03.Spring Boot源码剖析:SpringApplication初始化 about spring-boot-1.5.10.RELEASE
在进行完源码的编译后,本节我们来看一下SpringApplication初始化过程
导入Spring Boot源码工程spring-boot
新建maven工程spring-boot-study-001
pom.xml文件如下:
4.0.0
com.kevin.springboot.study
spring-boot-study-001
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
1.5.10.RELEASE
jar
UTF-8
UTF-8
1.7
1.2.8.RELEASE
1.3.2
5.1.45
1.4.2
1.1.0
1.2.47
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-aop
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-jdbc
mysql
mysql-connector-java
com.alibaba
druid-spring-boot-starter
${alibaba.druid.version}
com.alibaba
fastjson
${alibaba.fastjson.version}
org.apache.maven.plugins
maven-compiler-plugin
1.7
1.7
UTF-8
新建Application.java文件
package com.kevin;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
static {
System.out.println("静态代码块");
}
{
System.out.println("非静态代码块");
}
public Application(){
System.out.println("无参构造函数");
}
public static void print(String content){
System.out.println(content);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
print("Before springboot!");
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
print("After springboot!");
}
}
新建application.properties配置文件
server.port=8099
####################### MySQL #################################
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc\:mysql\://127.0.0.1\:3306/test?useUnicode\=true&characterEncoding\=UTF-8&zeroDateTimeBehavior\=convertToNull
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
#############################################################
spring.datasource.initialSize=1
spring.datasource.minIdle=5
spring.datasource.maxActive=10
spring.datasource.maxWait=60000
spring.datasource.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis=60000
spring.datasource.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis=300000
spring.datasource.validationQuery=select 1
spring.datasource.testWhileIdle=true
spring.datasource.testOnBorrow=false
spring.datasource.testOnReturn=false
spring.datasource.poolPreparedStatements=true
spring.datasource.maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize=20
spring.datasource.filters=stat,wall,log4j
spring.datasource.connectionProperties=druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=5000
spring.datasource.useGlobalDataSourceStat=true
########################################################
spring.mvc.throw-exception-if-no-handler-found=true
spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/*
spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/static/
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates/
spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html
spring.thymeleaf.mode=LEGACYHTML5
spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
########################################################
log4j.rootCategory=DEBUG,stdout,DebugAppender,InfoAppender,ErrorAppender
log4j.debug=true
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=[QC] %p [%t] %C.%M(%L) | %m%n
#logger input file
log4j.logger.DebugAppender.access=DEBUG
log4j.appender.DebugAppender=org.apache.log4j.DailyRollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.DebugAppender.File=../logs/a.log
log4j.appender.DebugAppender.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.DebugAppender.layout.ConversionPattern=%d-[TS] %p %t %c - %m%n
#logger input file
log4j.logger.InfoAppender.access=INFO
log4j.appender.InfoAppender=org.apache.log4j.DailyRollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.InfoAppender.File=../logs/b.log
log4j.appender.InfoAppender.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.InfoAppender.layout.ConversionPattern=%d-[TS] %p %t %c - %m%n
#error log input file
log4j.logger.ErrorAppender.access=ERROR
log4j.appender.ErrorAppender=org.apache.log4j.DailyRollingFileAppender
log4j.appender.ErrorAppender.File=../logs/c.log
log4j.appender.ErrorAppender.Append = true
log4j.appender.ErrorAppender.threshold = ERROR
log4j.appender.ErrorAppender.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.ErrorAppender.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} %c %-5p - %m%n
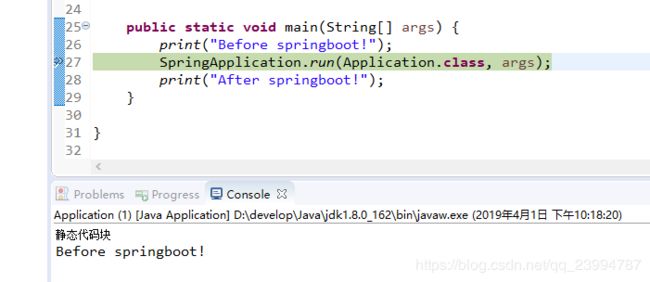
打个断点开始运行
可以看到程序打印了静态代码块与Before springboot,我们F5跟进后,程序进入如下代码:
