类中类
1. 反射介绍
反射这一概念最早由编程开发人员Smith在1982年提出,主要指应用程序访问、检测、修改自身状态与行为的能力。这一概念的提出立刻吸引了编程界的极大关注,各种研究工作随之展开,随之而来引发编程革命,出现了多种支持反射机制的面向对象语言。
在计算机科学领域,反射是指一类能够自我描述和自控制的应用。在Java编程语言中,反射是一种强有力的工具,是面向抽象编程一种实现方式,它能使代码语句更加灵活,极大提高代码的运行时装配能力。
2. 反射在java中的体现
Java反射说的是在运行状态中,对于任何一个类,我们都能够知道这个类有哪些方法和属性。对于任何一个对象,我们都能够对它的方法和属性进行调用。我们把这种动态获取对象信息和调用对象方法的功能称之为反射机制。案例:
和https://programmer.help/blogs/reflection-and-dynamic-agent-in-mybatis.html
意味着搞懂了反射,也就搞明白了大部分框架,且务必搞清楚:是技术难还是纷繁琐杂还是功能模块多导致工作量大,性质是不一样的
直觉告诉我,技术难占比很小,5~10%的比例就已经很不错了,是繁琐和模块多工作量的问题,几十上百上千的模块开发
2.1 获取Class对象
反射其实是获取类的字节码文件(在JVM的世界里只会有有一份,不管以不同的方式加载多少次),也就是.class文件,那么我们就可以通过Class这个对象进行获取,有三种方式:通过类名的class属性、对象的getClass()方法和java.lang.Class的静态方法forName(“类全路径”)
