剑指offer刷题
今天是2019年6日12日,前面的时间一直对找工作不太上心,最近还是要调整一下状态,好好准备一下面试笔试,因此鞭策自己每天刷题,作此记录。
(1)机器人的运动范围:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/22/
地上有一个 m 行和 n 列的方格,横纵坐标范围分别是 0∼m−1 和 0∼n−1。
一个机器人从坐标0,0的格子开始移动,每一次只能向左,右,上,下四个方向移动一格。
但是不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于k的格子。
请问该机器人能够达到多少个格子?
import collections
class Solution(object):
def movingCount(self, threshold, rows, cols):
"""
:type threshold: int
:type rows: int
:type cols: int
:rtype: int
"""
if rows == 0 and cols == 0:
return 0
Traversal = [[False for col in range(rows+1)] for row in range(cols+1)]
d = collections.deque()
dx = [0, 0, -1, 1]
dy = [1, -1, 0, -0]
d.append((0,0))
count = 0
while d:
#print(d)
cell = d.popleft()
x = cell[0]
y = cell[1]
if Traversal[x][y] or self.count_sum(x,y) > threshold:
continue
count += 1
Traversal[x][y] = True
for (d_x, d_y) in zip(dx,dy):
if x + d_x >= 0 and x + d_x < cols and y + d_y >= 0 and y + d_y < rows:
d.append((x+d_x,y+d_y))
#print(count)
return count
#计算横纵坐标的位数之和
def count_sum(self, x, y):
s = x%10 + x/10 + y%10 + y/10
return s
2.剪绳子:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/24/
给你一根长度为 n 绳子,请把绳子剪成 m 段(m、n 都是整数,2≤n≤58 并且 m≥2)。
每段的绳子的长度记为k[0]、k[1]、……、k[m]。k[0]k[1] … k[m] 可能的最大乘积是多少?
例如当绳子的长度是8时,我们把它剪成长度分别为2、3、3的三段,此时得到最大的乘积18。
import math
class Solution(object):
def maxProductAfterCutting(self,length):
"""
:type length: int
:rtype: int
"""
if length == 2:
return 1
if length == 3:
return 2
if length%3 == 0:
return self.multiply3(length)
if length%3 == 1:
return 2*2*self.multiply3(length-4)
if length%3 == 2:
return 2*self.multiply3(length-2)
def multiply3(self,x):
y = x / 3
return int(math.pow(3,y))
3.二进制中1的个数: https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/25/
输入一个32位整数,输出该数二进制表示中1的个数。
注意: 负数在计算机中用其绝对值的补码来表示。
样例1
输入:9
输出:2
解释:9的二进制表示是1001,一共有2个1。
样例2
输入:-2
输出:31
解释:-2在计算机里会被表示成11111111111111111111111111111110,
一共有31个1。
class Solution(object):
def NumberOf1(self,n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
i = 0
count = 0
while i<=31:
if ((a>>i)&1) == 1:
count += 1
i += 1
return count
4.树的子结构:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/35/

class Solution(object):
def hasSubtree(self, pRoot1, pRoot2):
"""
:type pRoot1: TreeNode
:type pRoot2: TreeNode
:rtype: bool
"""
if pRoot1 == None or pRoot2 == None:
return False
#遍历树A中的每个节点,看该节点为根节点的树是不是树B的母树
if self.isSame(pRoot1,pRoot2):
return True
return self.hasSubtree(pRoot1.left,pRoot2) or self.hasSubtree(pRoot1.right,pRoot2)
return False
#判断以p1,p2为根节点的树,p2是不是为p1的子树(即允许p1囊括p2)
def isSame(self,p1,p2):
#递归的临界条件一直是我比较棘手的一点
if p2 == None:
return True
if p1 == None or p1.val != p2.val:
return False
return self.isSame(p1.left,p2.left) and self.isSame(p1.right,p2.right)
5.如何在不排序的情况下求数组的中位数?