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Object source, String... args) {
return run(new Object[] { source }, args);
}这个方法可用于使用默认设置从指定源运行@link springapplication。其中sources要加载的源。args通常从java main方法传递参数。继续跟进程序进入到可配置应用程序上下文方法。
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Object[] sources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(sources).run(args);
}静态助手,可使用默认设置和用户提供的参数从指定的源运行{@link SpringApplication}。继续F5
该方法会创建一个新的{@LinkSpringApplication}实例。应用程序上下文将从指定的源加载bean。实例可以在调用之前进行自定义。
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
private void initialize(Object[] sources) {
if (sources != null && sources.length > 0) {
this.sources.addAll(Arrays.asList(sources));
}
this.webEnvironment = deduceWebEnvironment();
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
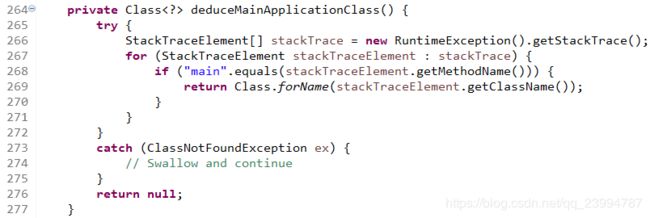
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}该方法涉及五步骤操作:
1.设置自定义源
2.演绎web环境
3.获取Spring工厂实例
4.设置应用程序监听器
5.推导主要应用类
推导主要应用类是通过栈中加载的application包含的main的方法的类
执行完上述步骤后,继续F5程序进入方法run中
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
//1.创建计时监控类
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
//2.启动计时监控类
stopWatch.start();
//3.1初始化应用上下文
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
//3.2初始化故障分析器
FailureAnalyzers analyzers = null;
//4.设置系统属性 `java.awt.headless` 的值,默认值为:true
configureHeadlessProperty();
//5.创建所有 Spring 运行监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
//6.发布应用启动事件
listeners.starting();
try {
//7.初始化默认应用参数类
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
//8.根据运行监听器和应用参数来准备 Spring 环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
//9.创建 Banner 打印类
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//10.创建应用上下文
context = createApplicationContext();
//11.创建故障分析器
analyzers = new FailureAnalyzers(context);
//12.准备应用上下文
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
//13.刷新应用上下文
refreshContext(context);
//14.应用上下文刷新后置处理
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
//15.发布监听完成事件
listeners.finished(context, null);
//16.停止计时监控类
stopWatch.stop();
//17.打印启动日志
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
//18.返回content
return context;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, listeners, analyzers, ex);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
}上边的方法会运行Spring应用程序,创建和刷新一个新的spring应用上下文,下面我们详细分解具体过程。
1.创建并启动计时监控类
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();其中StopWatch有start与stop两个关键方法,其源码如下:
/**
* 默认启动任务
*/
public void start() throws IllegalStateException {
start("");
}
/**
* 启动命名任务
*/
public void start(String taskName) throws IllegalStateException {
if (this.running) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Can't start StopWatch: it's already running");
}
this.running = true;
this.currentTaskName = taskName;
//获取当前系统毫秒数
this.startTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
/**
* 停止命名任务
*/
public void stop() throws IllegalStateException {
if (!this.running) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Can't stop StopWatch: it's not running");
}
//运行时为当前系统毫秒数减去启动记录毫秒数
long lastTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - this.startTimeMillis;
this.totalTimeMillis += lastTime;
this.lastTaskInfo = new TaskInfo(this.currentTaskName, lastTime);
if (this.keepTaskList) {
this.taskList.add(lastTaskInfo);
}
++this.taskCount;
this.running = false;
this.currentTaskName = null;
}从第2条注释stopWatch.start()到第16条注释stopWatch.stop()运行结束后,打印日志时通过如下方法获取计时器信息
private StringBuilder getStartedMessage(StopWatch stopWatch) {
StringBuilder message = new StringBuilder();
message.append("Started ");
message.append(getApplicationName());
message.append(" in ");
message.append(stopWatch.getTotalTimeSeconds());
try {
double uptime = ManagementFactory.getRuntimeMXBean().getUptime() / 1000.0;
message.append(" seconds (JVM running for " + uptime + ")");
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// No JVM time available
}
return message;
}这个运行到最后的结果就是我们常见的日志最后一行:
2.初始化应用上下文和故障分析器
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
FailureAnalyzers analyzers = null;3.设置系统属性 java.awt.headless 的值
configureHeadlessProperty();configureHeadlessProperty将headless值设置到java.awt.headless
设置该默认值为:true,Java.awt.headless = true 有什么作用?
