - 1; // Compensate for idx start at 1.
error = ptrViECapture->GetCaptureDevice(captureIdx, deviceName,
KMaxDeviceNameLength, uniqueId,
KMaxUniqueIdLength);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViECapture::GetCaptureDevice\n");
return -1;
}
int captureId = 0;
error = ptrViECapture->AllocateCaptureDevice(uniqueId, KMaxUniqueIdLength,
captureId);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViECapture::AllocateCaptureDevice\n");
return -1;
}
error = ptrViECapture->ConnectCaptureDevice(captureId, videoChannel);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViECapture::ConnectCaptureDevice\n");
return -1;
}
error = ptrViECapture->StartCapture(captureId);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViECapture::StartCapture\n");
return -1;
}
设置RTP/RTCP所采用的模式
error = ptrViERtpRtcp->SetRTCPStatus(videoChannel,
webrtc::kRtcpCompound_RFC4585);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViERTP_RTCP::SetRTCPStatus\n");
return -1;
}设置接收端解码器出问题的时候,比如关键帧丢失或损坏,如何重新请求关键帧的方式
error = ptrViERtpRtcp->SetKeyFrameRequestMethod(
videoChannel, webrtc::kViEKeyFrameRequestPliRtcp);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViERTP_RTCP::SetKeyFrameRequestMethod\n");
return -1;
}设置是否为当前channel使用REMB(Receiver Estimated Max Bitrate)包,发送端可以用它表明正在编码当前channel
接收端用它来记录当前channel的估计码率
error = ptrViERtpRtcp->SetRembStatus(videoChannel, true, true);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViERTP_RTCP::SetTMMBRStatus\n");
return -1;
}设置rendering用于显示
webrtc::ViERender* ptrViERender = webrtc::ViERender::GetInterface(ptrViE);
if (ptrViERender == NULL) {
printf("ERROR in ViERender::GetInterface\n");
return -1;
}显示本地摄像头数据,这里的window1和下面的window2都是显示窗口,更详细的内容后面再说
error
= ptrViERender->AddRenderer(captureId, window1, 0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViERender::AddRenderer\n");
return -1;
}
error = ptrViERender->StartRender(captureId);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViERender::StartRender\n");
return -1;
}显示接收端收到的解码数据
error = ptrViERender->AddRenderer(videoChannel, window2, 1, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0,
1.0);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViERender::AddRenderer\n");
return -1;
}
error = ptrViERender->StartRender(videoChannel);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViERender::StartRender\n");
return -1;
}设置编解码器
webrtc::ViECodec* ptrViECodec = webrtc::ViECodec::GetInterface(ptrViE);
if (ptrViECodec == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in ViECodec::GetInterface\n");
return -1;
}
VideoCodec videoCodec;
int numOfVeCodecs = ptrViECodec->NumberOfCodecs();
for (int i = 0; iGetCodec(i, videoCodec) != -1)
{
if (videoCodec.codecType == kVideoCodecVP8)
break;
}
}
videoCodec.targetBitrate = 256;
videoCodec.minBitrate = 200;
videoCodec.maxBitrate = 300;
videoCodec.maxFramerate = 25;
error = ptrViECodec->SetSendCodec(videoChannel, videoCodec);
assert(error != -1);
error = ptrViECodec->SetReceiveCodec(videoChannel, videoCodec);
assert(error != -1);
设置接收和发送地址,然后开始发送和接收
webrtc::ViENetwork* ptrViENetwork =
webrtc::ViENetwork::GetInterface(ptrViE);
if (ptrViENetwork == NULL)
{
printf("ERROR in ViENetwork::GetInterface\n");
return -1;
}
//VideoChannelTransport是由我们自己定义的类,后面将会详细介绍
VideoChannelTransport* video_channel_transport = NULL;
video_channel_transport = new VideoChannelTransport(
ptrViENetwork, videoChannel);
const char* ipAddress = "127.0.0.1";
const unsigned short rtpPort = 6000;
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "Using rtp port: " << rtpPort << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
error = video_channel_transport->SetLocalReceiver(rtpPort);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in SetLocalReceiver\n");
return -1;
}
error = video_channel_transport->SetSendDestination(ipAddress, rtpPort);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in SetSendDestination\n");
return -1;
}
error = ptrViEBase->StartReceive(videoChannel);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViENetwork::StartReceive\n");
return -1;
}
error = ptrViEBase->StartSend(videoChannel);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViENetwork::StartSend\n");
return -1;
}设置按下回车键即停止通话
printf("\n call started\n\n");
printf("Press enter to stop...");
while ((getchar()) != '\n')
;停止通话后的各种stop
error = ptrViEBase->StopReceive(videoChannel);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViEBase::StopReceive\n");
return -1;
}
error = ptrViEBase->StopSend(videoChannel);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViEBase::StopSend\n");
return -1;
}
error = ptrViERender->StopRender(captureId);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViERender::StopRender\n");