"""
根据快速排序的思想,首先将问题转化为求一列数字当中第(length/2+1)小的数的问题(其中length为数组的长度)
"""
def partition(arr,low,high):
key = arr[low]
while low < high:
while low < high and arr[high] >= key:
high -= 1
arr[low] = arr[high]
while low < high and arr[low] <= key:
low += 1
arr[high] = arr[low]
arr[low] = key
return low
def get_mid(arr):
low = 0
high = len(arr)-1
mid = (low+high)>>1
while True:
pos = partition(arr,low,high)
#找到中位数
if pos == mid:
break
#继续在左半部分查找
elif pos>mid:
high = pos - 1
#继续在左半部分查找
else:
low = pos + 1
#如果数据长度是奇数,中位数为中间的元素,否则就是中间两个数的平均值
return arr[mid] if len(arr)%2!=0 else (arr[mid]+arr[mid+1])/2
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [1,3,5,4,2,7,4,5,2,1,2]
low = 0
high = len(arr)-1
mid_number = get_mid(arr)
print(mid_number)
6.如何对数组进行循环移位?
"""
把一个含有N个元素的数组循环右移K为=位,要求时间复杂度为O(N),但只允许使用两个附加变量
以数据[1,2,3,4,5]为例
"""
#暴力法是每次右移一位,这样时间复杂度为O(k*n)
def loop_move_baoli(arr,k):
k %= len(arr)
while k:
temp = arr[-1]
i = len(arr) - 1
while i>0:
arr[i] = arr[i-1]
i -= 1
arr[0] = temp
k -= 1
print(arr)
#一种更简单的方法,翻转法 [1,2,3,4,5] k = 2, 则[1,2,3]->[3,2,1]; [4,5]->[5,4]; [3,2,1,5,4]->[4,5,1,2,3]
#此时时间复杂度为O(N)且只用了两个辅助空间
def reverse(arr,start,end):
while start < end:
temp = arr[start]
arr[start] = arr[end]
arr[end] = temp
start += 1
end -= 1
def loop_move_reverse(arr,k):
if arr == None:
return None
lens = len(arr)
k %= lens
reverse(arr,0,lens-k-1)
reverse(arr,lens-k,lens-1)
reverse(arr,0,lens-1)
return arr
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
result = loop_move_reverse(arr,1)
print(result)
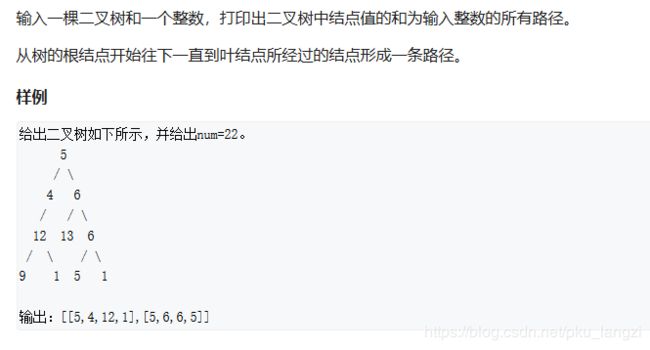
7.二叉树中和为某一值的路径: https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/45/
class Solution(object):
def findPath(self, root, sum):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type sum: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
self.ans = []
self.dfs(root,sum,[])
return self.ans
def dfs(self,root,sums,temp):
if not root:
return
temp.append(root.val)
if (not root.left) and (not root.right):
if root.val == sums:
self.ans.append(temp[:])
else:
self.dfs(root.left,sums-root.val,temp)
self.dfs(root.right,sums-root.val,temp)
#注意这条语句别掉了
temp.pop()
8. 如何求一个字符串的所有排序
"""
设计一个程序,当输入一个字符串时,要求输出这个字符串的所有排列。例如输入字符串abc,要求输出由字符a、b、c所能排列出来的所有字符串:
abc,acb,bac,bca,cba,cab。
下面的方法采用递归的方式来做
在使用递归方法求解的时候,需要注意下面两个问题:(1)逐渐缩小问题的规模,并且可以用同样的方法来求解子问题(2)递归一定要有终止条件,否则会导致程序陷入死循环
"""
#交换字符串数组中下标为i与j的字符
def swap(str,i,j):
tmp = str[i]
str[i] = str[j]
str[j] = tmp
"""
方法功能:对字符串进行全排序
输入参数:字符串str, start 为待排序的字符串的首字符的下标
"""
def permutation(str,start):
if start == None or start < 0:
return
#完成全排列之后,输出当前排列的字符串
if start == len(str) - 1:
print("".join(str),)
else:
i = start
while i<len(str):
#如果str[i]在str[start:i]之间已经出现过了,就不用交换了,避免重复
if not is_duplicate(str,start,i):
