Spring入门
目录
1.第一个spring运行实例
2.懒加载(lazy-init)
3.scope(包含属性有:singleton(单例,默认状态),prototype(多例),request,session)
4.init-method,destroy-method
5.属性注入
5.1 set方式注入(注入值类型(value)和引用类型(ref))
5.2 构造函数注入
5.3 复杂类型注入(array,list,set,map,properties)
6.注解配置
6.1 将对象注册到容器
6.2 注解配置-属性注入(值类型注入,引用类型注入)
7.Spring整合Junit单元测试(@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext_annotation.xml"))
8.主配置文件的分包配置()
使用javaEE
新建Dynamic Web Project(记得生成一个web.xml文件。在新建项目时别点finish,而是用两次next,勾选生成web.xml)
导入以下几个jar包
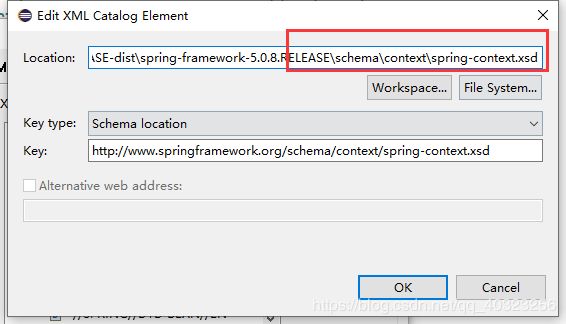
导入spring约束文件:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40323256/article/details/89738089
User.java:
package com.sikiedu.bean;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", password=" + password + "]";
}
}
1.第一个spring运行实例
applicationContext.xml:
测试代码:HelloSpring.java:
package com.sikiedu.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.sikiedu.bean.User;
public class HelloSpring {
@Test
public void Test1(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// User u=(User) ac.getBean("user");
User u=ac.getBean(User.class);
System.out.println(u);
}
}
运行结果:
2.懒加载(lazy-init)
lazy-init="true"时表示“延迟加载”,即创建容器时不加载配置的bean对象,在bean对象被获取的时候才创建
bean对象默认会在容器创建的时候被全部加载出来,如果配置的bean较多,这对硬件的要求较高。所以此时可用延迟加载,不让他一次性加载出来,而是需要bean对象的时候才加载bean对象。
applicationContext.xml:
3.scope(包含属性有:singleton(单例,默认状态),prototype(多例),request,session)
包含属性有:
singleton(单例,默认状态):常用。给对象的scope属性设为singleton后,无论创建多少个这个对象,这些对象都是相同的
prototype(多例):创建的每个对象都是不同的
request:不常用
session:不常用
4.init-method,destroy-method
User.java:
package com.sikiedu.bean;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
public User() {
System.out.println("空参构造方法");
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", password=" + password + "]";
}
public void InitUser(){
System.out.println("初始化对象");
}
public void DestroyUser(){
System.out.println("对象被消除");
}
}
applicationContext.xml:
HelloSpring.java:
@Test
public void Test2(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
User u1=ac.getBean(User.class);
User u2=ac.getBean(User.class);
User u3=ac.getBean(User.class);
System.out.println(u1==u2);
//关闭容器对象ac,就会触发bean的destroymethod
ac.close();
}运行结果:
5.属性注入
5.1 set方式注入(注入值类型(value)和引用类型(ref))
Pet.java:
package com.sikiedu.bean;
public class Pet {
private String petType;
private String color;
public String getPetType() {
return petType;
}
public void setPetType(String petType) {
this.petType = petType;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Pet [petType=" + petType + ", color=" + color + "]";
}
}
User.java:
package com.sikiedu.bean;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Pet pet;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Pet getPet() {
return pet;
}
public void setPet(Pet pet) {
this.pet = pet;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", password=" + password + ", pet=" + pet + "]";
}
}
applicationContext.xml:
HelloSpring.java:
package com.sikiedu.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.sikiedu.bean.User;
public class HelloSpring {
@Test
public void Test1(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
User u=ac.getBean(User.class);
System.out.println(u);
}
}
运行结果:
5.2 构造函数注入
User.java:
package com.sikiedu.bean;
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Pet pet;
public User() {
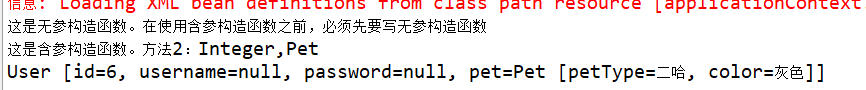
System.out.println("这是无参构造函数。在使用含参构造函数之前,必须先要写无参构造函数");
}
public User(String username, Pet pet) {
System.out.println("这是含参构造函数。方法1:String,Pet");
this.username = username;
this.pet = pet;
}
public User(Integer id, Pet pet) {
System.out.println("这是含参构造函数。方法2:Integer,Pet");
this.id = id;
this.pet = pet;
}
public User(Pet pet,Integer id) {
System.out.println("这是含参构造函数。方法3:Pet,Integer");
this.id = id;
this.pet = pet;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Pet getPet() {
return pet;
}
public void setPet(Pet pet) {
this.pet = pet;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", password=" + password + ", pet=" + pet + "]";
}
}
applicationContext.xml:
HelloSpring.java:
@Test
public void Test2(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
User u=(User) ac.getBean("user1");
System.out.println(u);
}运行结果:
5.3 复杂类型注入(array,list,set,map,properties)
MyCollection.java:
package com.sikiedu.bean;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
public class MyCollection {
private Object[] array;
private List list;
private Set set;
private Map map;
private Properties properties;
public Object[] getArray() {
return array;
}
public void setArray(Object[] array) {
this.array = array;
}
public List getList() {
return list;
}
public void setList(List list) {
this.list = list;
}
public Set getSet() {
return set;
}
public void setSet(Set set) {
this.set = set;
}
public Map getMap() {
return map;
}
public void setMap(Map map) {
this.map = map;
}
public Properties getProperties() {
return properties;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyCollection [array=" + Arrays.toString(array) + ", list=" + list + ", set=" + set + ", map=" + map
+ ", properties=" + properties + "]";
}
}
applicationContext.xml:
111
aaa
