并查集---Union-Find 算法
文章目录
- 基本概念
- 200. 岛屿数量
- 990. 等式方程的可满足性
- 128. 最长连续序列
- 130.被围绕的区域
- 547.朋友圈
- 721.账户合并
- 839.相似字符串组
基本概念
Union-Find 算法主要需要实现这两个 API:
class Union-Find {
/* 将 p 和 q 连接 */
public void union(int p, int q);
/* 判断 p 和 q 是否连通 */
public boolean connected(int p, int q);
/* 返回图中有多少个连通分量 */
public int count();
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if (rootP == rootQ)
return;
// 将两棵树合并为一棵
parent[rootP] = rootQ;
// parent[rootQ] = rootP 也一样
count--; // 两个分量合二为一
}
/* 返回某个节点 x 的根节点 */
private int find(int x) {
// 根节点的 parent[x] == x
while (parent[x] != x)
x = parent[x];
return x;
}
/* 返回当前的连通分量个数 */
public int count() {
return count;
}
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
return rootP == rootQ;
}
- 优化后的完整代码
class UF {
// 连通分量个数
private int count;
// 存储一棵树
private int[] parent;
// 记录树的“重量”
private int[] size;
public UF(int n) {
this.count = n;
parent = new int[n];
size = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if (rootP == rootQ)
return;
// 小树接到大树下面,较平衡
if (size[rootP] > size[rootQ]) {
parent[rootQ] = rootP;
size[rootP] += size[rootQ];
} else {
parent[rootP] = rootQ;
size[rootQ] += size[rootP];
}
count--;
}
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
return rootP == rootQ;
}
private int find(int x) {
while (parent[x] != x) {
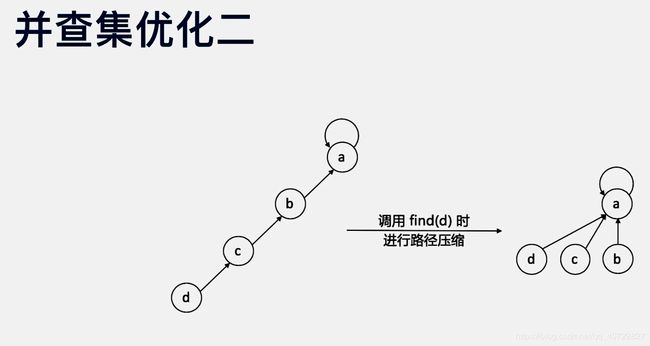
// 进行路径压缩
parent[x] = parent[parent[x]];
x = parent[x];
}
return x;
}
public int count() {
return count;
}
}
算法的关键点有 3 个:
- 1、用 parent 数组记录每个节点的父节点,相当于指向父节点的指针,所以 parent 数组内实际存储着一个森林(若干棵多叉树)。
- 2、用 size 数组记录着每棵树的重量,目的是让 union 后树依然拥有平衡性,而不会退化成链表,影响操作效率。
- 3、在 find 函数中进行路径压缩,保证任意树的高度保持在常数,使得 union 和 connected API 时间复杂度为 O(1)。
200. 岛屿数量
给定一个由 '1'(陆地)和 '0'(水)组成的的二维网格,计算岛屿的数量。一个岛被水包围,并且它是通过水平方向或垂直方向上相邻的陆地连接而成的。你可以假设网格的四个边均被水包围。
示例 1:
输入:
11110
11010
11000
00000
输出: 1
示例 2:
输入:
11000
11000
00100
00011
输出: 3
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int rows = grid.length;
if (rows == 0) {
return 0;
}
int cols = grid[0].length;
int size = rows * cols;
// 两个方向的方向向量(理解为向下和向右的坐标偏移)
int[][] directions = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}};
// +1 是认为虚拟的水域
UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind(size + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == '1') {
for (int[] direction : directions) {
int newX = i + direction[0];
int newY = j + direction[1];
if (newX < rows && newY < cols && grid[newX][newY] == '1') {
unionFind.union(cols * i + j, cols * newX + newY);
}
}
} else {
// 如果不是陆地,所有的水域和一个虚拟的水域连接
unionFind.union(cols * i + j, size);
}
}
}
// 减去那个一开始多设置的虚拟的水域
return unionFind.count - 1;
}
class UnionFind {
private int[] parent;
private int count;
public UnionFind(int n) {
this.count = n;
parent = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
//返回索引为 p 的元素的根结点
public int find(int p) {
// 在 find 的时候执行路径压缩
while (p != parent[p]) {
// 两步一跳完成路径压缩,这里是「隔代压缩」
// 说明:「隔代压缩」和「按秩合并」选择一个实现即可,「隔代压缩」的代码量少,所以选它
parent[p] = parent[parent[p]];
p = parent[p];
}
return p;
}
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
return pRoot == qRoot;
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if (pRoot == qRoot) {
return;
}
parent[qRoot] = pRoot;
// 每次 union 以后,连通分量减 1
count--;
}
}
}
990. 等式方程的可满足性
class Solution {
int[] parent = new int[26];
public boolean equationsPossible(String[] equations) {
for(int i = 0;i<26;i++){
parent[i] = i;
}
for(String s:equations){
if(s.charAt(1)=='='){
union(s.charAt(0),s.charAt(3));
}
}
for(String s:equations){
if(s.charAt(1)=='!'){
if(find(s.charAt(0))==find(s.charAt(3))){
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
public void union(int index1,int index2){
parent[find(index1)] = find(index2);
}
public int find(int index){
int x = index - 'a';
while(x!=parent[x]){
parent[x] = parent[parent[x]];
x = parent[x];
}
return x;
}
}
128. 最长连续序列
- 原题地址
class Solution {
public int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) {
if(nums==null||nums.length==0) return 0;
UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(nums);
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(uf.fatherMap.containsKey(nums[i]-1)){
uf.union(nums[i]-1,nums[i]);
}
}
return uf.max;
}
public class UnionFind{
int max;
HashMap<Integer,Integer> fatherMap;
HashMap<Integer,Integer> sizeMap;
public UnionFind(int[] nums){
max = 1;//处理nums中只有一个元素的情况下,默认为1
fatherMap = new HashMap<>();
sizeMap = new HashMap<>();
for(int val: nums){
fatherMap.put(val,val);
sizeMap.put(val,1);
}
}
public int findFather(int val){
int father = fatherMap.get(val);
if(father != val){
father = findFather(father);
}
fatherMap.put(val,father);
return father;
}
public void union(int a,int b){
int aFather = findFather(a);
int bFather = findFather(b);
if(aFather != bFather){
int aSize = sizeMap.get(aFather);
int bSize = sizeMap.get(bFather);
if(aSize<=bSize){
fatherMap.put(aFather,bFather);
sizeMap.put(bFather,aSize+bSize);
}else{
fatherMap.put(bFather,aFather);
sizeMap.put(aFather,aSize+bSize);
}
max = Math.max(max,aSize + bSize);
}
}
}
}
130.被围绕的区域
547.朋友圈
721.账户合并
839.相似字符串组
你知道的越多,你不知道的越多。
有道无术,术尚可求,有术无道,止于术。
如有其它问题,欢迎大家留言,我们一起讨论,一起学习,一起进步