【计算机视觉】图像检索
目录
一、图像检索概述
1.1 基于文本的图像检索(TBIR)
1.2 基于内容的图像检索技术(CBIR)
二、基于bow的图像检索原理
2.1 BOW (Bag of words)
2.2 BOF(Bag of features)
2.2.1 BOF概述
2.2.2 基于SIFT特征构建BoF的步骤
2.3 K-means聚类算法
三、代码实现过程及结果
一、图像检索概述
图像检索,简单的说,便是从图片检索数据库中检索出满足条件的图片,图像检索技术的研究根据描述图像内容方式的不同可以分为两类:
一类是基于文本的图像检索技术,简称TBIR,
一类为基于内容的图像检索技术,简称CBIR。
1.1 基于文本的图像检索(TBIR)
从20世纪70年代开始,有关图像检索的研究就已经开始,当时主要是基于文本的图像检索技术,利用文本描述的方式描述图像的特点,如一张照片,配以文字说明照片拍摄的时间,地点,事件的主要内容等。
但这种方法需要较多的人工参与,而且随着图像数目的增加,这种方法很难实现;由于图像所包含的信息量庞大,不同的人对于同一张图像的理解也不相同,这就导致对图像的标注没有一个统一的标准,因而检索的结果不能很好的符合用户的需求。
1.2 基于内容的图像检索技术(CBIR)
到90年代以后,出现了对图像的内容语义,如对图像颜色、纹理、布局等进行分析和检索的图像检索技术,即基于内容的图像检索。指的是查询条件本身就是一个图像,或者是对于图像内容的描述,它建立索引的方式是通过提取底层特征,然后通过计算比较这些特征和查询条件之间的距离,来决定两个图片的相似程度。
二、基于bow的图像检索原理
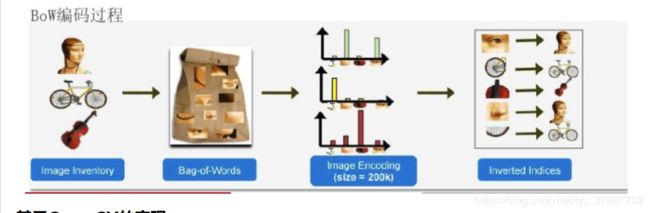
2.1 BOW (Bag of words)
BoW模型最初是为解决文档建模问题而提出的,因为文本本身就是由单词组成的。它忽略文本的词序,语法,句法,仅仅将文本当作一个个词的集合,并且假设每个词彼此都是独立的。这样就可以使用文本中词出现的频率来对文档进行描述,将一个文档表示成一个一维的向量。
BoW引入到计算机视觉中,就是将一幅图像看着文本对象,图像中的不同特征可以看着构成图像的不同词汇。和文本的BoW类似,这样就可以使用图像特征在图像中出现的频率,使用一个一维的向量来描述图像。
要将图像表示为BoW的向量,首先就是要得到图像的“词汇”。通常需要在整个图像库中提取图像的局部特征(例如,sift,orb等),然后使用聚类的方法,合并相近的特征,聚类的中心可以看着一个个的视觉词汇(visual word),视觉词汇的集合构成视觉词典(visual vocabulary) 。 得到视觉词汇集合后,统计图像中各个视觉词汇出现的频率,就得到了图像的BoW表示。
2.2 BOF(Bag of features)
2.2.1 BOF概述
BOF方法源自于文本处理的词袋模型。Bag-of-words model (BoW model) 最早出现在NLP和IR领域. 该模型忽略掉文本的语法和语序, 用一组无序的单词(words)来表达一段文字或一个文档. 近年来, BoW模型被广泛应用于计算机视觉中. 与应用于文本的BoW类比, 图像的特征(feature)被当作单词(Word)。
BoF(Bag Of Feature)借鉴文本处理的词袋(BoW,Bag Of Bag)算法,将图像表示成视觉关键词的统计直方图。就像上面对文本的处理一样,提取文本中出现单词组成词汇表,这里关键是得到图像库的“词汇表”。为了得到图像库的“词汇表",通常对提取到的图像特征进行聚类,得到一定个数的簇。这些聚类得到的簇,就是图像的”词汇“,可以称为视觉词(Visual Word)。聚类形成的簇,可以使用聚类中心来描述,所以,视觉词指的是图像的局部区域特征(如纹理,特征点)经过聚类形成的聚类中心。
2.2.2 基于SIFT特征构建BoF的步骤
这边sift算法原理省略SIFT原理
1、SIFT特征提取 :提取训练集中所有图像的SIFT特征,设有MM幅图像,共得到NN个SIFT特征。
2、构建视觉词汇表 对提取到的NN个SIFT特征进行聚类,得到KK个聚类中心,组成图像的视觉词汇表。
3、图像的视觉词向量表示,统计每幅图像中视觉词汇的出现的次数,得到图像的特征向量。在检索时,该特征向量就代表该幅图像。统计时,计算图像中提取到的SIFT特征点到各个视觉词(聚类中心)的距离,将其归类到聚类最近的视觉词中。
2.3 K-means聚类算法
聚类(Clustering)是一种无监督学习算法,其目的是将数据集中的样本划分为若干个不相交的子集,每个子集称为一个簇(Cluster)。聚类的时候并不关心某一类是什么,只根据数据的相似性,将数据划分到不同的组中。每个组内的成员具有相似的性质。
聚类算法可以分为三类:
- 原型聚类,此类算法假设聚类结构能够通过一组原型描述,这里原型指的是样本空间中具有代表性的点。
- 密度距离,该类算法假设聚类结构能够通过样本分布的紧密程度来确定。
- 层次聚类,在不同的层次对数据集进行划分,从而形成树形的聚结构。
K-Means算法是原型聚类的一种,对于给定的样本集,按照样本之间的距离大小,将样本集划分为K个簇。让簇内的点尽量紧密的连在一起,而让簇间的距离尽量的大。
如果用数据表达式表示,假设簇划分为(C1,C2,...Ck),则我们的目标是最小化平方误差E: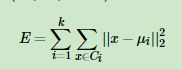
K-Means算法基本流程:
- 随机初始化 K 个聚类中心
- 重复下述步骤直至算法收敛:
- 对应每个特征,根据距离关系赋值给某个中心/类别
- 对每个类别,根据其对应的特征集重新计算聚类中心
三、代码实现过程及结果
- 提取图像库中所有图像的局部特征,这边提取图像的sift特征:
#获取图像列表
imlist = get_imlist('first1000/')
nbr_images = len(imlist)
#获取特征列表
featlist = [imlist[i][:-3]+'sift' for i in range(nbr_images)]
#提取文件夹下图像的sift特征
for i in range(nbr_images):
sift.process_image(imlist[i], featlist[i])
- 构建图像库的视觉词典
voc = vocabulary.Vocabulary('ukbenchtest')
voc.train(featlist, 1000, 10)
#保存词汇
# saving vocabulary
with open('first1000/vocabulary.pkl', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(voc, f)
print ('vocabulary is:', voc.name, voc.nbr_words)- 对提取到的图像特征进行聚类,如k-means,得到聚类中心就是图像库的视觉词汇词典,下面为
class Vocabulary(object):
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
self.voc = []
self.idf = []
self.trainingdata = []
self.nbr_words = 0
def train(self,featurefiles,k=100,subsampling=10):
""" Train a vocabulary from features in files listed
in featurefiles using k-means with k number of words.
Subsampling of training data can be used for speedup. """
nbr_images = len(featurefiles)
# read the features from file
descr = []
descr.append(sift.read_features_from_file(featurefiles[0])[1])
descriptors = descr[0] #stack all features for k-means
for i in arange(1,nbr_images):
descr.append(sift.read_features_from_file(featurefiles[i])[1])
descriptors = vstack((descriptors,descr[i]))
# k-means: last number determines number of runs
self.voc,distortion = kmeans(descriptors[::subsampling,:],k,1)
self.nbr_words = self.voc.shape[0]
# go through all training images and project on vocabulary
imwords = zeros((nbr_images,self.nbr_words))
for i in range( nbr_images ):
imwords[i] = self.project(descr[i])
nbr_occurences = sum( (imwords > 0)*1 ,axis=0)
self.idf = log( (1.0*nbr_images) / (1.0*nbr_occurences+1) )
self.trainingdata = featurefiles
def project(self,descriptors):
""" Project descriptors on the vocabulary
to create a histogram of words. """
# histogram of image words
imhist = zeros((self.nbr_words))
words,distance = vq(descriptors,self.voc)
for w in words:
imhist[w] += 1
return imhist
def get_words(self,descriptors):
""" Convert descriptors to words. """
return vq(descriptors,self.voc)[0]- 将前面得到的
Vocabulary和图像的特征集来创建数据库。
#载入词汇
with open('first1000/vocabulary.pkl', 'rb') as f:
voc = pickle.load(f)
#创建索引
indx = imagesearch.Indexer('testImaAdd.db',voc)
indx.create_tables()
# go through all images, project features on vocabulary and insert
#遍历所有的图像,并将它们的特征投影到词汇上
for i in range(nbr_images)[:1000]:
locs,descr = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[i])
indx.add_to_index(imlist[i],descr)
# commit to database
#提交到数据库
indx.db_commit()
con = sqlite.connect('testImaAdd.db')创建的数据库:![]()
- 测试
# index of query image and number of results to return
#查询图像索引和查询返回的图像数
q_ind = 0
nbr_results = 40
# regular query
# 常规查询(按欧式距离对结果排序)
res_reg = [w[1] for w in src.query(imlist[q_ind])[:nbr_results]]
print ('top matches (regular):', res_reg)
# load image features for query image
#载入查询图像特征
q_locs,q_descr = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[q_ind])
fp = homography.make_homog(q_locs[:,:2].T)
# RANSAC model for homography fitting
#用单应性进行拟合建立RANSAC模型
model = homography.RansacModel()
rank = {}
# load image features for result
#载入候选图像的特征
for ndx in res_reg[1:]:
locs,descr = sift.read_features_from_file(featlist[ndx]) # because 'ndx' is a rowid of the DB that starts at 1
# get matches
matches = sift.match(q_descr,descr)
ind = matches.nonzero()[0]
ind2 = matches[ind]
tp = homography.make_homog(locs[:,:2].T)
# compute homography, count inliers. if not enough matches return empty list
try:
H,inliers = homography.H_from_ransac(fp[:,ind],tp[:,ind2],model,match_theshold=4)
except:
inliers = []
# store inlier count
rank[ndx] = len(inliers)
# sort dictionary to get the most inliers first
sorted_rank = sorted(rank.items(), key=lambda t: t[1], reverse=True)
res_geom = [res_reg[0]]+[s[0] for s in sorted_rank]
print ('top matches (homography):', res_geom)
# 显示查询结果
imagesearch.plot_results(src,res_reg[:8]) #常规查询
imagesearch.plot_results(src,res_geom[:8]) #重排后的结果- imagesearch.py 包含计算图像的bow向量即直方图,通过直方图进行检索查找
class Indexer(object):
def __init__(self,db,voc):
""" Initialize with the name of the database
and a vocabulary object. """
self.con = sqlite3.connect(db)
self.voc = voc
def __del__(self):
self.con.close()
def db_commit(self):
self.con.commit()
def get_id(self,imname):
""" Get an entry id and add if not present. """
cur = self.con.execute(
"select rowid from imlist where filename='%s'" % imname)
res=cur.fetchone()
if res==None:
cur = self.con.execute(
"insert into imlist(filename) values ('%s')" % imname)
return cur.lastrowid
else:
return res[0]
def is_indexed(self,imname):
""" Returns True if imname has been indexed. """
im = self.con.execute("select rowid from imlist where filename='%s'" % imname).fetchone()
return im != None
def add_to_index(self,imname,descr):
""" Take an image with feature descriptors,
project on vocabulary and add to database. """
if self.is_indexed(imname): return
print ('indexing', imname)
# get the imid
imid = self.get_id(imname)
# get the words
imwords = self.voc.project(descr)
nbr_words = imwords.shape[0]
# link each word to image
for i in range(nbr_words):
word = imwords[i]
