mybatais架构原理
一、架构整体设计
功能架构讲解:
我们把Mybatis的功能架构分为三层:
(1)API接口层:提供给外部使用的接口API,开发人员通过这些本地API来操纵数据库。接口层一接收到调用请求就会调用数据处理层来完成具体的数据处理。
(2)数据处理层:负责具体的SQL查找、SQL解析、SQL执行和执行结果映射处理等。它主要的目的是根据调用的请求完成一次数据库操作。
(3)基础支撑层:负责最基础的功能支撑,包括连接管理、事务管理、配置加载和缓存处理,这些都是共用的东西,将他们抽取出来作为最基础的组件。为上层的数据处理层提供最基础的支撑。
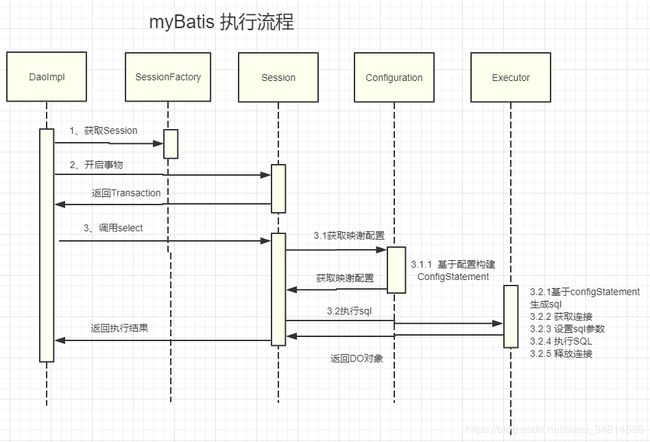
执行流程
下面作简要概述:
- SqlMapConfig.xml,此文件作为mybatis的全局配置文件,配置了mybatis的运行环境等信息。mapper.xml文件即sql映射文件,文件中配置了操作数据库的sql语句,此文件需要在SqlMapConfig.xml中加载。
- 通过mybatis环境等配置信息构造SqlSessionFactory(即会话工厂)。
- 由会话工厂创建sqlSession即会话,操作数据库需要通过sqlSession进行。
- mybatis底层自定义了Executor执行器接口操作数据库,Executor接口有两个实现,一个是基本执行器、一个是缓存执行器。
- MappedStatement也是mybatis一个底层封装对象,它包装了mybatis配置信息及sql映射信息等。mapper.xml文件中一个sql对应一个MappedStatement对象,sql的id即是MappedStatement的id。
- MappedStatement对sql执行输入参数进行定义,包括HashMap、基本类型、pojo,Executor通过MappedStatement在执行sql前将输入的java对象映射至sql中,输入参数映射就是JDBC编程中对preparedStatement设置参数。
- MappedStatement对sql执行输出结果进行定义,包括HashMap、基本类型、pojo,Executor通过MappedStatement在执行sql后将输出结果映射至java对象中,输出结果映射过程相当于JDBC编程中对结果的解析处理过程。
用代码表示如下:
@Test
public void getUserTest() {
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
InputStream input = getClass().getResourceAsStream("/mybatis-context-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactory devSession = builder.build(input);
System.out.println(devSession.toString());
UserInfoMapper mapper= devSession.openSession().getMapper(UserInfoMapper.class);
UserInfo userinfo = mapper.getUser(1);
System.out.println(userinfo.toString());
Assert.assertNotNull(userinfo);
}myBatis 执行流程时序图
组件分析:
1.API接口层
SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory:主要用来创建会话。
源码如下:
import java.sql.Connection;
/**
* Creates an {@link SqlSession} out of a connection or a DataSource
*
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public interface SqlSessionFactory {
SqlSession openSession();
SqlSession openSession(boolean autoCommit);
SqlSession openSession(Connection connection);
SqlSession openSession(TransactionIsolationLevel level);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, boolean autoCommit);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level);
SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType, Connection connection);
Configuration getConfiguration();
}
SqlSessionFactory接口的默认实现类为DefaultSqlSessionFactory,其关键部分源码如下:
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
private final Configuration configuration;
public DefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
/**
*默认采用SimpleExecutor类进行sql执行
*
/
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
@Override
public Configuration getConfiguration() {
return configuration;
}
/**
*最后使用DefaultSqlSession类进行执行
*
*/
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}DefaultSqlSessionFactory有一个属性为Configuration对象,即将会依赖于Configuration对象。DefaultSqlSessionFactory在开启回话前,就已经完成了Configuration对象的初始化。
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
SqlSessionFactory为整个框架的入口点,其主要生成方式采用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder的build构建,SqlSessionFactoryBuilder中共有许多build重载方法,参数共有如下几种:配置文件输入流(Reader、InputStream), Properties和Environment。它的作用就是返回一个SqlSessionFactory。其源码如下:
/**
* Builds {@link SqlSession} instances.
*
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader) {
return build(reader, null, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment) {
return build(reader, environment, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, Properties properties) {
return build(reader, null, properties);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties);
//注意parser.parse()将会返回一个Configuration对象
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) {
return build(inputStream, null, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment) {
return build(inputStream, environment, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, Properties properties) {
return build(inputStream, null, properties);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
}
从中我们可以看到:SqlSessionFactoryBuilder默认采用的是解析xml的方式,解析xml后就可以获得对应得Configuration,然后使用默认实现SqlSessionFactory接口的DefaultSqlSessionFactory类作为SqlSessionFactory。
SqlSession
SqlSession默认实现类为DefaultSqlSession,SqlSession接口源码如下:
public interface SqlSession extends Closeable {
/**
* Retrieve a single row mapped from the statement key
* @param the returned object type
* @param statement
* @return Mapped object
*/
T selectOne(String statement);
/**
* Retrieve a single row mapped from the statement key and parameter.
* @param the returned object type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @return Mapped object
*/
T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* Retrieve a list of mapped objects from the statement key and parameter.
* @param the returned list element type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @return List of mapped object
*/
List selectList(String statement);
/**
* Retrieve a list of mapped objects from the statement key and parameter.
* @param the returned list element type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @return List of mapped object
*/
List selectList(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* Retrieve a list of mapped objects from the statement key and parameter,
* within the specified row bounds.
* @param the returned list element type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @param rowBounds Bounds to limit object retrieval
* @return List of mapped object
*/
List selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds);
/**
* The selectMap is a special case in that it is designed to convert a list
* of results into a Map based on one of the properties in the resulting
* objects.
* Eg. Return a of Map[Integer,Author] for selectMap("selectAuthors","id")
* @param the returned Map keys type
* @param the returned Map values type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param mapKey The property to use as key for each value in the list.
* @return Map containing key pair data.
*/
Map selectMap(String statement, String mapKey);
/**
* The selectMap is a special case in that it is designed to convert a list
* of results into a Map based on one of the properties in the resulting
* objects.
* @param the returned Map keys type
* @param the returned Map values type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @param mapKey The property to use as key for each value in the list.
* @return Map containing key pair data.
*/
Map selectMap(String statement, Object parameter, String mapKey);
/**
* The selectMap is a special case in that it is designed to convert a list
* of results into a Map based on one of the properties in the resulting
* objects.
* @param the returned Map keys type
* @param the returned Map values type
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @param mapKey The property to use as key for each value in the list.
* @param rowBounds Bounds to limit object retrieval
* @return Map containing key pair data.
*/
Map selectMap(String statement, Object parameter, String mapKey, RowBounds rowBounds);
/**
* A Cursor offers the same results as a List, except it fetches data lazily using an Iterator.
* @param the returned cursor element type.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @return Cursor of mapped objects
*/
Cursor selectCursor(String statement);
/**
* A Cursor offers the same results as a List, except it fetches data lazily using an Iterator.
* @param the returned cursor element type.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @return Cursor of mapped objects
*/
Cursor selectCursor(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* A Cursor offers the same results as a List, except it fetches data lazily using an Iterator.
* @param the returned cursor element type.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @param rowBounds Bounds to limit object retrieval
* @return Cursor of mapped objects
*/
Cursor selectCursor(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds);
/**
* Retrieve a single row mapped from the statement key and parameter
* using a {@code ResultHandler}.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @param handler ResultHandler that will handle each retrieved row
*/
void select(String statement, Object parameter, ResultHandler handler);
/**
* Retrieve a single row mapped from the statement
* using a {@code ResultHandler}.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param handler ResultHandler that will handle each retrieved row
*/
void select(String statement, ResultHandler handler);
/**
* Retrieve a single row mapped from the statement key and parameter
* using a {@code ResultHandler} and {@code RowBounds}
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to use.
* @param rowBounds RowBound instance to limit the query results
* @param handler ResultHandler that will handle each retrieved row
*/
void select(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler);
/**
* Execute an insert statement.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to execute.
* @return int The number of rows affected by the insert.
*/
int insert(String statement);
/**
* Execute an insert statement with the given parameter object. Any generated
* autoincrement values or selectKey entries will modify the given parameter
* object properties. Only the number of rows affected will be returned.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to execute.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @return int The number of rows affected by the insert.
