pytorch框架使用LSTM预测股票价格
1.代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2020/5/11 11:18
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
import numpy as np
import tushare as ts
import torch
from torch import nn
DAYS_FOR_TRAIN = 10
EPOCHS = 1000
class LSTM_Regression(nn.Module):
"""
使用LSTM进行回归
参数:
- input_size: feature size
- hidden_size: number of hidden units
- output_size: number of output
- num_layers: layers of LSTM to stack
"""
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size=1, num_layers=2):
super().__init__()
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
def forward(self, _x):
x, _ = self.lstm(_x) # _x is input, size (seq_len, batch, input_size)
s, b, h = x.shape # x is output, size (seq_len, batch, hidden_size)
x = x.view(s * b, h)
x = self.fc(x)
x = x.view(s, b, -1) # 把形状改回来
return x
def create_dataset(data, days_for_train=5) -> (np.array, np.array):
"""
根据给定的序列data,生成数据集。
数据集分为输入和输出,每一个输入的长度为days_for_train,每一个输出的长度为1。
也就是说用days_for_train天的数据,对应下一天的数据。
若给定序列的长度为d,将输出长度为(d-days_for_train)个输入/输出对
"""
dataset_x, dataset_y = [], []
for i in range(len(data) - days_for_train):
_x = data[i:(i + days_for_train)]
dataset_x.append(_x)
dataset_y.append(data[i + days_for_train])
return (np.array(dataset_x), np.array(dataset_y))
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 取上证指数的收盘价
share_prices = ts.get_k_data('000001', start='2018-01-01', index=True)[
'close'].values
share_prices = share_prices.astype('float32') # 转换数据类型: obj ->float
# 上证指数收盘价作图
plt.plot(share_prices)
plt.savefig('share_prices.png', format='png', dpi=200)
plt.close()
# 将数据集标准化到 [-1,1] 区间
scaler = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(-1, 1)) # train data normalized
share_prices = scaler.fit_transform(share_prices.reshape(-1, 1))
# 数据集序列化,进行标签分离
dataset_x, dataset_y = create_dataset(share_prices, DAYS_FOR_TRAIN)
# 划分训练集和测试集,70%作为训练集,30%作为测试集
train_size = int(len(dataset_x) * 0.7)
train_x = dataset_x[:train_size]
train_y = dataset_y[:train_size]
test_x = dataset_x[train_size:]
test_y = dataset_y[train_size:]
# 改变数据集形状,RNN 读入的数据维度是 (seq_size, batch_size, feature_size)
train_x = train_x.reshape(-1, 1, DAYS_FOR_TRAIN)
train_y = train_y.reshape(-1, 1, 1)
# 数据集转为pytorch的tensor对象
train_x = torch.from_numpy(train_x)
train_y = torch.from_numpy(train_y)
# train model
model = LSTM_Regression(DAYS_FOR_TRAIN, 8, output_size=1, num_layers=2) # 网络初始化
loss_function = nn.MSELoss() # 损失函数
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-2) # 优化器
for epoch in range(EPOCHS):
out = model(train_x)
loss = loss_function(out, train_y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
if (epoch + 1) % 100 == 0:
print('Epoch: {}, Loss:{:.5f}'.format(epoch + 1, loss.item()))
# torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'model_params.pkl') # 可以保存模型的参数供未来使用
# predict
model = model.eval() # 转换成测试模式
# model.load_state_dict(torch.load('model_params.pkl')) # 读取参数
# 使用全部数据集dataset_x,模型的输出长度会比dataset_x少 DAYS_FOR_TRAIN
dataset_x = dataset_x.reshape(-1, 1, DAYS_FOR_TRAIN) # (seq_size, batch_size, feature_size)
dataset_x = torch.from_numpy(dataset_x) # 转为pytorch的tensor对象
pred_y = model(dataset_x) # 全量数据集的模型输出 (seq_size, batch_size, output_size)
pred_y = pred_y.view(-1).data.numpy()
# 对标准化数据进行还原
actual_pred_y = scaler.inverse_transform(pred_y.reshape(-1, 1))
actual_pred_y = actual_pred_y.reshape(-1, 1).flatten()
test_y = scaler.inverse_transform(test_y.reshape(-1, 1))
test_y = test_y.reshape(-1, 1).flatten()
actual_pred_y = actual_pred_y[-len(test_y):]
test_y = test_y.reshape(-1, 1)
assert len(actual_pred_y) == len(test_y)
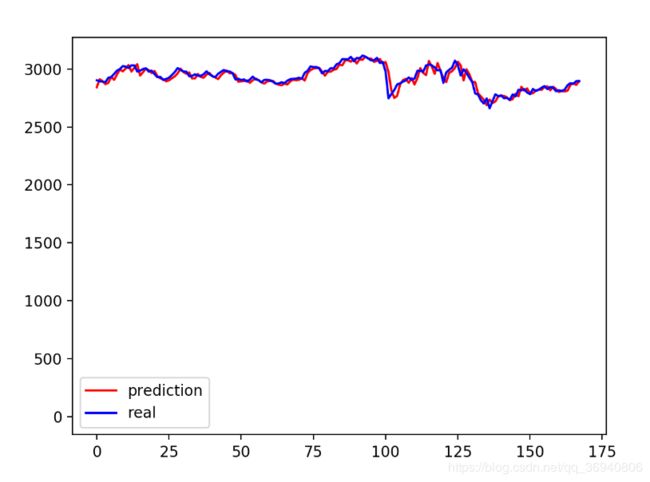
# 初始结果 - 预测结果
plt.plot(actual_pred_y, 'r', label='prediction')
plt.plot(test_y, 'b', label='real')
plt.plot((len(actual_pred_y), len(test_y)), (0, 1), 'g--') # 分割线 左边是训练数据 右边是测试数据的输出
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.savefig('result.png', format='png', dpi=200)
plt.close()
2.真实结果与预测结果对比