RabbitMQ 实例(一对一、一对多、多对多、多对一)
原理就不说了,自己先百度。 我们不做理论高手, 我们要实战。
现在网上的博客太混乱了,有些贴出来完全是错误的,很容易误导我们理解。
我这里主要是分享代码,让你们在电脑上跑起来。
在看下面之前,先看我上一篇博客 https://blog.csdn.net/shushugood/article/details/81076917, 在本地把自己的rabbitmq服务先跑起来把。
目录结构如下:
1.我们先看pom.xml
4.0.0
com.broadtech
springboot-rabbitmq
0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
1.4.0.RELEASE
1.8
UTF-8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
true
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-actuator
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-amqp
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-tomcat
provided
org.apache.tomcat.embed
tomcat-embed-jasper
provided
com.rabbitmq
amqp-client
3.6.5
2.看 application.properties
spring.application.name=springboot-rabbitmq
spring.rabbitmq.host=127.0.0.1
spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
spring.rabbitmq.username=mengl
spring.rabbitmq.password=123456
#spring.rabbitmq.publisher-confirms=true
#spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host=/
3.Application.java
package com.rabbit;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
public class Application {
public final static String HELLO = "helloQueue1";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@Bean
public Queue helloQueue() {
return new Queue(Application.HELLO); // 1
}
@Bean
public Queue userQueue() {
return new Queue("user");
}
}
4. 下面是生产 sender 和消费 receiver
4.1 HelloReceiver1.java
package com.rabbit.hello;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.rabbit.Application;
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = Application.HELLO) //3
public class HelloReceiver1 {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String hello) {
System.out.println("Receiver1 : " + hello);
}
}4.2 HelloReceiver2.java
package com.rabbit.hello;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.rabbit.Application;
@Component
//@RabbitListener(queues = Application.HELLO)
public class HelloReceiver2 {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String hello) {
System.out.println("Receiver2 : " + hello);
}
}4.3 HelloSender1.java
package com.rabbit.hello;
import java.util.Date;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.rabbit.Application;
@Component
public class HelloSender1 {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void send(String msg) {
String sendMsg = "hello孟梁,你在测试MQ " + new Date();
System.out.println("Sender1 : " + sendMsg);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(Application.HELLO, sendMsg); // 4
}
}4.4 HelloSender2.java
package com.rabbit.hello;
import java.util.Date;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import com.rabbit.Application;
@Component
public class HelloSender2 {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void send(String msg) {
String sendMsg = msg + new Date();
System.out.println("Sender2 : " + sendMsg);
this.rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(Application.HELLO, sendMsg);
}
}5. 下面是controller
5.1 RabbitTest.java
package com.rabbit.controller;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.rabbit.hello.HelloSender1;
import com.rabbit.hello.HelloSender2;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/rabbit")
public class RabbitTest {
@Autowired
private HelloSender1 helloSender1;
@Autowired
private HelloSender2 helloSender2;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
helloSender1.send("a");
return "/rabbit/hello的调用";
}
/**
* 单生产者-多消费者
*/
@GetMapping("/oneToMany")
public void oneToMany() {
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
System.out.println("执行"+i);
helloSender1.send("hellomsg:"+i);
}
}
/**
* 多生产者-多消费者
*/
@GetMapping("/manyToMany")
public void manyToMany() {
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
helloSender1.send("hellomsg:"+i);
helloSender2.send("hellomsg:"+i);
}
}
}
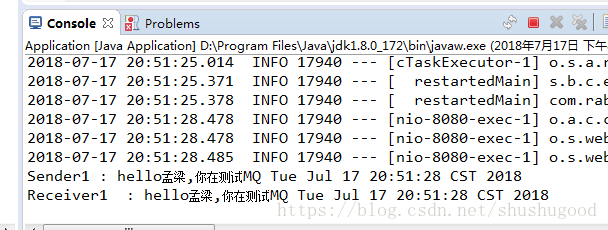
6.测试页面 + 控制台显示。
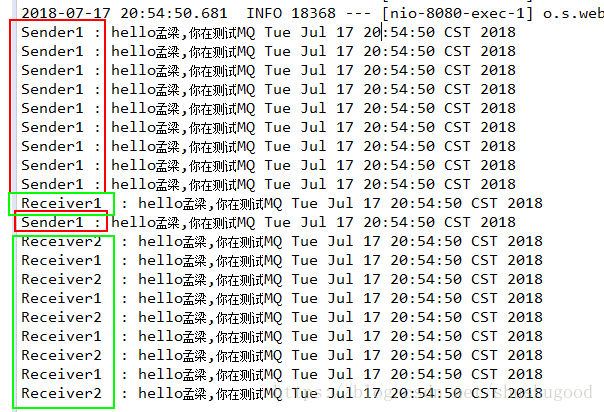
一对一:
一对多: ( 即1个生产者提供10个棒棒糖,2个消费者平均每人分5个棒棒糖)
http://localhost:8080/rabbit/oneToMany
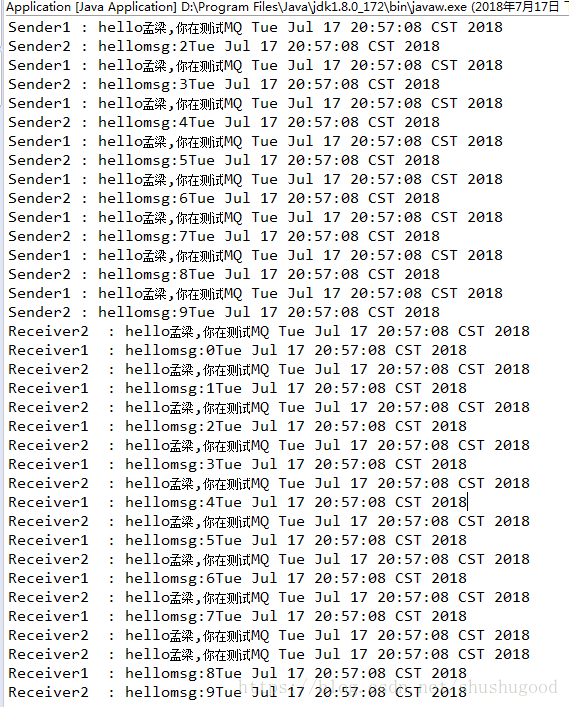
多对多: (生产者2个,消费者2个, 都是平均分配)
多对一:(省略。同上)
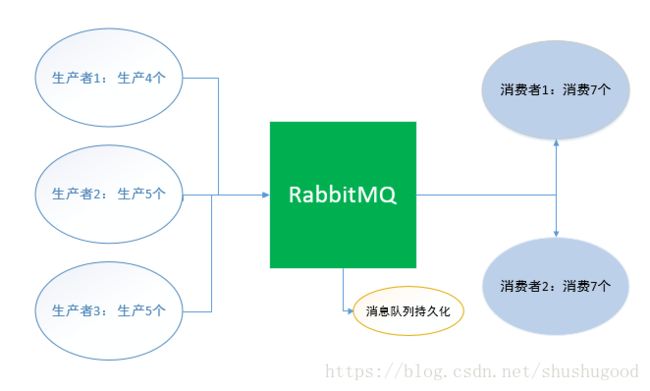
总结: