【Linux云计算架构:第三阶段-Linux高级运维架构】第6章——使用nginx-haproxy实现七层负载均衡笔记
本节内容:
•实战:使用nginx实现动静分离的负载均衡集群
•实战:使用haproxy实现负载均衡集群
LB负载均衡集群分两类:
LVS (四层)
nginx或haproxy (七层)
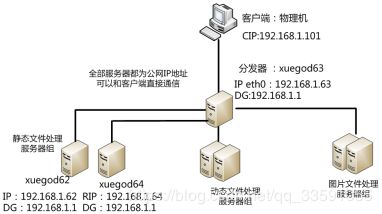
客户端通过访问分发器的VIP来访问网站:
现在应用更复杂,比如现在网站页面有: .php .html .png .jpeg .jsp 等, 有动态页面有静态页面。
静态页面一般是不变的,想访问更快些,前面学习过SQUID。
但是前面的LVS是四层的。基于IP的。现在需要在应用层基于不同的应用进行分发。
七层LB , Nginx / Haproxy都可以支持7层LB
工作中希望这样:
静态文件处理:可以使用nginx 或apache
动态文件处理: apache ,tomcat
图片文件处理: squid
使用nginx实现动静分离的负载均衡集群
Nginx 负载均衡基础知识:
Nginx 的 upstream 负载的5种方式,目前最常用前3 种方式:
1)、轮询(默认)
每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端服务器 down 掉,能自动剔除。
2)、weight
指定轮询几率,weight 和访问比率成正比,用于后端服务器性能不均的情况。
3)、ip_hash
每个请求按访问 ip 的 hash 结果分配,这样每个访客固定访问一个后端服务器,可以解决 session 的问题。
4)、fair(第三方)
按后端服务器的响应时间来分配请求,响应时间短的优先分配。
5)、url_hash(第三方) url哈西
按访问url的hash结果来分配请求,使同样的url定向到同一个后端服务器,后端服务器为缓存时比较有效
实例1:使用nginx实现负载均衡和动静分离
源码编译安装nginx :
一、安装nginx时必须先安装相应的编译工具和相关依赖
[root@xuegod63 ~]#yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ autoconf automake
yum -y install make zlib zlib-devel gcc-c++ libtool openssl openssl-devel
[root@xuegod63 ~]#yum -y install zlib zlib-devel openssl openssl-devel pcre pcre-devel
zlib:nginx提供gzip模块,需要zlib库支持
openssl:nginx提供ssl功能
pcre:支持地址重写rewrite功能
安装nginx:
[root@bogon src]# cd /usr/local/src/
[root@bogon src]# wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.6.2.tar.gz
[root@xuegod63 ~]# ll nginx-1.8.0.tar.gz -h #整个nginx文件不到只813K,很小
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 813K Jul 14 20:17 nginx-1.8.0.tar.gz
[root@xuegod63 ~]# tar -zxvf nginx-1.8.0.tar.gz -C /usr/local/src/
[root@xuegod63 ~]# cd /usr/local/src/nginx-1.8.0/
[root@xuegod63 ~]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_dav_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_addition_module --with-http_sub_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_mp4_module
查看参数:
[root@xuegod63 nginx-1.8.0]# ./configure --help | grep mp4
参数:
--with-http_dav_module 启用ngx_http_dav_module支持(增加PUT,DELETE,MKCOL:创建集合,COPY和MOVE方法)默认情况下为关闭,需编译开启
--with-http_stub_status_module 启用ngx_http_stub_status_module支持(获取nginx自上次启动以来的工作状态)
--with-http_addition_module 启用ngx_http_addition_module支持(作为一个输出过滤器,支持不完全缓冲,分部分响应请求)
--with-http_sub_module 启用ngx_http_sub_module支持(允许用一些其他文本替换nginx响应中的一些文本)
--with-http_flv_module 启用ngx_http_flv_module支持(提供寻求内存使用基于时间的偏移量文件)
--with-http_mp4_module 启用对mp4文件支持(提供寻求内存使用基于时间的偏移量文件)
编译和安装: (查看CPU逻辑数cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep processor | wc -l)
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_dav_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_addition_module --with-http_sub_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_mp4_module
[root@xuegod63 ~]#make -j 4
[root@xuegod63 ~]#make install
问题处理:
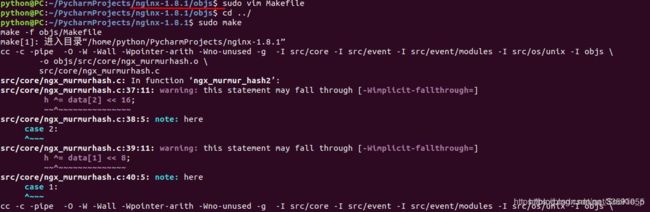
准备工作做好后,make编译时却出现问题,因为sudo,所以也不是权限问题,遇到的问题如下:
cc -c -pipe -O -W -Wall -Wpointer-arith -Wno-unused -Werror -g -I src/core -I src/event -I src/event/modules -I src/os/unix -I objs \ -o objs/src/core/ngx_murmurhash.o \ src/core/ngx_murmurhash.c src/core/ngx_murmurhash.c: In function ‘ngx_murmur_hash2’: src/core/ngx_murmurhash.c:37:11: error: this statement may fall through [-Werror=implicit-fallthrough=] h ^= data[2] << 16; ~~^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ src/core/ngx_murmurhash.c:38:5: note: here case 2: ^~~~ src/core/ngx_murmurhash.c:39:11: error: this statement may fall through [-Werror=implicit-fallthrough=] h ^= data[1] << 8; ~~^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ src/core/ngx_murmurhash.c:40:5: note: here case 1: ^~~~ cc1: all warnings being treated as errors objs/Makefile:431: recipe for target 'objs/src/core/ngx_murmurhash.o' failed make[1]: *** [objs/src/core/ngx_murmurhash.o] Error 1 make[1]: 离开目录“/home/python/PycharmProjects/nginx-1.8.1” Makefile:8: recipe for target 'build' failed make: *** [build] Error 2
去掉CFLAGS中的-Werror
再重新make
-Wall 表示打开gcc的所有警告
-Werror,它要求gcc将所有的警告当成错误进行处理
Nginx安装出现‘struct crypt_data’没有名为‘current_sal
centos 安装nginx 时出现src/os/unix/ngx_user.c:26:7: 错误:‘struct crypt_data’没有名为‘current_sal
解决办法: 将系统换成版本低的centos就可以了,亲测centos7.0 版本可以(centos7.0以上没试过),centos8以上不可以
问题: centos高版本的crypt库已从glibc切换到libxcrypt,所以nginx 安装一直失败,切确的说就是系统有问题,无法安装。
src/os/unix/ngx_user.c:26:7: 错误:‘struct crypt_data’没有名为‘current_sal
生成运行nginx的用户:
[root@xuegod63 nginx-1.8.0]# useradd -u 8000 -s /sbin/nologin nginx
[root@xuegod63 nginx-1.8.0]# id !$
id nginx
uid=8000(nginx) gid=8000(nginx) groups=8000(nginx)
nginx主要目录结构:
[root@xuegod63 /]# ls /server/nginx-1.8.0/
conf html logs sbin
conf #配置文件
html #网站根目录
logs #日志
sbin #nginx启动脚本
主配置文件:
[root@xuegod63 /]# ls /server/nginx-1.8.0/conf/nginx.conf
启动nginx:
[root@xuegod63 /]# /server/nginx-1.8.0/sbin/nginx
[root@xuegod63 /]# netstat -antup | grep :80
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 5281/httpd
[root@xuegod63 /]# netstat -antup | grep :80
开机启动:
[root@xuegod63 nginx-1.8.0]# echo '/server/nginx-1.8.0/sbin/nginx & ' >> /etc/rc.local
nginx服务日常操作:
测试配置文件语法:
