LIVE555再学习 -- live555实现RTSP直播服务器
分析完 testOnDemandRTSPServer 和 testH264VideoStreamer 的源码。我们现在就可以做相关的项目工程。
我之前写过一个,参看: DM368开发 -- 编码并实时播放
项目效果就是,编码 encode 然后通过 rtsp 传输在 VLC 上实时播放。用的是sensor 是 MT9P031。
但是这里的 RTSP 服务器不是用的 live555 的。
再有一个例子就是 Hi3516A 上也是有用到,买的开发板相关程序已经写好了的,一直没时间分析,现在可以看一下。
现在先研究一下 live555怎么实现 RTSP 直播服务器,这个网上资料有很多的。
参看:通过live555实现H264 RTSP直播(Windows版)
一、基础
我们之前已经做过在Windows下编译 live555 了。
参看:LIVE555再学习 -- Windows 下编译
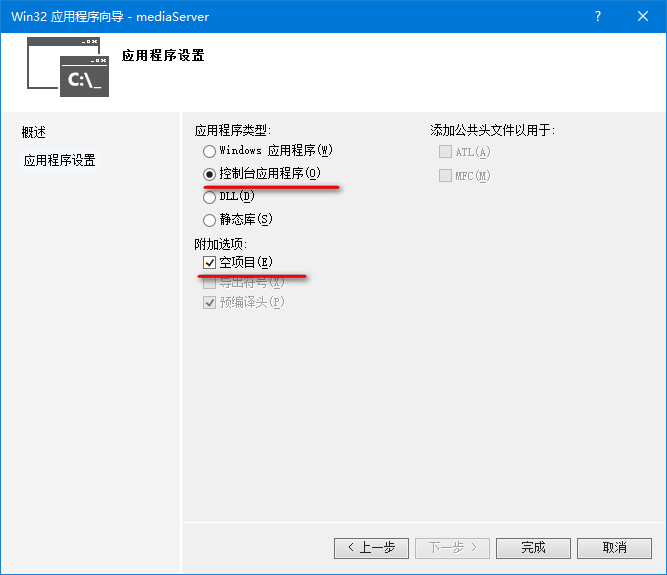
这就简单了,直接在这个工程上添加一个新的项目即可。
具体方法:
添加新建项目,选择win32控制台项目,项目名称为 h264LiveMediaServer
新建并添加 h264LiveMediaServer.cpp
然后将 testOnDemandRTSPServer.cpp 拷贝到 h264LiveMediaServer.cpp,接着做少量修改,只保留与H.264会话相关的部分。
拷贝代码如下:
其实看一下,和我们上一篇文章里的代码一样的,只不过这个可能注释的更清楚一些。
参看:LIVE555再学习 -- testOnDemandRTSPServer 源码分析
#include "liveMedia.hh"
#include "BasicUsageEnvironment.hh"
UsageEnvironment* env;
// True:后启动的客户端总是从当前第一个客户端已经播放到的位置开始播放
// False:每个客户端都从头开始播放影视频文件
Boolean reuseFirstSource = False;
//该函数打印相关信息
static void announceStream(RTSPServer* rtspServer, ServerMediaSession* sms,
char const* streamName, char const* inputFileName);
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
//创建任务调度器并初始化使用环境
TaskScheduler* scheduler = BasicTaskScheduler::createNew();
env = BasicUsageEnvironment::createNew(*scheduler);
UserAuthenticationDatabase* authDB = NULL;
//创建RTSP服务器,开始监听模客户端的连接
//注意这里的端口号不是默认的554端口,因此访问URL时,需指定该端口号
RTSPServer* rtspServer = RTSPServer::createNew(*env, 8554, authDB);
if (rtspServer == NULL)
{
*env << "Failed to create RTSP server: " << env->getResultMsg() << "\n";
exit(1);
}
char const* descriptionString
= "Session streamed by \"h264LiveMediaServer\"";
//流名字,媒体名
char const* streamName = "h264ESVideoTest";
//文件名,当客户端输入的流名字为h264ESVideoTest时,实际上打开的是test.264文件。
//这里需要特别注意一点,当通过IDE运行h264LiveMediaServer时,live555推送的是项目工作目录中的视频或音频。工作目录也就是和*.vcxproj同级的目录,
//此时视频应该放在这个目录下。当双击h264LiveMediaServer.exe运行时,视频理所当然的和h264LiveMediaServer.exe放在一个目录。
char const* inputFileName = "test.264";
//当客户点播时,要输入流名字streamName,告诉RTSP服务器点播的是哪个流。