i+=1
continue
swap(str,start,i)
permutation(str,start+1)
swap(str,start,i)
i += 1
def is_duplicate(str,begin,end):
i = begin
while i<end:
if str[i] == str[end]:
return False
i += 1
return True
def permutation_transe(s):
str = list(s)
permutation(str,0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "aab"
permutation_transe(s)
9.数字排列
class Solution:
def permutation(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
ans = []
if nums == [] or nums == None:
return ans
self.permunate(nums,0,ans)
return ans
def permunate(self,arr,start,ans):
if arr == None or arr == [] or start < 0:
return
if start == len(arr)-1:
#这儿arr[:]与arr是有很大的区别的
ans.append(arr[:])
else:
i = start
while i < len(arr):
if not self.is_duplicate(arr,start,i):
i += 1
continue
self.swap(arr,start,i)
self.permunate(arr,start+1,ans)
self.swap(arr,start,i)
i += 1
def swap(self,arr,i,j):
temp = arr[i]
arr[i] = arr[j]
arr[j] = temp
def is_duplicate(self,arr,begin,end):
i = begin
while i < end:
if arr[i] == arr[end]:
return False
i += 1
return True
10.字符串的最长公共子序列
"""
题目描述:求出两个字符串的最长公共字串,如字符串"abccade"与字符串"dgcadde"的最长公共字串为"cad"
"""
#动态规划法
"""
方法功能:获取两个字符串的最长公共字串"
输入参数:str1和str2为指向字符的指针
"""
def getMaxSubStr(str1,str2):
len1 = len(str1)
len2 = len(str2)
sb = ""
maxs = 0 #用来记录最长字串的长度
maxI = 0 #用来记录最长公共字串最后一个字符的位置
#申请新的空间来记录公共字串长度信息
M = [([None]*(len1+1)) for i in range(len2+1)]
i = 0
while i < len1 + 1:
M[i][0] = 0
i += 1
j = 0
while j < len2 + 1:
M[0][j] = 0
j += 1
#通过利用递归公式来填写新的二维数组(公共字符串的长度信息)
i = 1
while i < len1 + 1:
j = 1
while j < len2 + 1:
if list(str1)[i-1] == list(str2)[j-1]: #注意这儿是i-1与j-1,len1+1 * len2+1的形状,区别于字符串
M[i][j] = M[i-1][j-1] + 1
if M[i][j] > maxs:
maxs = M[i][j]
maxI = i
else:
M[i][j] = 0
j += 1
i += 1
#找出公共字串
i = maxI - maxs
return "".join(list(str1)[i:maxI])
if __name__ == '__main__':
str1 = "abccade"
str2 = "dgcadde"
print(getMaxSubStr(str1,str2))
11.字符串反转与字符中单词反转
def reverseStr(ch,start,end):
while start < end:
temp = ch[start]
ch[start] = ch[end]
ch[end] = temp
start += 1
end -= 1
def swapWord(ch):
lens = len(ch)
reverseStr(ch,0,lens-1)
i = 0
begin = 0
while i < lens:
if ch[i] == ' ':
reverseStr(ch,begin,i-1)
begin = i + 1
i += 1
reverseStr(ch,begin,lens-1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
str = "abcde"
ch = list(str)
lens = len(ch)
reverseStr(ch,0,lens-1)
print("".join(ch))
str2 = "how are you"
ch2 = list(str2)
swapWord(ch2)
print("".join(ch2))
#更简便的颠倒字符串单词的方法
str3 = "I love you"
lis = str3.split()[::-1]
print(" ".join(lis))
12.判断两个字符串是不是换位字符串
"""
换位字符串是指组成字符串的字符相同,但是位置不同。例如:由于字符串"aaaabbc"与字符串"abcbaaa"就是由相同字符组成的换位字符串
"""
#将字符串中每个字符构造字典,键为字符,值为出现的次数
def getDic(str):
ch = list(str)
dict = {}
for char in ch:
if char in dict:
dict[char] += 1
else:
dict[char] = 1