[root@xuegod63 nginx-1.8.0]# /server/nginx-1.8.0/sbin/nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /server/nginx-1.8.0/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /server/nginx-1.8.0/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
重新加载配置文件:
[root@xuegod63 nginx-1.8.0]# /server/nginx-1.8.0/sbin/nginx -s reload
关闭nginx:
[root@xuegod63 /]# /server/nginx-1.8.0/sbin/nginx -s stop
[root@xuegod63 /]# /server/nginx-1.8.0/sbin/nginx -s start #没有start参数
nginx: invalid option: "-s start"
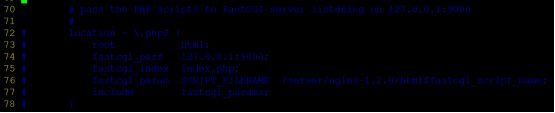
配置nginx成为分发器,实现动静分离:
[root@xuegod63 conf]# cd /server/nginx-1.8.0/conf #配置文件目录
[root@xuegod63 conf]# cp nginx.conf nginx.conf.back #备份一下配置文件
[root@xuegod63 conf]# vim nginx.conf
[root@xuegod63 nginx-1.8.0]# vim /server/nginx-1.8.0/conf/nginx.conf #指定启动nginx用户
改:# user nobody;
为:user nginx nginx;
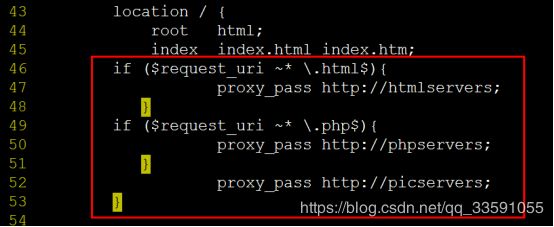
改:
43 location / {
44 root html;
45 index index.html index.htm; #在location / { 。。。} 中添加以下内容 #定义分发策略
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
if ($request_uri ~* \.html$){
proxy_pass http://htmlservers;
}
if ($request_uri ~* \.php$){
proxy_pass http://phpservers;
}
proxy_pass http://picservers;
}
把以下内容注释掉,否则php文件直接在nginx服务器上解析了,不再解析给后端服务器:
# location ~ \.php$ {
73 # root html;
74 # fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
75 # fastcgi_index index.php;
76 # fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /server/nginx-1.8.0/html$fastcgi_script_name;
77 # include fastcgi_params;
78 # }
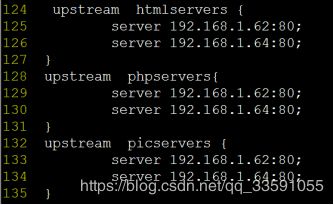
如图:
#定义负载均衡设备的 Ip
#定义负载均衡设备的 Ip
在配置文件nginx.conf的最后一行}前,添加以下内容:
upstream htmlservers { #定义负载均衡服务器组名称
server 192.168.1.62:80;
server 192.168.1.64:80;
}
upstream phpservers{
server 192.168.1.62:80;
server 192.168.1.64:80;
}
upstream picservers {
server 192.168.1.62:80;
server 192.168.1.64:80;
}
#后期工作中,根据工作中的需要,配置成具体业务的IP地址
重新加载nginx服务器配置文件:
[root@xuegod63 conf]# /server/nginx-1.8.0/sbin/nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /server/nginx-1.8.0/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /server/nginx-1.8.0/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@xuegod63 conf]# /server/nginx-1.8.0/sbin/nginx -s reload
配置后端服务器: xuegod62
配置web服务器:
[root@xuegod62 html]# yum install httpd php -y
生成静态测试文件:
root@xuegod62 html]#echo 192.168.1.62 > /var/www/html/index.html
生成动态测试文件:
[root@xuegod62 html]#vim /var/www/html/test.php #写如以下内容:
192.168.1.62-php
生成图片文件:
上传如下图片,到“xuegod62网站/var/www/html/目录下:

启动apache服务器:
[root@xuegod62 html]# service httpd restart
配置后端服务器: xuegod64