对于一个 Java 服务器来说经常要处理一些图形元素,例如地图的创建或者图形和图表等。这些API基本上总是需要运行一个X-server以便能使用AWT(Abstract Window Toolkit,抽象窗口工具集)。然而运行一个不必要的 X-server 并不是一种好的管理方式。有时你甚至不能运行 X-server,因此最好的方案是运行 headless 服务器,来进行简单的图像处理。
参考:www.cnblogs.com/princessd8251/p/4000016.html
4.创建所有 Spring 运行监听器并发布应用启动事件
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(); private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
Class[] types = new Class[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger, getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));
}这个通过getSpringFactoriesInstances 方法来获取配置的监听器名称并实例化所有的类,其源码为:
private Collection getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class type) {
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class[] {});
}
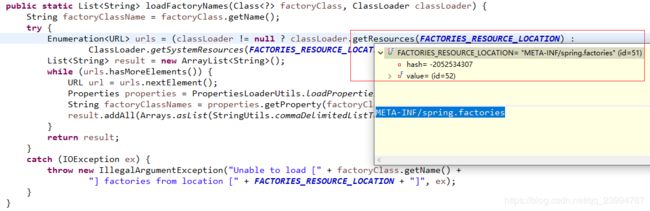
private Collection getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class type,
Class[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// 使用名称并确保惟一以防止重复
Set names = new LinkedHashSet(
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
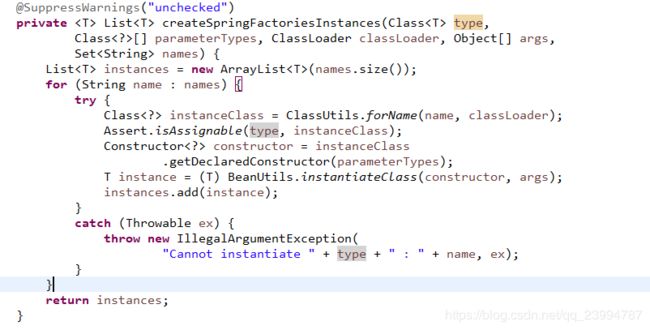
List instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes,
classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
} SpringApplicationRunListener 所有监听器配置在 spring-boot/META-INF/spring.factories 这个配置文件里面。
通过解析java源代码中的内部类名得到实例类,然后使用给定构造函数实例化类的方法。
private final List listeners;
SpringApplicationRunListeners(Log log,
Collection listeners) {
this.log = log;
this.listeners = new ArrayList(listeners);
} 得到监听集合后遍历启动
public void starting() {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.starting();
}
}事件发布运行侦听器EventPublishingRunListener实现了接口SpringApplicationRunListener的starting方法
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public void starting() {
this.initialMulticaster
.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartedEvent(this.application, this.args));
}5.初始化默认应用参数类
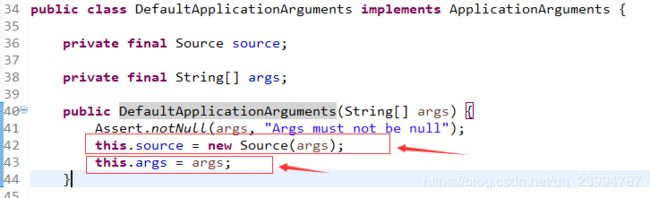
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);DefaultApplicationArguments实现了ApplicationArguments应用参数接口
其中Source为DefaultApplicationArguments的一个私有内部类,该类继承了SimpleCommandLinePropertySource ,该类提供了字符串数组支持的命令行属性源实现。其源码为:
private static class Source extends SimpleCommandLinePropertySource {
Source(String[] args) {
super(args);
}
@Override
public List getNonOptionArgs() {
return super.getNonOptionArgs();
}
@Override
public List getOptionValues(String name) {
return super.getOptionValues(name);
}
} 而SimpleCommandLinePropertySource 继承了类CommandLinePropertySource,该类是由命令行参数支持的{@link PropertySource}实现的抽象基类。
public class SimpleCommandLinePropertySource extends CommandLinePropertySource {
/**
*创建一个新的单例属性源,它具有指定的命令行参数。
*/
public SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(String... args) {
super(new SimpleCommandLineArgsParser().parse(args));
}
/**
* 创建一个新的单例属性源,它具有给定的名称,和指定的命令行参数。
*/
public SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(String name, String[] args) {
super(name, new SimpleCommandLineArgsParser().parse(args));
}
.....
} CommandLinePropertySource是一个抽象类,其继承了EnumerablePropertySource,EnumerablePropertySource实现能够询问其基础源对象以枚举所有可能的属性名称/值对。
public abstract class CommandLinePropertySource extends EnumerablePropertySource {
/** 实例的默认名称 */
public static final String COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "commandLineArgs";
/** 非选项参数的属性的默认名称 */
public static final String DEFAULT_NON_OPTION_ARGS_PROPERTY_NAME = "nonOptionArgs";
private String nonOptionArgsPropertyName = DEFAULT_NON_OPTION_ARGS_PROPERTY_NAME;
/**
* 创建一个新的命令行属性源,其默认名称为commandLineArgs,并由给定的源对象支持。
*/
public CommandLinePropertySource(T source) {
super(COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, source);
}
//......