return dict
def isSwapPos(str1,str2):
dict1 = getDic(str1)
dict2 = getDic(str2)
if len(dict1) != len(dict2):
return False
for key in dict1:
if key in dict2 and dict1[key] == dict2[key]:
pass
else:
return False
return True
#另一个更为简便的方法是开辟256大小的数组来记录各个字符出现的次数,过一遍str1对应位置+1,过一遍str2对应位置-1,看最后是不是所有位置都为0
def compare(str1,str2):
asc = [0] * 256
i = 0
while i < len(str1):
asc[ord(list(str1)[i]) - ord('0')] += 1
i += 1
j = 0
while j < len(str2):
asc[ord(list(str2)[j]) - ord('0')] -= 1
j += 1
for num in asc:
if num != 0:
return False
return True
if __name__ == '__main__':
str1 = "aaaabbce"
str2 = "abcbaaae"
#print(isSwapPos(str1,str2))
print(compare(str1,str2))
13.和为S的连续正数序列
"""
题目描述:
输入一个正数s,打印出所有和为s的连续正数序列(至少含有两个数)。
例如输入15,由于1+2+3+4+5=4+5+6=7+8=15,所以结果打印出3个连续序列1~5、4~6和7~8。
"""
#暴力法
class Solution(object):
def findContinuousSequence(self, sum):
"""
:type sum: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
#暴力法
if sum < 3:
return []
ans = []
start = 1
while start <= (sum>>1):
end = start
s = 0
temp = []
while end <= (sum>>1) + 1:
temp.append(end)
s += end
if s == sum:
ans.append(temp)
break
end += 1
start += 1
return ans
#双指针法
class Solution(object):
def findContinuousSequence(self, sum):
"""
:type sum: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
#双指针法
res = []
start = 1
end = 2
s = 3
if sum < 3:
return []
while start <= sum>>1:
#如果比sum小,则加上大数
if s < sum:
end += 1
s += end
#如果比sum大,则减去小数
elif s > sum:
s -= start
start += 1
else:
res.append(list(range(start,end+1)))
s -= start
start += 1
return res
14.判断一棵树是不是平衡二叉树
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution(object):
def isBalanced(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: bool
"""
if not root:
return True
leftDepth = self.depth(root.left)
rightDepth = self.depth(root.right)
if abs(leftDepth-rightDepth) <= 1:
return self.isBalanced(root.left) and self.isBalanced(root.right)
else:
return False
def depth(self,root):
if root == None:
return 0
return max(self.depth(root.left),self.depth(root.right)) + 1
15.寻找字符串中最长的回文字符串
"""
回文字符串是指一个字符串从左到右与从右到左遍历得到的序列是相同的
"""
#解法1:动态规划法
def getLongestPalindrome(str):
if str == None:
return
n = len(str)
if n < 1:
return
startIndex = 0 #用来记录回文字符串的起始位置
lens = 1 #用来记录回文字符串的长度
#申请额外的存储空间来记录查找的历史信息
dp = [[None] * n for i in range(n)]
i = 0
while i < n:
j = 0
while j < n:
dp[i][j] = 0
#初始化长度为1的回文字符串的信息
if i == j:
dp[i][j] = 1
#初始化长度为2的回文字符串的信息
if j + 1 < n and list(str)[j] == list(str)[j+1]:
dp[j][j+1] = 1
startIndex = j
lens = 2
j += 1
i += 1
#查找长度为3开始的回文字符串
pLen = 3
while pLen <= n:
i = 0
while i < n - pLen + 1:
j = i + pLen - 1
if list(str)[i] == list(str)[j] and dp[i+1][j-1] == 1:
dp[i][j] = 1
startIndex = i
lens = pLen
i += 1
pLen += 1