IP: 192.168.1.64
配置web服务器:
[root@xuegod64 html]# yum install httpd php -y
生成静态测试文件:
echo 192.168.1.64 > /var/www/html/index.html
生成动态测试文件:
vim /var/www/html/test.php #写如以下内容:
192.168.1.64-php
生成图片文件:
上传如下图片,到“xuegod64网站/var/www/html/目录下:

[root@xuegod64 html]# service httpd restart
到此nginx实现负载均衡结束。
测试转发静态页面:
http://192.168.1.63/
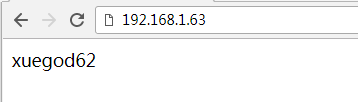
http://192.168.1.63/
测试转发动态页面:
http://192.168.1.63/test.php
http://192.168.1.63/test.php
测试转发图片:
http://192.168.1.63/pic.jpg

http://192.168.1.63/pic.jpg

测试自动剔除坏的节点:
[root@xuegod64 html]# service httpd stop
Stopping httpd: [ OK ]
访问:
http://192.168.1.63/pic.jpg
http://192.168.1.63/pic.jpg
都访问到
测试性能:
扩展: 文件打开数过多
[root@xuegod64 html]# ab -n 1000 -c 1000 http://192.168.1.62/index.html #运行正常
[root@xuegod64 html]# ab -n 2000 -c 2000 http://192.168.1.62/index.html #报错
This is ApacheBench, Version 2.3 <$Revision: 655654 $>
Copyright 1996 Adam Twiss, Zeus Technology Ltd, http://www.zeustech.net/
Licensed to The Apache Software Foundation, http://www.apache.org/
Benchmarking 192.168.1.62 (be patient)
socket: Too many open files (24) # 测试时,一次打开的socket文件太多。
#ulimit -a #查看
#ulimit -n
1024
系统默认一个进程最多同时允许打开1024个文件
解决:
#ulimit -n 10240 #报错的解决方法
Nginx负载的5种策略设置方法:
1、轮询(默认)
每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端服务器down掉,能自动剔除。
upstream backserver {
server 192.168.1.62;
server 192.168.1.64;
}
2、指定权重
指定轮询几率,weight和访问比率成正比,用于后端服务器性能不均的情况。
upstream backserver {
server 192.168.1.62 weight=1;
server 192.168.1.64 weight=2;
}
3、IP绑定 ip_hash
每个请求按访问ip的hash结果分配,这样每个访客固定访问一个后端服务器,可以解决session的问题。
upstream backserver {
ip_hash;
server 192.168.1.62:80;
server 192.168.1.64:80;
}
4、fair(第三方)
按后端服务器的响应时间来分配请求,响应时间短的优先分配。
upstream backserver {
server server1;
server server2;
fair;
}
5、url_hash(第三方)
按访问url的hash结果来分配请求,使每个url定向到同一个后端服务器,后端服务器为缓存时比较有效。
upstream backserver {
server squid1:3128;
server squid2:3128;
hash $request_uri;
hash_method crc32;
}
总结,扩展:
如有tomcat ,apache,squid 配置为如下:
[root@xuegod63 conf]# vim nginx.conf # 在最后添加以下内容。 定义服务器组
upstream tomcat_servers {
server 192.168.1.2:8080;
server 192.168.1.1:8080;
server 192.168.1.11:8080;
}
upstream apache_servers {
server 192.168.1.5:80;
server 192.168.1.177:80;
server 192.168.1.15:80;
}
upstream squid_servers {
server 192.168.1.26:3128;
server 192.168.1.55:3128;
server 192.168.1.18:3128;
}
HAProxy概述:
HAProxy提供高可用性、负载均衡以及基于TCP和HTTP应用的代理,支持虚拟主机,它是免费、快速并且可靠的一种解决方案。根据官方数据,其最高极限支持10G的并发。
HAProxy特别适用于那些负载特大的web站点, 这些站点通常又需要会话保持或七层处理。HAProxy运行在当前的硬件上,完全可以支持数以万计的并发连接。并且它的运行模式使得它可以很简单安全的整合进您当前的架构中, 同时可以保护你的web服务器不被暴露到网络上。