} EnumerablePropertySource也是一个抽象类,该类继承了PropertySource,PropertySource表示名称/值属性对的源的抽象基类。
public abstract class EnumerablePropertySource extends PropertySource {
public EnumerablePropertySource(String name, T source) {
super(name, source);
}
protected EnumerablePropertySource(String name) {
super(name);
}
//....
} public abstract class PropertySource {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
protected final String name;
protected final T source;
/**
* 使用给定的名称和源对象创建一个新的{@code PropertySource}。
*/
public PropertySource(String name, T source) {
Assert.hasText(name, "Property source name must contain at least one character");
Assert.notNull(source, "Property source must not be null");
this.name = name;
this.source = source;
}
/**
* 创建一个具有给定名称新实例作为底层源
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public PropertySource(String name) {
this(name, (T) new Object());
}
//.....
} 6.根据运行监听器和应用参数来准备 Spring 环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);6.1我们看一下环境准备器prepareEnvironment的源码
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
//1.获取或创建环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
//2.配置环境
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
//3.环境准备监听
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
if (!this.webEnvironment) {
//4.将给定环境转换为标准环境。如果环境已经是一个标准环境,并且不是可配置的Web环境,则不执行转换,并且它将被不改变地返回。
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader())
.convertToStandardEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment);
}
return environment;
}首先我们看一下获取和和创建环境的源码
private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() {
//如果环境已创建,则返回已创建的环境
if (this.environment != null) {
return this.environment;
}
//如果为web环境则创建servlet的启动环境
if (this.webEnvironment) {
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
}
//返回标准环境
return new StandardEnvironment();
}其中StandardServletEnvironment的源码如下,其继承了类StandardEnvironment 并同时实现了接口ConfigurableWebEnvironment
public class StandardServletEnvironment extends StandardEnvironment implements ConfigurableWebEnvironment {
/** servlet上下文init参数属性源名称 */
public static final String SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "servletContextInitParams";
/** Servlet配置init参数属性源名称 */
public static final String SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "servletConfigInitParams";
/** JNDI属性源名称 */
public static final String JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "jndiProperties";
/**
* 使用超类提供的属性源以及适用于基于servlet的标准环境的属性源集进行自定义
*
*/
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
if (JndiLocatorDelegate.isDefaultJndiEnvironmentAvailable()) {
propertySources.addLast(new JndiPropertySource(JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
}
super.customizePropertySources(propertySources);
}
/**
*初始化属性源
*/
@Override
public void initPropertySources(ServletContext servletContext, ServletConfig servletConfig) {
WebApplicationContextUtils.initServletPropertySources(getPropertySources(), servletContext, servletConfig);
}
}其中StandardEnvironment的源码如下,其继承了类AbstractEnvironment,其源码如下:
public class StandardEnvironment extends AbstractEnvironment {
/** 系统环境属性源名称 */
public static final String SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemEnvironment";
/** JVM系统属性源名称 */
public static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemProperties";
/**
* 使用适用于任何标准Java环境的属性源集自定义
*/
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(new MapPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));
propertySources.addLast(new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));
}
}
6.2 接下来环境配置器源码
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
String[] args) {
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
configureProfiles(environment, args);
}首先是配置属性源configurePropertySources:
protected void configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,String[] args) {
MutablePropertySources sources = environment.getPropertySources();
if (this.defaultProperties != null && !this.defaultProperties.isEmpty()) {
sources.addLast(
new MapPropertySource("defaultProperties", this.defaultProperties));
}
if (this.addCommandLineProperties && args.length > 0) {
String name = CommandLinePropertySource.COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;
if (sources.contains(name)) {
PropertySource source = sources.get(name);
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(name);
composite.addPropertySource(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource( name + "-" + args.hashCode(), args));
composite.addPropertySource(source);
sources.replace(name, composite);
}
else {
sources.addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args));
}
}
}其次配置活动的配置文件
protected void configureProfiles(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
//确保初始化
environment.getActiveProfiles();
Set profiles = new LinkedHashSet(this.additionalProfiles);
profiles.addAll(Arrays.asList(environment.getActiveProfiles()));
environment.setActiveProfiles(profiles.toArray(new String[profiles.size()]));
} 7.获取banner对象及打印banner
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);我们来看一下程序是如何打印banner的
private Banner printBanner(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
//1.是否开启打印banner
if (this.bannerMode == Banner.Mode.OFF) {
return null;
}
//加载banner资源