*/
int insert(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* Execute an update statement. The number of rows affected will be returned.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to execute.
* @return int The number of rows affected by the update.
*/
int update(String statement);
/**
* Execute an update statement. The number of rows affected will be returned.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to execute.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @return int The number of rows affected by the update.
*/
int update(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* Execute a delete statement. The number of rows affected will be returned.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to execute.
* @return int The number of rows affected by the delete.
*/
int delete(String statement);
/**
* Execute a delete statement. The number of rows affected will be returned.
* @param statement Unique identifier matching the statement to execute.
* @param parameter A parameter object to pass to the statement.
* @return int The number of rows affected by the delete.
*/
int delete(String statement, Object parameter);
/**
* Flushes batch statements and commits database connection.
* Note that database connection will not be committed if no updates/deletes/inserts were called.
* To force the commit call {@link SqlSession#commit(boolean)}
*/
void commit();
/**
* Flushes batch statements and commits database connection.
* @param force forces connection commit
*/
void commit(boolean force);
/**
* Discards pending batch statements and rolls database connection back.
* Note that database connection will not be rolled back if no updates/deletes/inserts were called.
* To force the rollback call {@link SqlSession#rollback(boolean)}
*/
void rollback();
/**
* Discards pending batch statements and rolls database connection back.
* Note that database connection will not be rolled back if no updates/deletes/inserts were called.
* @param force forces connection rollback
*/
void rollback(boolean force);
/**
* Flushes batch statements.
* @return BatchResult list of updated records
* @since 3.0.6
*/
List flushStatements();
/**
* Closes the session
*/
@Override
void close();
/**
* Clears local session cache
*/
void clearCache();
/**
* Retrieves current configuration
* @return Configuration
*/
Configuration getConfiguration();
/**
* Retrieves a mapper.
*获取被代理的类
* @param the mapper type
* @param type Mapper interface class
* @return a mapper bound to this SqlSession
*/
T getMapper(Class type);
/**
* Retrieves inner database connection
* @return Connection
*/
Connection getConnection();
}
DefaultSqlSession
在 DefaultSq!Session 中使用到了策略模式, DefaultSq!Session 扮演了 Context 的角色,而将
所有数据库相关的操作全部封装到 Executor 接口实现中,并通过 executor 字段选择不同的
Executor 实现。
其关键源码如下:
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private final Configuration configuration;
private final Executor executor;
private final boolean autoCommit;
private boolean dirty;
private List> cursorList;
}
2.基础支撑层
Configuration
mybatis的所有配置信息都存储到org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration类中,可通过xml配置或者手动实例化获取到Configuration信息。也就是Configuration管理了所有的配置信息。其关键属性如下:
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public class Configuration {
//Environment主要用于配置数据源和事务信息
protected Environment environment;
//一些默认配置
protected boolean safeRowBoundsEnabled;
protected boolean safeResultHandlerEnabled = true;
protected boolean mapUnderscoreToCamelCase;
protected boolean aggressiveLazyLoading;
protected boolean multipleResultSetsEnabled = true;
protected boolean useGeneratedKeys;
protected boolean useColumnLabel = true;
protected boolean cacheEnabled = true;
protected boolean callSettersOnNulls;
protected boolean useActualParamName = true;
protected boolean returnInstanceForEmptyRow;
}
Environment主要用于配置数据源和事务信息,Environment的属性源码设置如下
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
*/
public final class Environment {