其支持从4层至7层的网络交换,即覆盖所有的TCP协议。就是说,Haproxy 甚至还支持 Mysql的均衡负载。
相同点:
在功能上,proxy通过反向代理方式实现 WEB均衡负载。和 Nginx,ApacheProxy,lighttpd,Cheroke 等一样。
不同点:
Haproxy 并不是 web 服务器。以上提到所有带反向代理均衡负载的产品,都清一色是 WEB 服务器。简单说,就是他们能处理解析页面的。而Haproxy 仅仅是一款的用于均衡负载的应用代理。其自身并不能提供web服务。
但其配置简单,拥有非常不错的服务器健康检查功能还有专门的系统状态监控页面,当其代理的后端服务器出现故障, HAProxy会自动将该服务器摘除,故障恢复后再自动将该服务器加入。
www.haproxy.org #打不开
http://haproxy.com/ #收费
http://haproxy.1wt.eu/ 社区版地址, 打不开
https://github.com/haproxy/haproxy/releases/ 在github 可以下载
实验拓扑图:
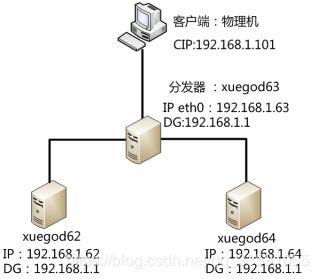
安装:
[root@xuegod63 ~]# tar -zxvf haproxy-1.7.9.tar.gz
[root@xuegod63 haproxy-1.7.9]# cd /root/haproxy-1.7.9
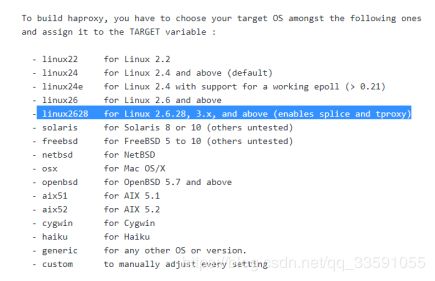
[root@xuegod63 haproxy-1.7.9]# uname -r #查看内核版本
[root@xuegod63 haproxy-1.7.9]# make TARGET=linux2628 PREFIX=/usr/local/haproxy #指定操作系统内核类型和安装的路径。也可以直接修改Makefile配置文件中这两个变量的值。如下:
[root@xuegod63 haproxy-1.7.9]# vim Makefile
[root@xuegod63 haproxy-1.7.9]#make install PREFIX=/usr/local/haproxy
#如果没有修改Makefile配置文件中PREFIX变量的值,就必须在此重新对,PREFIX=/usr/local/haproxy赋值,否则直接执行 make install 时,make install会直接读取Makefile文件中PREFIX的变量值。
[root@xuegod63 haproxy-1.7.9]# ls /usr/local/haproxy/
doc sbin share
没有生成配置文件,自己手动写一个HAproxy配置文件:
[root@xuegod63 etc]# mkdir /usr/local/haproxy/etc
[root@xuegod63 ~]# vim /usr/local/haproxy/etc/haproxy.cfg #手动创建配置文件
global
log 127.0.0.1 local0
#log 127.0.0.1 local1 notice
#log loghost local0 info
maxconn 4096
chroot /usr/local/haproxy
uid 99 #所属运行的用户uid
gid 99 #所属运行的用户组
daemon #以后台形式运行haproxy
nbproc 1 #启动1个haproxy实例。# #工作进程数量(CPU数量) ,实际工作中,应该设置成和CPU核心数一样。 这样可以发挥出最大的性能。
pidfile /usr/local/haproxy/run/haproxy.pid #将所有进程写入pid文件
#debug #调试错误时用
#quiet #安静
defaults
log global
log 127.0.0.1 local3 #日志文件的输出定向。产生的日志级别为local3. 系统中local1-7,用户自己定义
mode http #工作模式,所处理的类别,默认采用http模式,可配置成tcp作4层消息转发
option httplog #日志类别,记载http日志
option httpclose #每次请求完毕后主动关闭http通道,haproxy不支持keep-alive,只能模拟这种模式的实现
option dontlognull #不记录空连接,产生的日志
option forwardfor #如果后端服务器需要获得客户端真实ip需要配置的参数,可以从Http Header中获得客户端ip
option redispatch #当serverid对应的服务器挂掉后,强制定向到其他健康服务器
retries 2 #2次连接失败就认为服务器不可用,主要通过后面的check检查
maxconn 2000 #最大连接数
balance roundrobin #负载均衡算法
stats uri /haproxy-stats #haproxy 监控页面的访问地址 # 可通过 http://localhost:80/haproxy-stats 访问
timeout connect 5000 #连接超时时间。 单位:ms 毫秒
timeout client 50000 #客户端连接超时时间
timeout server 50000 #服务器端连接超时时间
mode http
option httpchk GET /index.html #健康检测#注意实际工作中测试时,应该下载某一个页面来进行测试,因此这个页面应该是个小页面,而不要用首页面。这里是每隔一秒检查一次页面。
frontend http #前端配置,http名称可自定义