333
ccc
老李
25
HelloSpring.java:
@Test
public void Test3(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
MyCollection mc = (MyCollection) ac.getBean("myCollection");
System.out.println(mc);
}运行结果:
6.注解配置
6.1 将对象注册到容器
@Component("user2") //不够精细,因为里面太杂了,什么都有
以后常用的是下面这种,因为分的更细
@Controller() //对应web层
@Service() //对应service层
@Repository() //对应dao层
导入aop包
配置约束
如果已经装了springIDE插件,只需要
如果没有按照springIde插件,添加约束方式参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40323256/article/details/89738089
如果需要按照springIDE插件,安装视频教程:http://www.sikiedu.com/course/267/task/13547/show
User2.java:
package com.sikiedu.bean;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
//
//@Component("user2") //不够精细,因为里面太杂了,什么都有
//@Controller() //对应web层
//@Service() //对应service层
//@Repository() //对应dao层
@Service("user2")
public class User2 {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
public User2() {
System.out.println("这是无参构造函数。在使用含参构造函数之前,必须先要写无参构造函数");
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User2 [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", password=" + password + "]";
}
@PostConstruct()
public void initUser2(){
System.out.println("init User2");
}
@PreDestroy()
public void destroyUser2(){
System.out.println("destroy User2");
}
}
applicationContext_annotation.xml:
HelloSpring.java:
@Test
public void Test4(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext_annotation.xml");
User2 u2= (User2) ac.getBean("user2");
System.out.println(u2);
}运行结果:
6.2 注解配置-属性注入(值类型注入,引用类型注入)
值类型注入:@Value(“”)
引用类型注入: @Autowired() //自动装配。不推荐
@Resource(name="") //手动装配。推荐
Pet.java:
package com.sikiedu.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("pet")
public class Pet {
private String petType;
private String color;
public String getPetType() {
return petType;
}
@Value("金毛")
public void setPetType(String petType) {
this.petType = petType;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
@Value("黄色")
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Pet [petType=" + petType + ", color=" + color + "]";
}
}
User2.java:
package com.sikiedu.bean;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
//
//@Component("user2") //不够精细,因为里面太杂了,什么都有
//@Controller() //对应web层
//@Service() //对应service层
//@Repository() //对应dao层
@Service("user2")
public class User2 {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private Pet pet;
public User2() {
System.out.println("这是无参构造函数。在使用含参构造函数之前,必须先要写无参构造函数");
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
@Value("2")
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
@Value("李疆疆")
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
@Value("2333")
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public Pet getPet() {
return pet;
}
// @Autowired() //自动装配。不推荐
@Resource(name="pet") //手动装配。推荐
public void setPet(Pet pet) {
this.pet = pet;
}
@PostConstruct()
public void initUser2(){
System.out.println("init User2");
}
@PreDestroy()
public void destroyUser2(){
System.out.println("destroy User2");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User2 [id=" + id + ", username=" + username + ", password=" + password + ", pet=" + pet + "]";
}
}
HelloSpring.java:
@Test
public void Test4(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext_annotation.xml");
User2 u2= (User2) ac.getBean("user2");
System.out.println(u2);
}运行结果:
7.Spring整合Junit单元测试(@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext_annotation.xml"))
导入test包![]()
Pet.java:
package com.sikiedu.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("pet")
public class Pet {
private String petType;
private String color;
public String getPetType() {
return petType;
}
@Value("金毛")
public void setPetType(String petType) {
this.petType = petType;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
@Value("黄色")
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Pet [petType=" + petType + ", color=" + color + "]";
}
}
applicationContext_annotation.xml:
test.java:
package com.sikiedu.test;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import com.sikiedu.bean.Pet;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext_annotation.xml")
public class test {
@Resource(name="pet")
private Pet pet;
@Test
public void Test(){
System.out.println(pet);
}
}
运行结果:
8.主配置文件的分包配置(
Pet.java:
package com.sikiedu.bean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("pet")
public class Pet {
private String petType;
private String color;
public String getPetType() {
return petType;
}
@Value("金毛")
public void setPetType(String petType) {
this.petType = petType;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
@Value("黄色")
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Pet [petType=" + petType + ", color=" + color + "]";
}
}
applicationContext_test.xml:
applicationContext_annotation.xml:
test.java:
package com.sikiedu.test;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
import com.sikiedu.bean.Pet;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext_test.xml")
public class test {
@Resource(name="pet")
private Pet pet;
@Test
public void Test(){
System.out.println(pet);
}
}
运行结果: