java-异常处理
异常处理
- 什么是异常
1.定义
导致程序的正常流程被中断的事件,叫做异常。
2.实例
文件不存在异常
比如要打开d盘的LOL.exe文件,这个文件是有可能不存在的
Java中通过 new FileInputStream(f) 试图打开某文件,就有可能抛出文件不存在异常FileNotFoundException
如果不处理该异常,就会有编译错误 。

其他常见异常
NullPointerException 空指针异常
ArithmeticException 除数为零
ClassCastException 类型转换异常
OutOfIndexException 数组下标越界异常
ParseException 解析异常,日期字符串转换为日期对象的时候,有可能抛出的异常
OutOfMemoryError 内存不足
package exception;
public class exception_text {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// NullPointerException 空指针异常
String s = null;
System.out.println(s.length());
// ArithmeticException 除数为零
int i = 1,j = 0,m;
System.out.println(m=i/j);
// ClassCastException 类型转换异常
System.out.println("运行时异常,大多数发生在强制转换以及SQL映射异常时等才有");
// OutOfIndexException 数组下标越界异常
char[] cs = new char[10];
cs[11] = 'o';
// ParseException 解析异常,日期字符串转换为日期对象的时候,有可能抛出的异常
// OutOfMemoryError 内存不足
}
}
- 处理
1.常见手段:try catch finally throws
2.try catch
package exception;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class TestException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f= new File("d:/LOL.exe");
try{
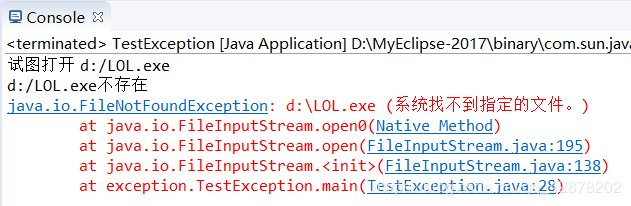
System.out.println("试图打开 d:/LOL.exe");
new FileInputStream(f);
System.out.println("成功打开");
}
catch(FileNotFoundException e){
System.out.println("d:/LOL.exe不存在");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package exception;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class TestException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f= new File("d:/LOL.exe");
try{
System.out.println("试图打开 d:/LOL.exe");
new FileInputStream(f);
System.out.println("成功打开");
}
catch(Exception e){
System.out.println("d:/LOL.exe不存在");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
4.多异常捕捉办法
解决办法之一:抛出文件不存在异常 FileNotFoundException 和 解析异常ParseException,分别进行catch。
package exception;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class TestException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f = new File("d:/LOL.exe");
try {
System.out.println("试图打开 d:/LOL.exe");
new FileInputStream(f);
System.out.println("成功打开");
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date d = sdf.parse("2016/06-03");
System.out.println(d);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("d:/LOL.exe不存在");
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (ParseException e) {
System.out.println("日期格式解析错误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
注:两个都产生异常,只显示了一个异常,需要先处理先出现的异常。
解决办法之二:把多个异常,放在一个catch里统一捕捉
这种方式从 JDK7开始支持,好处是捕捉的代码更紧凑,不足之处是,一旦发生异常,不能确定到底是哪种异常,需要通过instanceof 进行判断具体的异常类型。
package exception;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class TestException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f = new File("d:/LOL.exe");
try {
System.out.println("试图打开 d:/LOL.exe");
new FileInputStream(f);
System.out.println("成功打开");
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date d = sdf.parse("2016/06-03");
} catch (FileNotFoundException | ParseException e) {
if (e instanceof FileNotFoundException)
System.out.println("d:/LOL.exe不存在");
if (e instanceof ParseException)
System.out.println("日期格式解析错误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

5.finally:无论是否出现异常,finally中的代码都会被执行。
package exception;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class TestException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f= new File("d:/LOL.exe");
try{
System.out.println("试图打开 d:/LOL.exe");
new FileInputStream(f);
System.out.println("成功打开");
}
catch(FileNotFoundException e){
System.out.println("d:/LOL.exe不存在");
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally{
System.out.println("无论文件是否存在, 都会执行的代码");
}
}
}
6.throws
考虑如下情况:
主方法调用method1
method1调用method2
method2中打开文件
method2中需要进行异常处理
但是method2不打算处理,而是把这个异常通过throws抛出去
那么method1就会接到该异常。 处理办法也是两种,要么是try catch处理掉,要么也是抛出去。
method1选择本地try catch住 一旦try catch住了,就相当于把这个异常消化掉了,主方法在调用method1的时候,就不需要进行异常处理了
package exception;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class TestException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
method1();
}
private static void method1() {
try {
method2();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void method2() throws FileNotFoundException {
File f = new File("d:/LOL.exe");
System.out.println("试图打开 d:/LOL.exe");
new FileInputStream(f);
System.out.println("成功打开");
}
}
- throws 出现在方法声明上,而throw通常都出现在方法体内。
- throws 表示出现异常的一种可能性,并不一定会发生这些异常;throw则是抛出了异常,执行throw则一定抛出了某个异常对象。
8.练习
假设有一个方法 public int method(), 会返回一个整数
在这个方法中有try catch 和 finally.