bind 0.0.0.0:80 #发起http请求80端口,会被转发到设置的ip及端口
default_backend http_back #转发到后端 写上后端名称
backend http_back #后端配置,名称上下关联
server s1 10.10.10.68:80 weight 3 check #后端的主机 IP &权衡
server s2 10.10.10.69:80 weight 3 check #后端的主机 IP &权衡
#server node1 192.168.179.131:8081 check inter 2000 rise 3 fall 3 weight 30
# inter 2000 健康检查时间间隔2秒
# rise 3 检测多少次才认为是正常的
# fall 3 失败多少次才认为是不可用的
# weight 30 权重
关于负载均衡算法
#source 根据请求源IP
#static-rr 根据权重
#leastconn 最少连接者先处理
#uri 根据请求的uri
#url_param 根据请求的url参数
#rdp-cookie 据据cookie(name)来锁定并哈希每一次请求
#hdr(name) 根据HTTP请求头来锁定每一次HTTP请求
#roundrobin 轮询方式
使用nobody用户运行haproxy:
[root@xuegod63 haproxy-1.7.9]# id nobody
uid=99(nobody) gid=99(nobody) groups=99(nobody) #id 为99
复制haproxy启动脚本,到/etc/init.d下:
[root@xuegod63 ~]# cp ./haproxy-1.7.9/examples/haproxy.init /etc/init.d/haproxy
[root@xuegod63 ~]# chmod 755 /etc/init.d/haproxy
[root@xuegod63 ~]# vim /etc/init.d/haproxy #此脚本需修改地方较多
#!/bin/sh
# chkconfig: - 85 15
# description: HA-Proxy server
# processname: haproxy
# config: /usr/local/haproxy/etc/haproxy.cfg
# pidfile: /usr/local/haproxy/run/haproxy.pid
# Source function library.
if [ -f /etc/init.d/functions ]; then
. /etc/init.d/functions
elif [ -f /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions ] ; then
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
else
exit 0
fi
# Source networking configuration.
. /etc/sysconfig/network
# Check that networking is up.
[ "$NETWORKING" = "no" ] && exit 0
# This is our service name
BASENAME=`haproxy`
BIN=/usr/sbin/haproxy
CFG=/usr/local/haproxy/etc/haproxy.cfg
[ -f $CFG ] || exit 1
PIDFILE=/usr/local/haproxy/run/haproxy.pid
LOCKFILE=/usr/local/haproxy/run/haproxy
RETVAL=0
start() {
quiet_check
if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then
echo "Errors found in configuration file, check it with '$BASENAME check'."
return 1
fi
echo -n "Starting $BASENAME: "
daemon $BIN -D -f $CFG -p $PIDFILE
RETVAL=$?
echo
[ $RETVAL -eq 0 ] && touch $LOCKFILE
return $RETVAL
}
stop() {
echo -n "Shutting down $BASENAME: "
killproc $BASENAME -USR1
RETVAL=$?
echo
[ $RETVAL -eq 0 ] && rm -f $LOCKFILE
[ $RETVAL -eq 0 ] && rm -f $PIDFILE
return $RETVAL
}
restart() {
quiet_check
if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then
echo "Errors found in configuration file, check it with '$BASENAME check'."
return 1
fi
stop
start
}
reload() {
if ! [ -s $PIDFILE ]; then
return 0
fi
quiet_check
if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then
echo "Errors found in configuration file, check it with '$BASENAME check'."