输出效果:
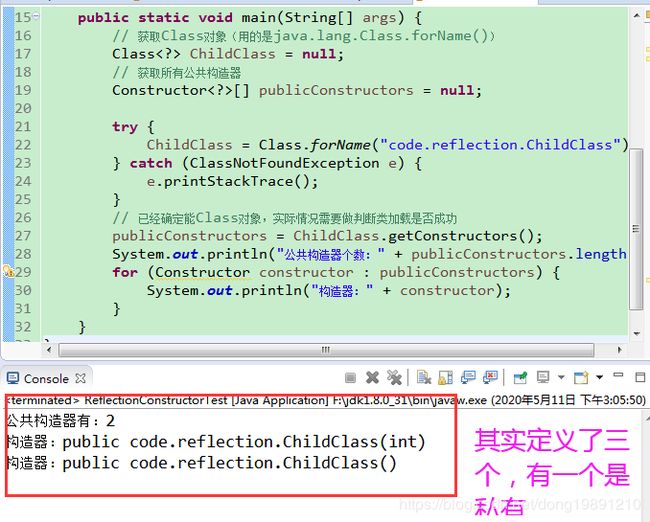
2.2 获取类所有的公共public构造器
可用getConstructors()返回类的所有公共构造器
输出效果:
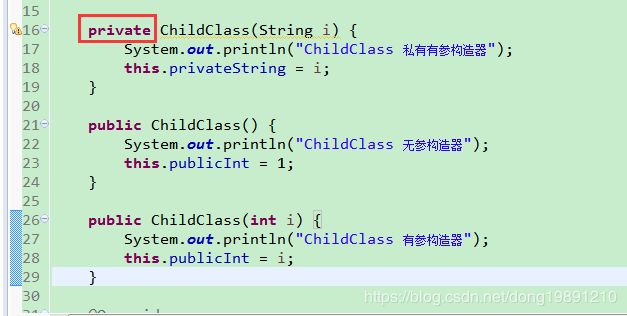
源文件的构造器:
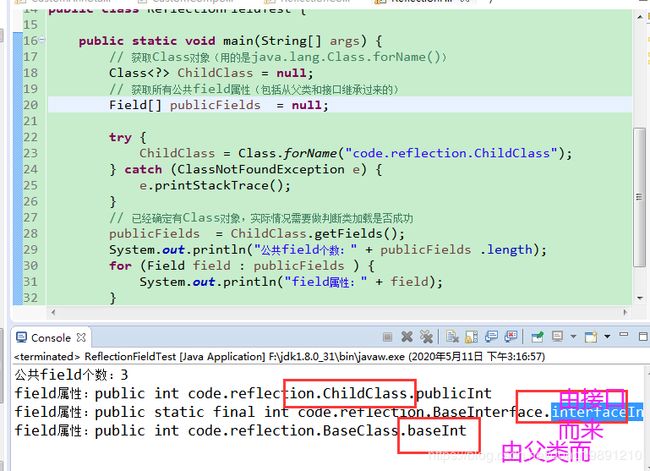
2.3 获取类所有的公共public field属性
可用getFields()返回类的所有公共属性(包括从父类和接口继承过来的)
输出效果:
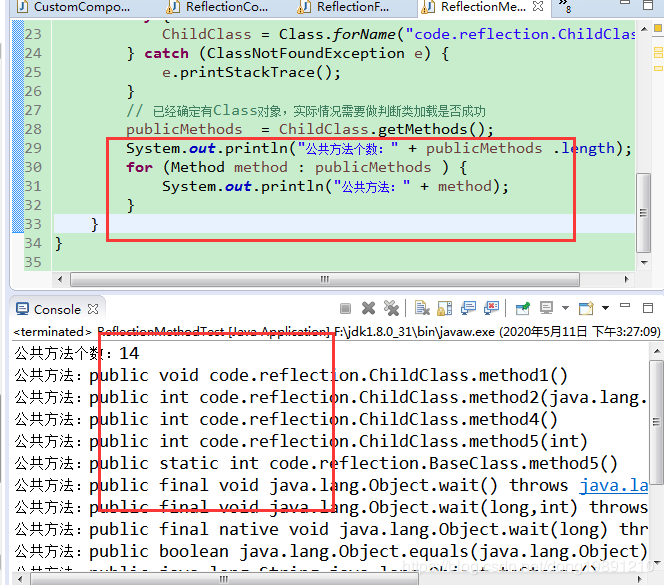
2.4 获取类所有的公共public方法
可用getMethods()返回类的所有公共方法(包括从父类和接口继承过来的)
输出:
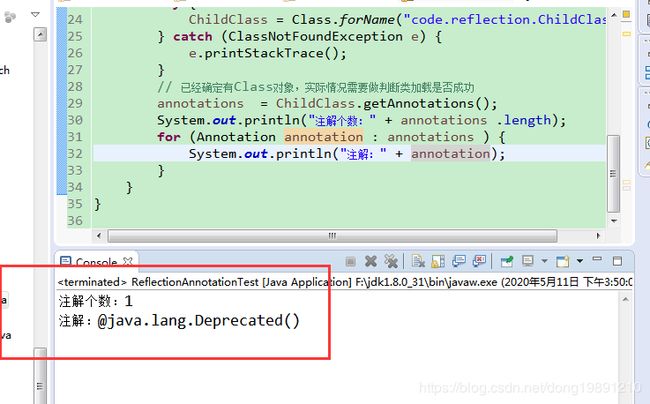
2.5 获取类所有的注解
可用getAnnotations()返回类的所有注解
测试代码:
输出效果:
3. 如何使用通过反射得到构造器、field属性、方法、注解
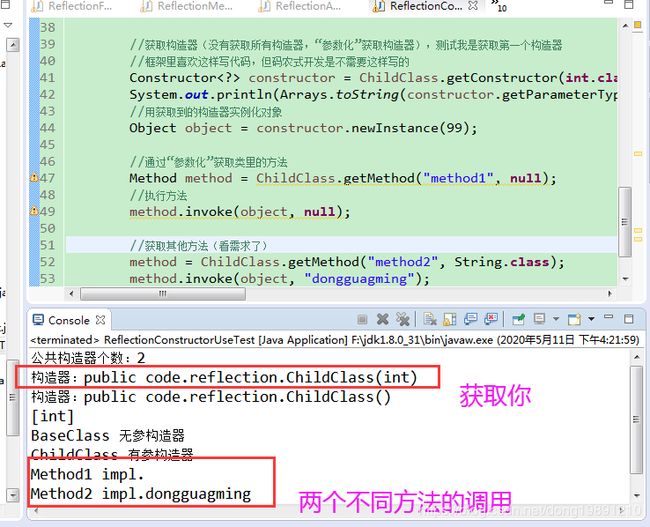
3.1 使用构造器
既可以一次性获取所有构造器,不过也可以单独参数化获取构造器
输出效果:
3.2 使用方法
既可以一次性获取所有方法,不过也可以单独参数化获取方法