try 里返回 1
catch 里 返回 2
finally 里 返回3
那么,这个方法到底返回多少?

结果是3,但不代表没执行过try catch(如果不处理,编译器,就不让你通过),所以带返回类型的绝不应该在finally中带有返回值,否则try catch将毫无意义。
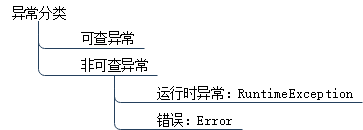
1.可查异常
可查异常即必须进行处理的异常,要么try catch住,要么往外抛,谁调用,谁处理,比如 FileNotFoundException。
package exception;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
public class TestException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f= new File("d:/LOL.exe");
try{
System.out.println("试图打开 d:/LOL.exe");
new FileInputStream(f);
System.out.println("成功打开");
}
catch(FileNotFoundException e){
System.out.println("d:/LOL.exe不存在");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.非可查异常
运行时异常:RuntimeException
不是必须进行try catch的异常
常见运行时异常:
除数不能为0异常:ArithmeticException
下标越界异常:ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
空指针异常:NullPointerException
在编写代码的时候,依然可以使用try catch throws进行处理,与可查异常不同之处在于,即便不进行try catch,也不会有编译错误
Java之所以会设计运行时异常的原因之一,是因为下标越界,空指针这些运行时异常太过于普遍,如果都需要进行捕捉,代码的可读性就会变得很糟糕。
package exception;
public class TestException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//任何除数不能为0:ArithmeticException
int k = 5/0;
//下标越界异常:ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
int j[] = new int[5];
j[10] = 10;
//空指针异常:NullPointerException
String str = null;
str.length();
}
}

错误:Error
错误Error,指的是系统级别的异常,通常是内存用光了
在默认设置下,一般java程序启动的时候,最大可以使用16m的内存
如例不停的给StringBuffer追加字符,很快就把内存使用光了。抛出OutOfMemoryError,与运行时异常一样,错误也是不要求强制捕捉的
package exception;
public class TestException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sb =new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE; i++) {
sb.append('a');
}
}
}
3.总结
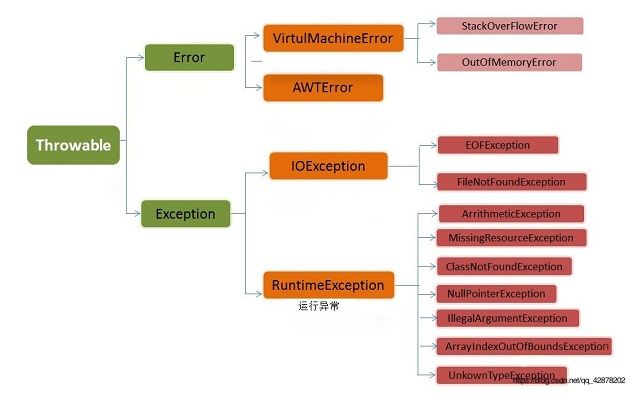
总体上异常分三类:
- Throwable
1.Throwable类
Throwable是类,Exception和Error都继承了该类
所以在捕捉的时候,也可以使用Throwable进行捕捉
如图: 异常分Error和Exception
Exception里又分运行时异常和可查异常。
package exception;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
public class TestException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f = new File("d:/LOL.exe");
try {
new FileInputStream(f);
//使用Throwable进行异常捕捉
} catch (Throwable t) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
t.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.练习
在方法声明上,可以抛出指定的异常,比如FileNotFoundException
那么能否抛出Throwable这个类?