return 1
fi
$BIN -D -f $CFG -p $PIDFILE -sf $(cat $PIDFILE)
}
check() {
$BIN -c -q -V -f $CFG
}
quiet_check() {
$BIN -c -q -f $CFG
}
rhstatus() {
status $BASENAME
}
condrestart() {
[ -e $LOCKFILE ] && restart || :
}
# See how we were called.
case "$1" in
start)
start
;;
stop)
stop
;;
restart)
restart
;;
reload)
reload
;;
condrestart)
condrestart
;;
status)
rhstatus
;;
check)
check
;;
*)
echo $"Usage: $BASENAME {start|stop|restart|reload|condrestart|status|check}"
exit 1
esac
exit $?
复制haproxy文件到/usr/sbin下
因为上面的haproxy.init启动脚本默认会去/usr/sbin下找
[root@xuegod63 ~]#cp /usr/local/haproxy/sbin/haproxy /usr/sbin/
创建目录和权限
[root@xuegod63 ~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/haproxy/run
[root@xuegod63 ~]# chown nobody /usr/local/haproxy/ -R
配置日志收集
[root@xuegod63 ~]# vim /etc/rsyslog.conf #打开以下两行的注释,不打开收不到日志
$ModLoad imudp #取消注释
$UDPServerRun 514 #取消注释
local7.* /var/log/boot.log #下面添加两行
local3.* /var/log/haproxy.log
local0.* /var/log/haproxy.log
[root@xuegod63 ~]# systemctl restart rsyslog
启动和停止服务:
特殊启动方法1
[root@xuegod63 etc]# /usr/local/haproxy/sbin/haproxy -f /usr/local/haproxy/etc/haproxy.cfg
查看状态:
[root@xuegod63 etc]# ps -axu | grep haproxy
nobody 3871 0.0 0.0 12228 1036 ? Ss 21:53 0:00 /usr/local/haproxy/sbin/haproxy -f /usr/local/haproxy/etc/haproxy.cfg
[root@xuegod63 etc]# netstat -antup | grep 80
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3871/haproxy
停止:
[root@xuegod63 etc]# killall haproxy #没有killall命令?安装yum -y install psmisc
HAproxy脚本启动方法2
[root@xuegod63 ~]# /etc/init.d/haproxy start 或 systemctl restart haproxy
配置后端服务器: xuegod62
配置web服务器:
[root@xuegod62 html]# yum install httpd php -y
生成测试文件:
root@xuegod62 html]#echo 192.168.1.62 > /var/www/html/index.html
启动apache服务器:
[root@xuegod62 html]# service httpd restart
配置后端服务器: xuegod64
IP: 192.168.1.64
配置web服务器:
[root@xuegod64 html]# yum install httpd php -y
生成测试文件:
echo 192.168.1.64 > /var/www/html/index.html
[root@xuegod64 html]# service httpd restart
查看HAproxy的监控页面:
http://192.168.1.63/haproxy-stats
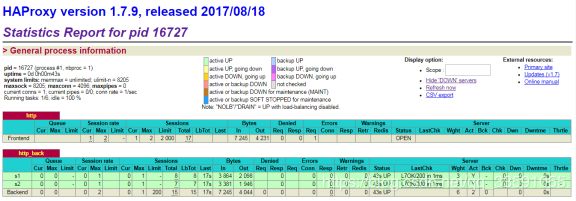
测试:反向代理功能
http://192.168.1.63/
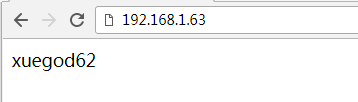
http://192.168.1.63/
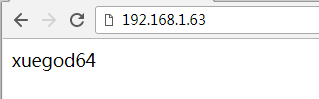
注:
相关配置文件和启动脚本可以从这个配置模版中获得
[root@xuegod63 haproxy-1.7.9]# cd /root/haproxy-1.7.9/examples/
[root@xuegod63 examples]# ls
配置随机启动:
[root@xuegod63 examples]# chkconfig --add haproxy
[root@xuegod63 examples]# chkconfig haproxy on