return -1;
}
error = ptrViERender->RemoveRenderer(captureId);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViERender::RemoveRenderer\n");
return -1;
}
error = ptrViERender->StopRender(videoChannel);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViERender::StopRender\n");
return -1;
}
error = ptrViERender->RemoveRenderer(videoChannel);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViERender::RemoveRenderer\n");
return -1;
}
error = ptrViECapture->StopCapture(captureId);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViECapture::StopCapture\n");
return -1;
}
error = ptrViECapture->DisconnectCaptureDevice(videoChannel);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViECapture::DisconnectCaptureDevice\n");
return -1;
}
error = ptrViECapture->ReleaseCaptureDevice(captureId);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViECapture::ReleaseCaptureDevice\n");
return -1;
}
error = ptrViEBase->DeleteChannel(videoChannel);
if (error == -1)
{
printf("ERROR in ViEBase::DeleteChannel\n");
return -1;
}
delete video_channel_transport;
int remainingInterfaces = 0;
remainingInterfaces = ptrViECodec->Release();
remainingInterfaces += ptrViECapture->Release();
remainingInterfaces += ptrViERtpRtcp->Release();
remainingInterfaces += ptrViERender->Release();
remainingInterfaces += ptrViENetwork->Release();
remainingInterfaces += ptrViEBase->Release();
if (remainingInterfaces > 0)
{
printf("ERROR: Could not release all interfaces\n");
return -1;
}
bool deleted = webrtc::VideoEngine::Delete(ptrViE);
if (deleted == false)
{
printf("ERROR in VideoEngine::Delete\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
以上就是VideoEngine的基本使用流程,下面说一下显示窗口如何创建
这里使用了webrtc已经为我们定义好的类ViEWindowCreator,它有一个成员函数CreateTwoWindows可以直接创建两个窗口,只需实现定义好窗口名称、窗口大小以及坐标即可,如下
ViEWindowCreator windowCreator;
ViEAutoTestWindowManagerInterface* windowManager =
windowCreator.CreateTwoWindows();
VideoEngineSample(windowManager->GetWindow1(),
windowManager->GetWindow2());这里的VideoEngineSample就是我们在前面所写的包含全部流程的示例程序,它以两个窗口的指针作为参数
至于前面提到的VideoChannelTransport定义如下
class VideoChannelTransport : public webrtc::test::UdpTransportData {
public:
VideoChannelTransport(ViENetwork* vie_network, int channel);
virtual ~VideoChannelTransport();
// Start implementation of UdpTransportData.
virtual void IncomingRTPPacket(const int8_t* incoming_rtp_packet,
const int32_t packet_length,
const char* /*from_ip*/,
const uint16_t /*from_port*/) OVERRIDE;
virtual void IncomingRTCPPacket(const int8_t* incoming_rtcp_packet,
const int32_t packet_length,
const char* /*from_ip*/,
const uint16_t /*from_port*/) OVERRIDE;
// End implementation of UdpTransportData.
// Specifies the ports to receive RTP packets on.
int SetLocalReceiver(uint16_t rtp_port);
// Specifies the destination port and IP address for a specified channel.
int SetSendDestination(const char* ip_address, uint16_t rtp_port);
private:
int channel_;
ViENetwork* vie_network_;
webrtc::test::UdpTransport* socket_transport_;
};
VideoChannelTransport::VideoChannelTransport(ViENetwork* vie_network,
int channel)
: channel_(channel),
vie_network_(vie_network) {
uint8_t socket_threads = 1;
socket_transport_ = webrtc::test::UdpTransport::Create(channel, socket_threads);
int registered = vie_network_->RegisterSendTransport(channel,
*socket_transport_);
}
VideoChannelTransport::~VideoChannelTransport() {
vie_network_->DeregisterSendTransport(channel_);
webrtc::test::UdpTransport::Destroy(socket_transport_);
}
void VideoChannelTransport::IncomingRTPPacket(
const int8_t* incoming_rtp_packet,
const int32_t packet_length,
const char* /*from_ip*/,
const uint16_t /*from_port*/) {
vie_network_->ReceivedRTPPacket(
channel_, incoming_rtp_packet, packet_length, PacketTime());
}
void VideoChannelTransport::IncomingRTCPPacket(
const int8_t* incoming_rtcp_packet,
const int32_t packet_length,
const char* /*from_ip*/,
const uint16_t /*from_port*/) {
vie_network_->ReceivedRTCPPacket(channel_, incoming_rtcp_packet,
packet_length);
}
int VideoChannelTransport::SetLocalReceiver(uint16_t rtp_port) {
int return_value = socket_transport_->InitializeReceiveSockets(this,
rtp_port);
if (return_value == 0) {
return socket_transport_->StartReceiving(500);
}
return return_value;
}
int VideoChannelTransport::SetSendDestination(const char* ip_address,
uint16_t rtp_port) {
return socket_transport_->InitializeSendSockets(ip_address, rtp_port);
}
继承自UdpTransportData类,主要重写了IncomingRTPPacket和IncomingRTCPPacket两个成员函数,分别调用了vie_network的ReceivedRTPPacket和ReceivedRTCPPacket方法,当需要将接收到的RTP和RTCP包传给VideoEngine时就应该使用这两个函数。
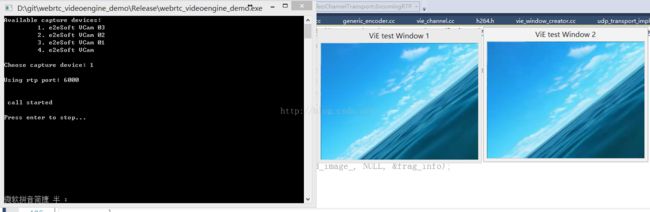
该示例程序最后效果如下,我这里是几个虚拟摄像头,然后会有两个窗口,一个是摄像头画面,一个是解码的画面。