//创建媒体会话,流名字和文件名的对应关系是通过增加子会话建立起来的。媒体会话对会话描述、会话持续时间、流名字等与会话有关的信息进行管理。
//第2个参数:媒体名、3:媒体信息、4:媒体描述
ServerMediaSession* sms= ServerMediaSession::createNew(*env, streamName, streamName,descriptionString);
//添加264子会话 这里的文件名才是真正要打开文件的名字
//H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession类派生自FileServerMediaSubsession派生自OnDemandServerMediaSubsession
//而OnDemandServerMediaSubsession和PassiveMediaSubsession共同派生自ServerMediaSubsession
//关于读取文件之类都在这个类中实现的,如果要将点播改为直播就是要新建类继承此类然后添加新的方法
sms->addSubsession(H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession::createNew(*env, inputFileName, reuseFirstSource));
//为rtspserver添加session
rtspServer->addServerMediaSession(sms);
//答应信息到标准输出
announceStream(rtspServer, sms, streamName, inputFileName);
//试图为RTSP-over-HTTP通道创建一个HTTP服务器.
if (rtspServer->setUpTunnelingOverHTTP(80) || rtspServer->setUpTunnelingOverHTTP(8000) || rtspServer->setUpTunnelingOverHTTP(8080))
{
*env << "\n(We use port " << rtspServer->httpServerPortNum() << " for optional RTSP-over-HTTP tunneling.)\n";
}
else
{
*env << "\n(RTSP-over-HTTP tunneling is not available.)\n";
}
//进入事件循环,对套接字的读取事件和对媒体文件的延时发送操作都在这个循环中完成。
env->taskScheduler().doEventLoop();
return 0;
}
static void announceStream(RTSPServer* rtspServer, ServerMediaSession* sms,
char const* streamName, char const* inputFileName) {
char* url = rtspServer->rtspURL(sms);
UsageEnvironment& env = rtspServer->envir();
env << "\n\"" << streamName << "\" stream, from the file \""
<< inputFileName << "\"\n";
env << "Play this stream using the URL \"" << url << "\"\n";
delete[] url;
} 此刻再编译 h264LiveMediaServer,OK 编译成功,生成 h264LiveMediaServer.exe。
将一个 test.264 文件拷贝到 h264LiveMediaServer.exe 目录下
测试:
CMD命令执行 h264LiveMediaServer.exe
在VLC下添加 URL 地址 rtsp://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:8554/h264ESVideoTest
OK,成功播放。
项目下载:
下载:单播 test.264文件的 RTSP服务器工程
ps:上例在 Linux下 就是将上面的代码粘贴到 testOnDemandRTSPServer.cpp,它就是testOnDemandRTSPServer.cpp 的简化版,然后重新 make clean && make。
执行 testOnDemandRTSPServer 即可!!