这个方法的调用者又该如何处理?
package exception;
public class exception_test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
method();
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("出现异常,请检查");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void method() throws Throwable{
int m = 1/0;
System.out.println(m);
}
}
注:可以抛出Throwable,因为是父类,但是catch方法也要捕捉 Throwable。
- 自定义异常
1.创建-抛出自定义异常
package charactor;
public class Hero {
public String name;
protected float hp;
public void attackHero(Hero h) throws EnemyHeroIsDeadException{
if(h.hp == 0){
throw new EnemyHeroIsDeadException(h.name + " 已经挂了,不需要施放技能" );
}
}
public String toString(){
return name;
}
class EnemyHeroIsDeadException extends Exception{
public EnemyHeroIsDeadException(){
}
public EnemyHeroIsDeadException(String msg){
super(msg);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hero garen = new Hero();
garen.name = "盖伦";
garen.hp = 616;
Hero teemo = new Hero();
teemo.name = "提莫";
teemo.hp = 0;
try {
garen.attackHero(teemo);
} catch (EnemyHeroIsDeadException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
//e.getMessage()是父类的父类(Throwable)的方法,返回的是有参构造方法的参数(String类型)
//简单说就是e.getMessage()得到有参构造方法的参数,所以上面有throw new EnemyHeroIsDeadException(h.name + " 已经挂了,不需要施放技能" );
System.out.println("异常的具体原因:"+e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
2.练习
对MyStringBuffer的插入和删除方法中的边界条件判断,用抛出异常来解决
例: insert(int pos, String b) , 当pos 是负数的时候,抛出自定义异常
需要实现自定义两种异常
IndexIsNagetiveException 下标为负异常
IndexIsOutofRangeException 下标超出范围异常
以下是需要调用这些异常的场景:
pos<0
抛出 IndexIsNagetiveException
pos>length
抛出 IndexIsOutofRangeException
null==b
抛出 NullPointerException
start<0
抛出 IndexIsNagetiveException
start>length
抛出 IndexIsOutofRangeException
end<0
抛出 IndexIsNagetiveException
end>length
抛出 IndexIsOutofRangeException
start>=end
抛出 IndexIsOutofRangeException
注意: 接口IStringBuffer中声明的方法需要抛出异常
public class MyStringBuffer {
int capacity = 16;
int length = 0;
char[] value;
public MyStringBuffer(){
value = new char[capacity];
}
//有参构造方法
public MyStringBuffer(String str){
this();
if(null==str)
return;
if(capacity<str.length()){
capacity = value.length*2;
value=new char[capacity];
}
if(capacity>=str.length())
System.arraycopy(str.toCharArray(), 0, value, 0, str.length());
length = str.length();
}
public void insert(int pos, char b) throws Exception {
insert(pos,String.valueOf(b));
}
public void delete(int start) throws Exception {
delete(start,length);
}
public int length() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return length;
}
public String toString(){
char[] realValue = new char[length];
System.arraycopy(value, 0, realValue, 0, length);
return new String(realValue);
}
class IndexIsNagetiveException extends Exception {
public IndexIsNagetiveException() {
}
public IndexIsNagetiveException(String msg) {
super (msg);
}
}
//通过构造方法自定义异常
class IndexIsOutofRangeException extends Exception{
public IndexIsOutofRangeException() {
}
public IndexIsOutofRangeException(String s) {
super (s);
}
}
public void delete(int start, int end) throws Exception{
//边界条件判断
if(start<0) {
throw new IndexIsNagetiveException("下标为负异常");
}
if(start>length) {
throw new IndexIsOutofRangeException("下标超出范围异常");
}
if(end<0) {
throw new IndexIsNagetiveException("下标为负异常");
}
if(end>length) {
throw new IndexIsOutofRangeException("下标超出范围异常");
}
if(start>=end) {
throw new IndexIsOutofRangeException("下标超出范围异常");
}
System.arraycopy(value, end, value, start, length- end);
length-=end-start;
}
public void insert(int pos, String b) throws Exception{
//边界条件判断
if(pos<0) {
throw new IndexIsNagetiveException("下标为负异常");
}
if(pos>length) {
throw new IndexIsOutofRangeException("下标超出范围异常");
}
if(null==b) {
throw new NullPointerException("为空");
}
//扩容
while(length+b.length()>capacity){
capacity = (int) ((length+b.length())*1.5f);
char[] newValue = new char[capacity];
System.arraycopy(value, 0, newValue, 0, length);
value = newValue;
}