return "".join(list(s)[startIndex:startIndex+lens])
#解法2:将字符串s逆转s1,然后转化为求s1与s2的最长公共子序列的问题
def getLongestCommon(s1):
s2 = "".join(list(s1)[::-1])
endIndex = 0
Lens = 0 #表示公共子序列的长度
len1 = len(s1)
len2 = len(s2)
dp = [[None]*(len1+1) for i in range(len2+1)]
for i in range(len1+1):
dp[i][0] = 0
for j in range(len2+1):
dp[0][j] = 0
i = 1
while i < len1 + 1:
j = 1
while j < len2 + 1:
if list(s1)[i-1] == list(s2)[j-1]:
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1
if dp[i][j] > Lens:
Lens = dp[i][j]
endIndex = i
else:
dp[i][j] = 0
j += 1
i += 1
return "".join(list(s)[endIndex-Lens:endIndex])
#解法三,中心扩展法
def expandBothSide(str,c1,c2):
n = len(str)
while c1>=0 and c2<n and list(str)[c1]==list(str)[c2]:
c1 -= 1
c2 += 1
startIndex = c1 + 1
Lens = c2 - c1 - 1
return (startIndex,Lens)
def getLongestPalin(s):
n = len(s)
start = 0
Lens = 0
i = 0
while i < n:
#找回文字符串为长度为奇数的情况(从第i个字符向两边扩展),比如aba
(tmpStartIndex,tmpLens) = expandBothSide(s,i,i)
if tmpLens > Lens:
Lens = tmpLens
start = tmpStartIndex
#找回文字符串为偶数的情况 (从第i和i+1个字符向两边扩展),比如baab
(tmpStartIndex,tmpLens) = expandBothSide(s,i,i+1)
if tmpLens > Lens:
Lens = tmpLens
start = tmpStartIndex
i += 1
return "".join(list((s)[start:start+Lens]))
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = "aabcdefgfedxyz"
print(getLongestPalindrome(s))
print(getLongestCommon(s))
print(getLongestPalin(s))
16.数组中唯一只出现一次的数字
"""
在一个数组中除了一个数字只出现一次之外,其他数字都出现了三次。
请找出那个只出现一次的数字。
你可以假设满足条件的数字一定存在
"""
class Solution(object):
def findNumberAppearingOnce(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
#通过统计二进制每一位1的个数,%3等于所求数相应位置对应的二进制数
a = [0] * 32
for num in nums:
for i in range(32):
a[i] += (num>>i)&1
i += 1
ans = 0
for i in range(32):
if a[i]%3 == 1:
ans += pow(2,i)
return ans
17.最长不含重复字符的字符串
"""
请从字符串中找出一个最长的不包含重复字符的子字符串,计算该最长子字符串的长度。
假设字符串中只包含从’a’到’z’的字符。
样例
输入:"abcabc"
输出:3
"""
#解法1,暴力法 时间复杂度为o(n^2),空间复杂度为o(n)
class Solution:
def longestSubstringWithoutDuplication(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: int
"""
if s == None:
return 0
maxLength = 0
ch = list(s)
n = len(ch)
i = 0
while i < n:
j = i
dic = {}
tempLength = 0
while j < n:
if ch[j] not in dic:
dic[ch[j]] = 1
tempLength += 1
if tempLength > maxLength:
maxLength = tempLength
j += 1
else:
break
i += 1
return maxLength
#解法2,动态规划法
class Solution:
def longestSubstringWithoutDuplication(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: int
"""
if s == "":
return 0
d = {}
dp = [0]*len(s)
max = 0
i = 0
while i < len(s):
if s[i] not in d:
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + 1 #这儿就算是i=0也没事,因为dp[-1]=0对结果没有影响
else:
if i - d[s[i]] > dp[i-1]:
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + 1
else:
dp[i] = i - d[s[i]]
if dp[i] > max:
max = dp[i]
d[s[i]] = i
i += 1
return max