二、实现
在 Windows 通过live555实现H264 RTSP直播。
在Windows中实现的流程图如下所示:
这里需要提一下,FIFO队列实际上是Linux下的命名管道,而 Windows 下也有命名管道。
管道这部分我们在讲 UNIX 的时候讲到过的,参看:UNIX再学习 -- 进程间通信之管道
这里不使用命名管道来实现,而是直接读取本地 H264 文件,分解成 StartCode+NALU 内存块,然后拷贝到Live555 Server。这样一来,就很容易改成命名管道的形式,命名管道的客户端只需读取本地 H264 文件,分解成StartCode(0x000001或0x00000001)+NALU 内存块,并写入管道,命名管道服务器端(在Live555 Server中)读取管道数据,并拷贝到Live555 Server。
通过“基础”中的分析可以得出,想实现自定义服务器,需要将 sms->addSubsession(H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession::createNew(*env, inputFileName,reuseFirstSource)), 中的 H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession 替换成自己的子会话。H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession 类在其 createNewStreamSource(unsigned /*clientSessionId*/, unsigned& estBitrate) 函数中调用了 ByteStreamFileSource::createNew(envir(), fFileName),而 frame 的获取正是在 ByteStreamFileSource 类中的 doGetNextFrame() 函数中实现的。因此,这里需要继承H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession 和 ByteStreamFileSource 类,并重写其中的 createNewStreamSource 和 doGetNextFrame 函数。
这部分分析,参看:LIVE555再学习 -- testOnDemandRTSPServer 源码分析
继续项目 h264LiveMediaServer
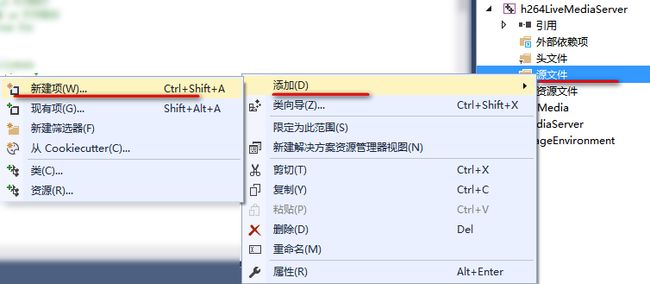
在头文件筛选器添加新项 h264LiveFramedSource.hh、h264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion.hh、spsdecode.h
源文件筛选器添加新项 h264LiveFramedSource.cpp、h264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion.cpp
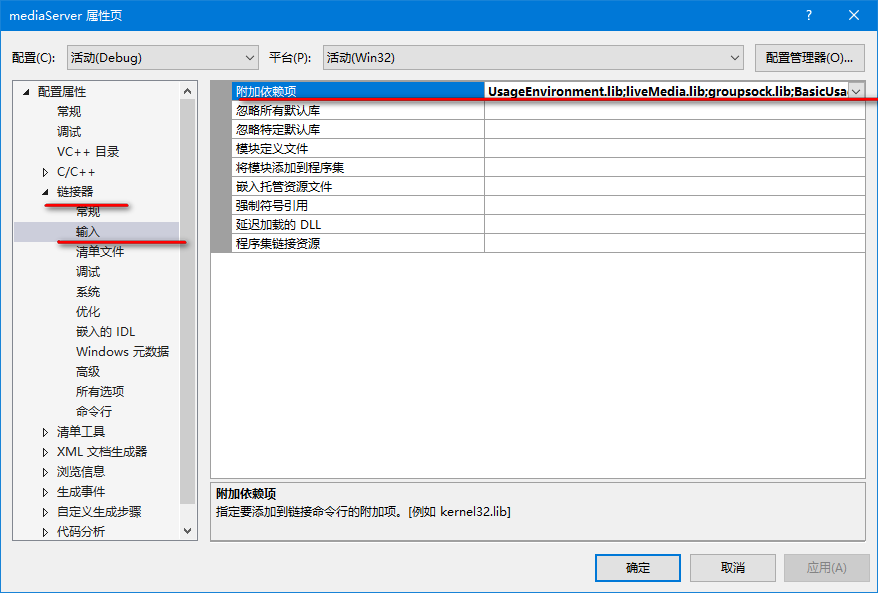
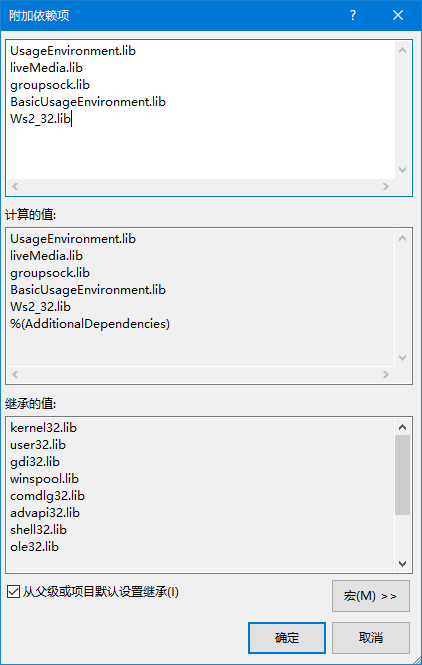
并在 h264LiveMediaServer.cpp 中做相应的修改
具体相关代码如下:
h264LiveFramedSource.hh
#ifndef _H264LIVEFRAMEDSOURCE_HH
#define _H264LIVEFRAMEDSOURCE_HH
#include
class H264LiveFramedSource : public ByteStreamFileSource
{
public:
static H264LiveFramedSource* createNew(UsageEnvironment& env, unsigned preferredFrameSize = 0, unsigned playTimePerFrame = 0);
protected:
H264LiveFramedSource(UsageEnvironment& env, unsigned preferredFrameSize, unsigned playTimePerFrame);
~H264LiveFramedSource();
private:
//重定义虚函数
virtual void doGetNextFrame();
};
#endif h264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion.hh
#ifndef _H264LIVEVIDEOSERVERMEDIASUBSSION_HH
#define _H264LIVEVIDEOSERVERMEDIASUBSSION_HH
#include "H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession.hh"
class H264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion : public H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession {
public:
static H264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion* createNew(UsageEnvironment& env, Boolean reuseFirstSource);
protected:
H264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion(UsageEnvironment& env, Boolean reuseFirstSource);
~H264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion();
protected:
//重定义虚函数
FramedSource* createNewStreamSource(unsigned clientSessionId, unsigned& estBitrate);
};
#endif spsdecode.h
#include
#include
#include
#include
typedef unsigned int UINT;
typedef unsigned char BYTE;
typedef unsigned long DWORD;
UINT Ue(BYTE *pBuff, UINT nLen, UINT &nStartBit)