# wordid is the word number itself
self.con.execute("insert into imwords(imid,wordid,vocname) values (?,?,?)", (imid,word,self.voc.name))
# store word histogram for image
# use pickle to encode NumPy arrays as strings
self.con.execute("insert into imhistograms(imid,histogram,vocname) values (?,?,?)", (imid,pickle.dumps(imwords),self.voc.name))
def create_tables(self):
""" Create the database tables. """
self.con.execute('create table imlist(filename)')
self.con.execute('create table imwords(imid,wordid,vocname)')
self.con.execute('create table imhistograms(imid,histogram,vocname)')
self.con.execute('create index im_idx on imlist(filename)')
self.con.execute('create index wordid_idx on imwords(wordid)')
self.con.execute('create index imid_idx on imwords(imid)')
self.con.execute('create index imidhist_idx on imhistograms(imid)')
self.db_commit()
class Searcher(object):
def __init__(self,db,voc):
""" Initialize with the name of the database. """
self.con = sqlite3.connect(db)
self.voc = voc
def __del__(self):
self.con.close()
def get_imhistogram(self,imname):
""" Return the word histogram for an image. """
im_id = self.con.execute(
"select rowid from imlist where filename='%s'" % imname).fetchone()
s = self.con.execute(
"select histogram from imhistograms where rowid='%d'" % im_id).fetchone()
# use pickle to decode NumPy arrays from string
return pickle.loads(s[0])
def candidates_from_word(self,imword):
""" Get list of images containing imword. """
im_ids = self.con.execute(
"select distinct imid from imwords where wordid=%d" % imword).fetchall()
return [i[0] for i in im_ids]
def candidates_from_histogram(self,imwords):
""" Get list of images with similar words. """
# get the word ids
words = imwords.nonzero()[0]
# find candidates
candidates = []
for word in words:
c = self.candidates_from_word(word)
candidates+=c
# take all unique words and reverse sort on occurrence
tmp = [(w,candidates.count(w)) for w in set(candidates)]
tmp.sort(key=cmp_to_key(lambda x,y:operator.gt(x[1],y[1])))
tmp.reverse()
# return sorted list, best matches first
return [w[0] for w in tmp]
def query(self,imname):
""" Find a list of matching images for imname. """
h = self.get_imhistogram(imname)
candidates = self.candidates_from_histogram(h)
matchscores = []
for imid in candidates:
# get the name
cand_name = self.con.execute(
"select filename from imlist where rowid=%d" % imid).fetchone()
cand_h = self.get_imhistogram(cand_name)
cand_dist = sqrt( sum( self.voc.idf*(h-cand_h)**2 ) )
matchscores.append( (cand_dist,imid) )
# return a sorted list of distances and database ids
matchscores.sort()
return matchscores
def get_filename(self,imid):
""" Return the filename for an image id. """
s = self.con.execute(
"select filename from imlist where rowid='%d'" % imid).fetchone()
return s[0]
def tf_idf_dist(voc,v1,v2):
v1 /= sum(v1)
v2 /= sum(v2)
return sqrt( sum( voc.idf*(v1-v2)**2 ) )
def compute_ukbench_score(src,imlist):
""" Returns the average number of correct
images on the top four results of queries. """
nbr_images = len(imlist)
pos = zeros((nbr_images,4))
# get first four results for each image
for i in range(nbr_images):
pos[i] = [w[1]-1 for w in src.query(imlist[i])[:4]]
# compute score and return average
score = array([ (pos[i]//4)==(i//4) for i in range(nbr_images)])*1.0
return sum(score) / (nbr_images)
# import PIL and pylab for plotting
from PIL import Image
from pylab import *
def plot_results(src,res):
""" Show images in result list 'res'. """
figure()
nbr_results = len(res)
for i in range(nbr_results):
imname = src.get_filename(res[i])
subplot(1,nbr_results,i+1)
imshow(array(Image.open(imname)))
axis('off')
show()- web演示:
class SearchDemo:
def __init__(self):
# 载入图像列表
self.path = 'first1000/'
#self.path = 'D:/python_web/isoutu/first500/'
self.imlist = [os.path.join(self.path,f) for f in os.listdir(self.path) if f.endswith('.jpg')]
#self.imlist = get_imlist('./first500/')
#self.imlist = get_imlist('E:/python/isoutu/first500/')
self.nbr_images = len(self.imlist)
print (self.imlist)
print (self.nbr_images)
self.ndx = list(range(self.nbr_images))
print (self.ndx)
# 载入词汇
# f = open('first1000/vocabulary.pkl', 'rb')
with open('first1000/vocabulary.pkl','rb') as f:
self.voc = pickle.load(f)
#f.close()
# 显示搜索返回的图像数
self.maxres = 10
#header and footer html
self.header = """
Image search
"""
self.footer = """