private final String id;
private final TransactionFactory transactionFactory;
private final DataSource dataSource;
}
3.数据处理层
Executor
Executor:Executor 是 MyBati s 的核心接口之一 , 其中定义了数据库操作的基本方法。在实际应用中
经常涉及的 SqISession 接口的功能,都是基于 Executor 接口实现的 。
BaseExecutor:BaseExecutor 是一个实现了 Executor 接口的抽象类 ,它实现了 Executor 接口的大部分方法,
其中就使用了模板方法模式。
SimpleExecutor:SimpleExecutor 继承了 BaseExecutor 抽象类 , 它是最简单的 Executor 接口实现。
SimpleExecutor是Mybatis执行Mapper语句时默认使用的Executor。它提供最基本的Mapper语句执行功能,没有过多的封装的。
正如前面所说, Executor 使用了模板方法模式, 一级缓存等固定不变的操作都封装到了 BaseExecutor 中 ,
在 SimpleExecutor 中就不必再关心一级缓存等操作,只需要专注实现 4 个基本方法的实现即可。
ReuseExecutor:ReuseExecutor,顾名思义,是可以重用的Executor。它重用的是Statement对象,它会在内部利用一个Map把创建的Statement都缓存起来,每次在执行一条SQL语句时,它都会去判断之前是否存在基于该SQL缓存的Statement对象,
存在而且之前缓存的Statement对象对应的Connection还没有关闭的时候就继续用之前的Statement对象,否则将创建一个新的Statement对象,并将其缓存起来。
因为每一个新的SqlSession都有一个新的Executor对象,所以我们缓存在ReuseExecutor上的Statement的作用域是同一个SqlSession。
BatchExecutor:BatchExecutor的设计主要是用于做批量更新操作的。其底层会调用Statement的executeBatch()方法实现批量操作。以下是BatchExecutor的源码。
动态代理
同动态代理模式的设计原则,mybatis也主要是两个大步骤:
1.代理对象的创建
2.使用代理对象,即实现InvocationHandler接口
mybatis代理对象的创建使用了工厂模式,使用MapperProxyFactory类进行创建。源码如下:
/**
* @author Lasse Voss
*/
public class MapperProxyFactory {
private final Class mapperInterface;
private final Map methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy mapperProxy = new MapperProxy(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
mybatis实现InvocationHandler接口的类为MapperProxy,源码如下:
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
* @author Eduardo Macarron
*/
public class MapperProxy implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class mapperInterface;
private final Map methodCache;
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class mapperInterface, Map methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
MapperMethod
执行被代理的类所要执行的方法,通过调用execute方法
MapperMethod有一个成员内部类SqlCommand和静态内部类MethodSignature
SqlCommand :MapperMethod的一个成员内部类,有两个属性:name和Type。name成员就是节点的ID,type成员表示查寻还是更新或是删除
MethodSignature:他用于说明方法的一些信息,主要有返回信息。
execute实现源码如下:
/**
* @author Clinton Begin
* @author Eduardo Macarron
* @author Lasse Voss
*/
public class MapperMethod {
private final SqlCommand command;
private final MethodSignature method;
public MapperMethod(Class mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {
this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);
this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);
}
/**
* 执行被代理的方法
*
*
*/
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
}
最后到executor组件
@Override
public List selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
} 最后到SimpleExecutor的doQuery方法
@Override
public List doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
StatementHandler
StatementHandler 接口是 MyBatis 的核心接口之一,它完成了 MyBatis 中最核心的工作,也
是后面要介绍的 Executor 接口实现的基础。
StatementHandler 接口中的功能很多,例如创建 Statement 对象,为 SQL 语句绑定实参,执
行 select、 insert、 update 、 delete 等多种类型的 SQL 语句,批量执行 SQL 语句,将结果集映射
成结果对象。
RoutingStatementHandler 会根据 MappedStatement 中 指定的 statementType 宇段,创建对应
的 StatementHandler 接口实现。可以把它理解为下面三个类的代理类。
PreparedStatementHandler 底层依赖于 java.sq1.PreparedStatement 对象来完成数据库的相关操
作 ,默认的实现就是PreparedStatementHandler
常见问题:
1. #{}和${}的区别是什么?
#{}是预编译处理,${}是字符串替换。
Mybatis在处理#{}时,会将sql中的#{}替换为?号,调用PreparedStatement的set方法来赋值;相当于JDBC中的PreparedStatement
Mybatis在处理${}时,就是把${}替换成变量的值。
简单说,#{}是经过预编译的,是安全的;${}是未经过预编译的,仅仅是替换变量的值,是非安全的,存在SQL注入。
2. 通常一个Xml映射文件,都会写一个Dao接口与之对应,请问,这个Dao接口的工作原理是什么?Dao接口里的方法,参数不同时,方法能重载吗?
Dao接口,就是人们常说的Mapper接口,接口的全限名,就是映射文件中的namespace的值.
接口的方法名,就是映射文件中MappedStatement的id值,接口方法内的参数,就是传递给sql的参数。
Mapper接口是没有实现类的,当调用接口方法时,接口全限名+方法名拼接字符串作为key值,可唯一定位一个MappedStatement,举例:com.mybatis3.mappers.StudentDao.findStudentById,可以唯一找到namespace为com.mybatis3.mappers.StudentDao下面id = findStudentById的MappedStatement。
在Mybatis中,每一个
Dao接口里的方法,是不能重载的,因为是全限名+方法名的保存和寻找策略,寻找时与入参类型及个数没有多大关系。
Dao接口的工作原理是JDK动态代理,Mybatis运行时会使用JDK动态代理为Dao接口生成代理proxy对象,代理对象proxy会拦截接口方法,转而执行MappedStatement所代表的sql,然后将sql执行结果返回。