{
//计算0bit的个数
UINT nZeroNum = 0;
while (nStartBit < nLen * 8)
{
if (pBuff[nStartBit / 8] & (0x80 >> (nStartBit % 8))) //&:按位与,%取余
{
break;
}
nZeroNum++;
nStartBit++;
}
nStartBit ++;
//计算结果
DWORD dwRet = 0;
for (UINT i=0; i> (nStartBit % 8)))
{
dwRet += 1;
}
nStartBit++;
}
return (1 << nZeroNum) - 1 + dwRet;
}
int Se(BYTE *pBuff, UINT nLen, UINT &nStartBit)
{
int UeVal=Ue(pBuff,nLen,nStartBit);
double k=UeVal;
int nValue=ceil(k/2);//ceil函数:ceil函数的作用是求不小于给定实数的最小整数。ceil(2)=ceil(1.2)=cei(1.5)=2.00
if (UeVal % 2==0)
nValue=-nValue;
return nValue;
}
DWORD u(UINT BitCount,BYTE * buf,UINT &nStartBit)
{
DWORD dwRet = 0;
for (UINT i=0; i> (nStartBit % 8)))
{
dwRet += 1;
}
nStartBit++;
}
return dwRet;
}
/**
* H264的NAL起始码防竞争机制
*
* @param buf SPS数据内容
*
* @无返回值
*/
void de_emulation_prevention(BYTE* buf,unsigned int* buf_size)
{
int i=0,j=0;
BYTE* tmp_ptr=NULL;
unsigned int tmp_buf_size=0;
int val=0;
tmp_ptr=buf;
tmp_buf_size=*buf_size;
for(i=0;i<(tmp_buf_size-2);i++)
{
//check for 0x000003
val=(tmp_ptr[i]^0x00) +(tmp_ptr[i+1]^0x00)+(tmp_ptr[i+2]^0x03);
if(val==0)
{
//kick out 0x03
for(j=i+2;j>7;
int constraint_set1_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);//(buf[1] & 0x40)>>6;
int constraint_set2_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);//(buf[1] & 0x20)>>5;
int constraint_set3_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);//(buf[1] & 0x10)>>4;
int reserved_zero_4bits=u(4,buf,StartBit);
int level_idc=u(8,buf,StartBit);
int seq_parameter_set_id=Ue(buf,nLen,StartBit);
if( profile_idc == 100 || profile_idc == 110 ||
profile_idc == 122 || profile_idc == 144 )
{
int chroma_format_idc=Ue(buf,nLen,StartBit);
if( chroma_format_idc == 3 )
int residual_colour_transform_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);
int bit_depth_luma_minus8=Ue(buf,nLen,StartBit);
int bit_depth_chroma_minus8=Ue(buf,nLen,StartBit);
int qpprime_y_zero_transform_bypass_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);
int seq_scaling_matrix_present_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);
int seq_scaling_list_present_flag[8];
if( seq_scaling_matrix_present_flag )
{
for( int i = 0; i < 8; i++ ) {
seq_scaling_list_present_flag[i]=u(1,buf,StartBit);
}
}
}
int log2_max_frame_num_minus4=Ue(buf,nLen,StartBit);
int pic_order_cnt_type=Ue(buf,nLen,StartBit);
if( pic_order_cnt_type == 0 )
int log2_max_pic_order_cnt_lsb_minus4=Ue(buf,nLen,StartBit);
else if( pic_order_cnt_type == 1 )
{
int delta_pic_order_always_zero_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);
int offset_for_non_ref_pic=Se(buf,nLen,StartBit);
int offset_for_top_to_bottom_field=Se(buf,nLen,StartBit);
int num_ref_frames_in_pic_order_cnt_cycle=Ue(buf,nLen,StartBit);
int *offset_for_ref_frame=new int[num_ref_frames_in_pic_order_cnt_cycle];
for( int i = 0; i < num_ref_frames_in_pic_order_cnt_cycle; i++ )
offset_for_ref_frame[i]=Se(buf,nLen,StartBit);
delete [] offset_for_ref_frame;
}
int num_ref_frames=Ue(buf,nLen,StartBit);
int gaps_in_frame_num_value_allowed_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);
int pic_width_in_mbs_minus1=Ue(buf,nLen,StartBit);
int pic_height_in_map_units_minus1=Ue(buf,nLen,StartBit);
width=(pic_width_in_mbs_minus1+1)*16;
height=(pic_height_in_map_units_minus1+1)*16;
int frame_mbs_only_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);
if(!frame_mbs_only_flag)
int mb_adaptive_frame_field_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);
int direct_8x8_inference_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);
int frame_cropping_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);
if(frame_cropping_flag)
{
int frame_crop_left_offset=Ue(buf,nLen,StartBit);
int frame_crop_right_offset=Ue(buf,nLen,StartBit);
int frame_crop_top_offset=Ue(buf,nLen,StartBit);
int frame_crop_bottom_offset=Ue(buf,nLen,StartBit);
}
int vui_parameter_present_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);
if(vui_parameter_present_flag)
{
int aspect_ratio_info_present_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);
if(aspect_ratio_info_present_flag)
{
int aspect_ratio_idc=u(8,buf,StartBit);
if(aspect_ratio_idc==255)
{
int sar_width=u(16,buf,StartBit);
int sar_height=u(16,buf,StartBit);
}
}
int overscan_info_present_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);
if(overscan_info_present_flag)
int overscan_appropriate_flagu=u(1,buf,StartBit);
int video_signal_type_present_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);
if(video_signal_type_present_flag)
{
int video_format=u(3,buf,StartBit);
int video_full_range_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);
int colour_description_present_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);
if(colour_description_present_flag)
{
int colour_primaries=u(8,buf,StartBit);
int transfer_characteristics=u(8,buf,StartBit);
int matrix_coefficients=u(8,buf,StartBit);
}
}
int chroma_loc_info_present_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);
if(chroma_loc_info_present_flag)
{
int chroma_sample_loc_type_top_field=Ue(buf,nLen,StartBit);
int chroma_sample_loc_type_bottom_field=Ue(buf,nLen,StartBit);
}
int timing_info_present_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);
if(timing_info_present_flag)
{
int num_units_in_tick=u(32,buf,StartBit);
int time_scale=u(32,buf,StartBit);
fps=time_scale/num_units_in_tick;
int fixed_frame_rate_flag=u(1,buf,StartBit);
if(fixed_frame_rate_flag)
{
fps=fps/2;
}
}
}
return true;
}
else
return false;
} h264LiveFramedSource.cpp
#include "h264LiveFramedSource.hh"
#include "GroupsockHelper.hh"
#include "spsdecode.h"
int findStartCode(unsigned char *buf, int zeros_in_startcode)
{
int info;
int i;
info = 1;
for (i = 0; i < zeros_in_startcode; i++)
if (buf[i] != 0)
info = 0;
if (buf[i] != 1)
info = 0;
return info;
}
//此处的NALU包括StartCode
int getNextNalu(FILE* inpf, unsigned char* buf)
{
int pos = 0;
int startCodeFound = 0;
int info2 = 0;
int info3 = 0;
while (!feof(inpf) && (buf[pos++] = fgetc(inpf)) == 0);
while (!startCodeFound)
{
if (feof(inpf))
{
return pos - 1;
}
buf[pos++] = fgetc(inpf);
info3 = findStartCode(&buf[pos - 4], 3);
startCodeFound = (info3 == 1);
if (info3 != 1)
info2 = findStartCode(&buf[pos - 3], 2);
startCodeFound = (info2 == 1 || info3 == 1);
}
if (info2)
{
fseek(inpf, -3, SEEK_CUR);
return pos - 3;
}
if (info3)
{
fseek(inpf, -4, SEEK_CUR);
return pos - 4;
}
}
FILE * inpf;
unsigned char* inBuf;
int inLen;
int nFrameRate;
H264LiveFramedSource::H264LiveFramedSource(UsageEnvironment& env, unsigned preferredFrameSize, unsigned playTimePerFrame)
: ByteStreamFileSource(env, 0, preferredFrameSize, playTimePerFrame)
{
char *fname = "test.264";
inpf = NULL;
inpf = fopen(fname, "rb");
inBuf = (unsigned char*)calloc(1024 * 100, sizeof(char));
inLen = 0;
inLen = getNextNalu(inpf, inBuf);
// 读取SPS帧
unsigned int nSpsLen = inLen - 4;
unsigned char *pSps = (unsigned char*)malloc(nSpsLen);
memcpy(pSps, inBuf + 4, nSpsLen);
// 解码SPS,获取视频图像宽、高信息
int width = 0, height = 0, fps = 0;
h264_decode_sps(pSps, nSpsLen, width, height, fps);
nFrameRate = 0;
if (fps)
nFrameRate = fps;
else
nFrameRate = 25;
}
H264LiveFramedSource* H264LiveFramedSource::createNew(UsageEnvironment& env, unsigned preferredFrameSize, unsigned playTimePerFrame)
{
H264LiveFramedSource* newSource = new H264LiveFramedSource(env, preferredFrameSize, playTimePerFrame);
return newSource;
}
H264LiveFramedSource::~H264LiveFramedSource()
{
free(inBuf);
fclose(inpf);
}
// This function is called when new frame data is available from the device.
// We deliver this data by copying it to the 'downstream' object, using the following parameters (class members):
// 'in' parameters (these should *not* be modified by this function):
// fTo: The frame data is copied to this address.
// (Note that the variable "fTo" is *not* modified. Instead,
// the frame data is copied to the address pointed to by "fTo".)
// fMaxSize: This is the maximum number of bytes that can be copied
// (If the actual frame is larger than this, then it should
// be truncated, and "fNumTruncatedBytes" set accordingly.)
// 'out' parameters (these are modified by this function):
// fFrameSize: Should be set to the delivered frame size (<= fMaxSize).
// fNumTruncatedBytes: Should be set iff the delivered frame would have been
// bigger than "fMaxSize", in which case it's set to the number of bytes
// that have been omitted.
// fPresentationTime: Should be set to the frame's presentation time
// (seconds, microseconds). This time must be aligned with 'wall-clock time' - i.e., the time that you would get
// by calling "gettimeofday()".
// fDurationInMicroseconds: Should be set to the frame's duration, if known.
// If, however, the device is a 'live source' (e.g., encoded from a camera or microphone), then we probably don't need
// to set this variable, because - in this case - data will never arrive 'early'.