char[] cs = b.toCharArray();
//先把已经存在的数据往后移
System.arraycopy(value, pos, value,pos+ cs.length, length-pos);
//把要插入的数据插入到指定位置
System.arraycopy(cs, 0, value, pos, cs.length);
length = length+cs.length;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyStringBuffer sb = new MyStringBuffer("there ligtht");
System.out.println(sb);
try {
sb.insert(-4, "let ");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("异常的具体原因:"+e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(sb);
try {
sb.delete(0,44);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("异常的具体原因:"+e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
- 异常综合练习
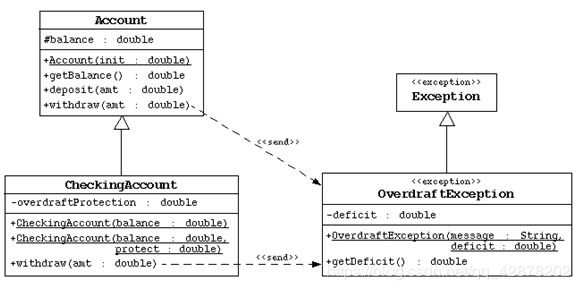
这是一个类图
Account类: 银行账号
属性: balance 余额
方法: getBalance() 获取余额
方法: deposit() 存钱
方法: withdraw() 取钱
OverdraftException: 透支异常,继承Exception
属性: deficit 透支额

类: CheckingAccount 支票账户,具备透支额度,继承Account
属性:overdraftProtection 透支额度
package exception;
public class BankTest{
public static void main(String [] args) {
Account A = new Account(10000);
CheckingAccount CA = new CheckingAccount(10000,20000);
// 银行账户
try {
// 取现金额
int w1 = 21000;
//抛出异常后,第二句就不执行了
System.out.println("该银行账户成功取现" + A.withdraw(w1) + "元");
System.out.println("余额为" + A.getBalance() + "元");
} catch (OverdraftException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
if (e.getDeficit() > 0) {
System.out.println("超出余额" + e.getDeficit() + "元");
}
}
System.out.println("\n\n");
// 支票账户
try {
// 取现金额
int w2 = 21000;
System.out.println("该支票账户成功取现" + CA.withdraw(w2) + "元");
System.out.println("余额为" + CA.getBalance() + "元");
System.out.println("总额度" + CA.getOverdraftProtection() + "元");
} catch (OverdraftException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
if (e.getDeficit() > 0) {
System.out.println("超出额度" + e.getDeficit() + "元");
}
}
//try语句有异常,执行catch里的语句,catch的语句来源于方法的判断,根据条件选取出相应的语句
//try单条语句异常处理后,进行对第二条进行处理。
}
}
class Account {
protected double balance;
// 构造方法
public Account(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
// 获取余额的方法
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
// 存款方法
public void deposit(double money) throws OverdraftException {
if (money >= 0) {
balance += money;
} else {
throw new OverdraftException("存入金额不能为负数");
}
}
// 取现方法
public double withdraw(double money) throws OverdraftException {
if (money >= 0) {
double temp = balance - money;
if (temp >= 0) {
balance = temp;
return money;
} else {
throw new OverdraftException("余额不足", -temp);
}
} else {
throw new OverdraftException("取现金额不能为负数");
}
}
}
class CheckingAccount extends Account {
private double overdraftProtection;
// 构造方法
public CheckingAccount(double balance) {
super(balance);
}
public CheckingAccount(double balance, double overdraftProtection) {
super(balance);
this.overdraftProtection = overdraftProtection;
}
// 获取额度
public double getOverdraftProtection(){
return overdraftProtection;
}
// 更改额度
public void setOverdraftProtection(double overdraftProtection) {
this.overdraftProtection = overdraftProtection;
}
// 重写支票账户的取现方法
public double withdraw(double money) throws OverdraftException {
if (money >= 0) {
double temp = balance - money;
if (temp >= 0) {
balance = temp;
return money;
} else if (temp >= -overdraftProtection && temp < 0) {
balance = temp;
System.out.println("账户已透支" + -temp + "元,透支额度剩余" + (overdraftProtection + temp) + "元");
return money;
} else {
throw new OverdraftException("额度不足", -(overdraftProtection + temp));
}
} else {
throw new OverdraftException("取现金额不能为负数");
}
}
}
class OverdraftException extends Exception {
private double deficit;
public OverdraftException () {
}
public OverdraftException (String message) {
super(message);
}
public OverdraftException (String message, double deficit) {
super(message);
this.deficit = deficit;
}
public double getDeficit() {
return deficit;
}
}

注:
Account A = new Account(10000);
CheckingAccount CA = new CheckingAccount(10000,20000);两者分开理解
思路:一个自定义异常,一个取钱类,和一个可以透支类(继承取钱类)