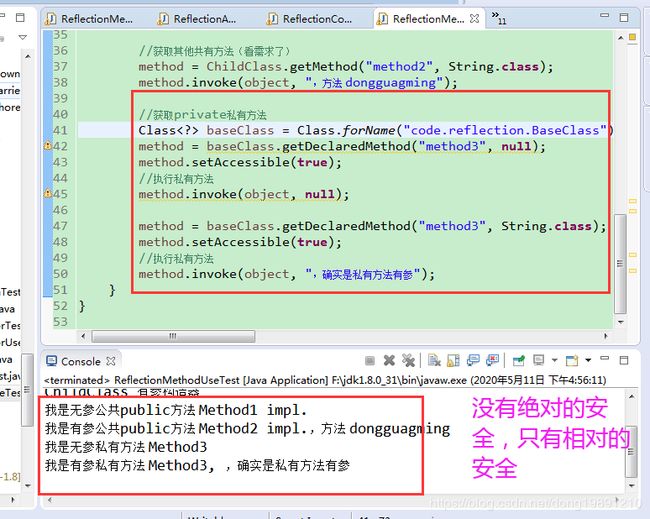
3.2.1 获取公有方法(参数化和非参数化)
3.2.2 获取私有方法(无参和有参数化)
最终输出:
3.3 使用field属性
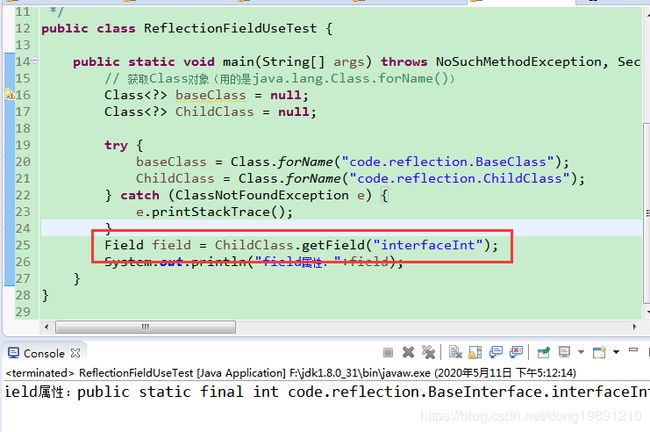
3.3.1 参数化获取某个具体的field属性
输出:
3.3.2 获取field属性的从属类或接口
输出:
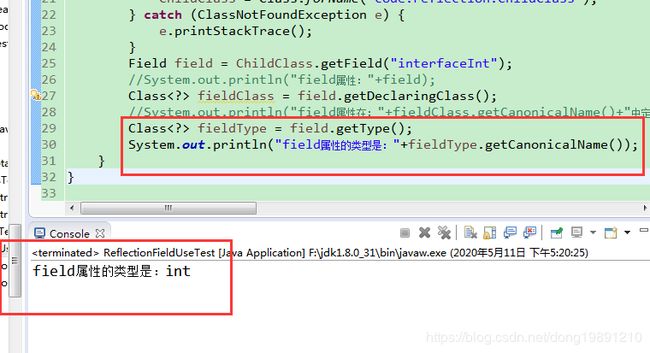
3.3.3 获取field属性的类
只写了核心代码“:
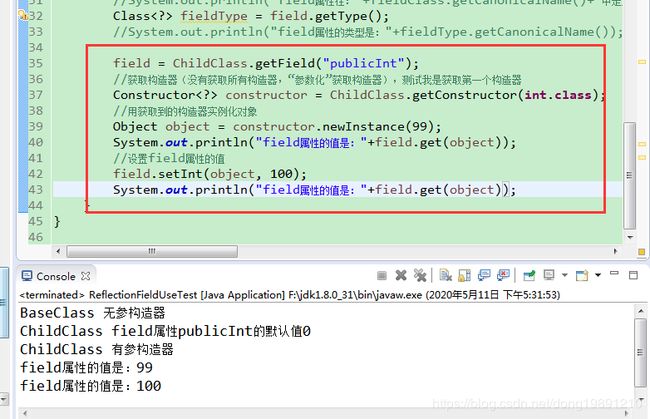
3.3.4 设置和获取公用public field属性的值
只写了核心代码“:
输出:
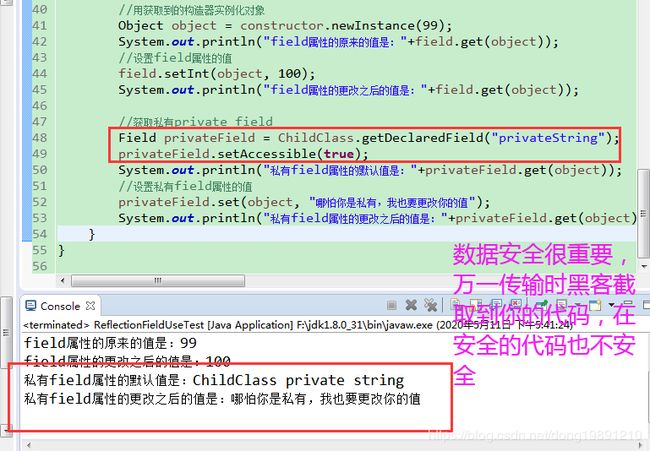
3.3.5 设置和获取私有private field属性的值
只写了核心代码“:
输出:
3.4 使用注解
不细分了,要不然又写不完了
定义注解
具体类中使用,只写核心代码:
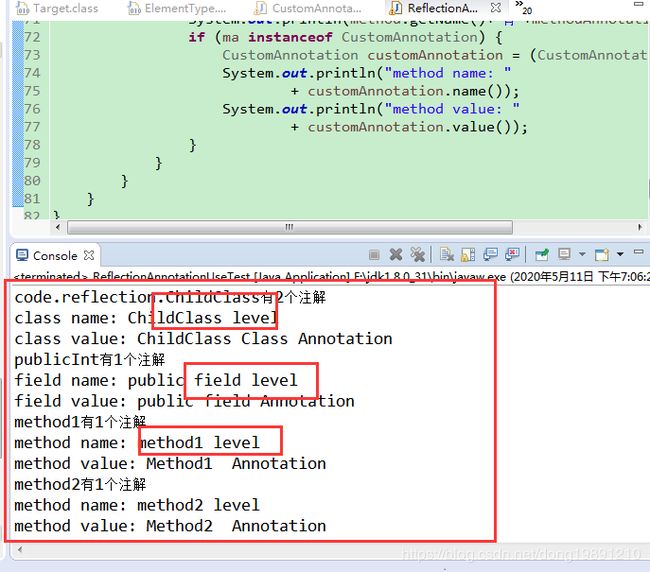
测试代码:
出结果:
总结: 构造器、方法、注解,一句话反射很重要!!!
参考:
0 java反射 : https://baike.baidu.com/item/JAVA%E5%8F%8D%E5%B0%84%E6%9C%BA%E5%88%B6/6015990
1. Interface AnnotatedElement
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/reflect/AnnotatedElement.html
2. Reflection and Dynamic Agent in Mybatis
https://programmer.help/blogs/reflection-and-dynamic-agent-in-mybatis.html
3. Understanding Java Annotations – Java @annotations Tutorial
https://crunchify.com/understanding-java-annotation-annotation-examples/
4. Java Reflection Tutorial http://tutorials.jenkov.com/java-reflection/index.html
5. Java Reflection Example Tutorial https://www.journaldev.com/1789/java-reflection-example-tutorial
6. The Reflection API https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/reflect/index.html