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = this.resourceLoader != null ? this.resourceLoader
: new DefaultResourceLoader(getClassLoader());
//实例化banner打印对象
SpringApplicationBannerPrinter bannerPrinter = new SpringApplicationBannerPrinter(
resourceLoader, this.banner);
//日志输出
if (this.bannerMode == Mode.LOG) {
return bannerPrinter.print(environment, this.mainApplicationClass, logger);
}
//控制台输出
return bannerPrinter.print(environment, this.mainApplicationClass, System.out);
}其中在加载banner资源的过程中,如果在resouces下配置了名为banner.txt的文件,则程序将会打印其里边的内容
,否则打印spring boot默认的banner内容
8.创建应用上下文
context = createApplicationContext();该方法的源码为:
/*
* 配置应用程序上下文
* 该方法根据不同的应用类型初始化不同的上下文应用类
*/
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
//如果为web环境则返回org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext
//否则返回org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
contextClass = Class.forName(this.webEnvironment ? DEFAULT_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS : DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException( "Unable create a default ApplicationContext, " + "please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex);
}
}
//使用类的无参构造函数实例化bean
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiate(contextClass);
}9.初始化故障分析器
analyzers = new FailureAnalyzers(context);加载故障分析器中关键方法代码
FailureAnalyzers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.notNull(context, "Context must not be null");
this.classLoader = (classLoader == null ? context.getClassLoader() : classLoader);
this.analyzers = loadFailureAnalyzers(this.classLoader);
prepareFailureAnalyzers(this.analyzers, context);
}
private List loadFailureAnalyzers(ClassLoader classLoader) {
List analyzerNames = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(FailureAnalyzer.class, classLoader);
List analyzers = new ArrayList();
for (String analyzerName : analyzerNames) {
try {
Constructor constructor = ClassUtils.forName(analyzerName, classLoader).getDeclaredConstructor();
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(constructor);
analyzers.add((FailureAnalyzer) constructor.newInstance());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.trace("Failed to load " + analyzerName, ex);
}
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(analyzers);
return analyzers;
}
private void prepareFailureAnalyzers(List analyzers, ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
for (FailureAnalyzer analyzer : analyzers) {
prepareAnalyzer(context, analyzer);
}
}
private void prepareAnalyzer(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, FailureAnalyzer analyzer) {
if (analyzer instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) analyzer).setBeanFactory(context.getBeanFactory());
}
} 10.准备应用上下文
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,printedBanner);该方法的源码为:
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,ApplicationArguments applicationArguments,Banner printedBanner) {
//1.绑定环境到上下文
context.setEnvironment(environment);
//2.配置上下文的 bean 生成器及资源加载器
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
//3.为上下文应用所有初始化器
applyInitializers(context);
//4.触发所有 SpringApplicationRunListener 监听器的 contextPrepared 事件方法
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
//5.记录启动日志
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
//6.添加特定于引导的单例bean
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
//7.加载所有资源
Set11.刷新应用上下文
refreshContext(context);该方法源码为:
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
//刷新应用上下文
refresh(context);
//注册关闭钩子
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
}
protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(AbstractApplicationContext.class, applicationContext);
((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh();
}
AbstractApplicationContext中refresh方法源码如下
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// 准备此上下文以进行刷新
prepareRefresh();
// 告诉子类刷新内部bean工厂
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 准备bean工厂以在此上下文中使用。
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 允许在上下文子类中对bean工厂进行后处理。
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 在上下文中调用注册为bean的工厂处理器。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 注册拦截bean创建的bean处理器
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 初始化此上下文的消息源
initMessageSource();
// 初始化此上下文的事件多播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 在特定的上下文子类中初始化其他特殊bean。
onRefresh();
// 检查监听器bean并注册它们。
registerListeners();
// 实例化所有剩余(非延迟初始化)单例。
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 发布相应的事件
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - "+ "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// 销毁已创建的单例资源
destroyBeans();
// 重置'有效'标志。
cancelRefresh(ex);
// 向调用者传播异常.
throw ex;
}
finally {
//重置Spring核心中常见的内部缓存,因为我们可能不再需要单例bean的元数据了...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}12.应用上下文刷新后置处理
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);protected void afterRefresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
callRunners(context, args);
}private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List13.通知监听完成
listeners.finished(context, null);14.停止计时监控类
stopWatch.stop();15.打印启动日志
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}16.返回应用程序上下文
return context;以上就是SpringApplication的run方法启动全过程的粗略分析,希望能给大家提供一点参考和思路,也希望能给正在 Spring Boot 学习路上的朋友一点收获。