void H264LiveFramedSource::doGetNextFrame()
{
fFrameSize = inLen;
if (fFrameSize > fMaxSize)
{
fNumTruncatedBytes = fFrameSize - fMaxSize;
fFrameSize = fMaxSize;
}
else
{
fNumTruncatedBytes = 0;
}
memmove(fTo, inBuf, fFrameSize);
inLen = 0;
inLen = getNextNalu(inpf, inBuf);
gettimeofday(&fPresentationTime, NULL);//时间戳
fDurationInMicroseconds = 1000000 / nFrameRate;//控制播放速度
//表示延迟0秒后再执行afterGetting函数,也可以直接用afterGetting(this)
nextTask() = envir().taskScheduler().scheduleDelayedTask(0, (TaskFunc*)FramedSource::afterGetting, this);
}h264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion.cpp
#include "h264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion.hh"
#include "h264LiveFramedSource.hh"
#include "H264VideoStreamFramer.hh"
H264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion* H264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion::createNew(UsageEnvironment& env, Boolean reuseFirstSource)
{
return new H264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion(env, reuseFirstSource);
}
H264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion::H264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion(UsageEnvironment& env, Boolean reuseFirstSource)
: H264VideoFileServerMediaSubsession(env, 0, reuseFirstSource)
{
}
H264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion::~H264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion()
{
}
FramedSource* H264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion::createNewStreamSource(unsigned clientSessionId, unsigned& estBitrate)
{
//estimate bitrate:估计的比特率,记得根据需求修改
estBitrate = 1000; // kbps
//创建视频源
H264LiveFramedSource* liveSource = H264LiveFramedSource::createNew(envir());
if (liveSource == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
//为视频流创建Framer
return H264VideoStreamFramer::createNew(envir(), liveSource);
} 在h264LiveMediaServer.cpp中做相应的修改
#include "liveMedia.hh"
#include "BasicUsageEnvironment.hh"
#include "h264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion.hh"
UsageEnvironment* env;
// True:后启动的客户端总是从当前第一个客户端已经播放到的位置开始播放
// False:每个客户端都从头开始播放影视频文件
Boolean reuseFirstSource = True;
//该函数打印相关信息
static void announceStream(RTSPServer* rtspServer, ServerMediaSession* sms, char const* streamName);
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
//创建任务调度器并初始化使用环境
TaskScheduler* scheduler = BasicTaskScheduler::createNew();
env = BasicUsageEnvironment::createNew(*scheduler);
UserAuthenticationDatabase* authDB = NULL;
//创建RTSP服务器,开始监听模客户端的连接
//注意这里的端口号不是默认的554端口,因此访问URL时,需指定该端口号
RTSPServer* rtspServer = RTSPServer::createNew(*env, 8554, authDB);
if (rtspServer == NULL)
{
*env << "Failed to create RTSP server: " << env->getResultMsg() << "\n";
exit(1);
}
char const* descriptionString = "Session streamed by \"h264LiveMediaServer\"";
//流名字,媒体名
char const* streamName = "h264ESVideoTest";
//当客户点播时,要输入流名字streamName,告诉RTSP服务器点播的是哪个流。
//创建媒体会话,流名字和文件名的对应关系是通过增加子会话建立起来的。媒体会话对会话描述、会话持续时间、流名字等与会话有关的信息进行管理。
//第2个参数:媒体名、3:媒体信息、4:媒体描述
ServerMediaSession* sms= ServerMediaSession::createNew(*env, streamName, streamName ,descriptionString);
//修改为自己实现的H264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion
sms->addSubsession(H264LiveVideoServerMediaSubssion::createNew(*env, reuseFirstSource));
//为rtspserver添加session
rtspServer->addServerMediaSession(sms);
//答应信息到标准输出
announceStream(rtspServer, sms, streamName);
//进入事件循环,对套接字的读取事件和对媒体文件的延时发送操作都在这个循环中完成。
env->taskScheduler().doEventLoop();
return 0;
}
static void announceStream(RTSPServer* rtspServer, ServerMediaSession* sms,char const* streamName)
{
char* url = rtspServer->rtspURL(sms);
UsageEnvironment& env = rtspServer->envir();
env << "\n\"" << streamName << "\" stream\"\n";
env << "Play this stream using the URL \"" << url << "\"\n";
delete[] url;
} 来一个效果图:
此刻再编译 h264LiveMediaServer,OK 编译成功,生成 h264LiveMediaServer.exe。
将一个 test.264 文件拷贝到 h264LiveMediaServer.exe 目录下
测试:
CMD命令执行 h264LiveMediaServer.exe
在VLC下添加 URL 地址 rtsp://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:8554/h264ESVideoTest
OK,成功播放。
项目下载:
下载:通过live555实现H264 RTSP直播工程
![]()