3. Mybatis是如何进行分页的?分页插件的原理是什么?
Mybatis使用RowBounds对象进行分页,它是针对ResultSet结果集执行的内存分页,而非物理分页,可以在sql内直接书写带有物理分页的参数来完成物理分页功能,也可以使用分页插件来完成物理分页。
分页插件的基本原理是使用Mybatis提供的插件接口,实现自定义插件,在插件的拦截方法内拦截待执行的sql,然后重写sql,根据dialect方言,添加对应的物理分页语句和物理分页参数。
4. Mybatis是如何将sql执行结果封装为目标对象并返回的?都有哪些映射形式?
第一种是使用
第二种是使用sql列的别名功能,将列别名书写为对象属性名,比如T_NAME AS NAME,对象属性名一般是name,小写,但是列名不区分大小写,Mybatis会忽略列名大小写,智能找到与之对应对象属性名,你甚至可以写成T_NAME AS NaMe,Mybatis一样可以正常工作。
有了列名与属性名的映射关系后,Mybatis通过反射创建对象,同时使用反射给对象的属性逐一赋值并返回,那些找不到映射关系的属性,是无法完成赋值的。
6. 简述Mybatis的插件运行原理,以及如何编写一个插件(待续)
Mybatis仅可以编写针对ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler、StatementHandler、Executor这4种接口的插件,
Mybatis使用JDK的动态代理,为需要拦截的接口生成代理对象以实现接口方法拦截功能,每当执行这4种接口对象的方法时,就会进入拦截方法,具体就是InvocationHandler的invoke()方法,当然,只会拦截那些你指定需要拦截的方法。实现Mybatis的Interceptor接口并复写intercept()方法,
然后在给插件编写注解,指定要拦截哪一个接口的哪些方法即可,记住,还需要在配置文件中配置你编写的插件。
7. 一级、二级缓存
1)一级缓存: 基于 PerpetualCache 的 HashMap 本地缓存,其存储作用域为 Session,当 Session flush 或 close 之后,该 Session 中的所有 Cache 就将清空。
2)二级缓存与一级缓存其机制相同,默认也是采用 PerpetualCache,HashMap 存储,不同在于其存储作用域为 Mapper(Namespace),并且可自定义存储源,如 Ehcache。要开启二级缓存,你需要在你的 SQL 映射文件中添加一行:
3)对于缓存数据更新机制,当某一个作用域(一级缓存 Session/二级缓存Namespaces)的进行了C/U/D 操作后,默认该作用域下所有 select 中的缓存将被 clear。
8. Mybatis是否支持延迟加载?如果支持,它的实现原理是什么?
Mybatis仅支持association关联对象和collection关联集合对象的延迟加载,association指的就是一对一,collection指的就是一对多查询。在Mybatis配置文件中,可以配置是否启用延迟加载lazyLoadingEnabled=true|false。默认为false。
它的原理是,使用CGLIB创建目标对象的代理对象,当调用目标方法时,进入拦截器方法,比如调用a.getB().getName(),拦截器invoke()方法发现a.getB()是null值,那么就会单独发送事先保存好的查询关联B对象的sql,把B查询上来,然后调用a.setB(b),于是a的对象b属性就有值了,
接着完成a.getB().getName()方法的调用。这就是延迟加载的基本原理。
9. Mybatis映射文件中,如果A标签通过include引用了B标签的内容,请问,B标签能否定义在A标签的后面,还是说必须定义在A标签的前面?
虽然Mybatis解析Xml映射文件是按照顺序解析的,但是,被引用的B标签依然可以定义在任何地方,Mybatis都可以正确识别。
原理是,Mybatis解析A标签,发现A标签引用了B标签,但是B标签尚未解析到,尚不存在,此时,Mybatis会将A标签标记为未解析状态,然后继续解析余下的标签,包含B标签,待所有标签解析完毕,
Mybatis会重新解析那些被标记为未解析的标签,此时再解析A标签时,B标签已经存在,A标签也就可以正常解析完成了。
10. 简述Mybatis的Xml映射文件和Mybatis内部数据结构之间的映射关系?
Mybatis将所有Xml配置信息都封装到All-In-One重量级对象Configuration内部。
在Xml映射文件中,
每一个
11.mybatis与hibernate区别?
1.mybatis支持很多的动态语句,编写sql更加灵活。但同时也是一个缺点就是需要自己手写很多sql。hibernate封装了很多的sql.
2.hibernate数据库移植性远大于mybatis。
3.hibernate有更好的二级缓存机制,可以使用第三方缓存。mybatis二级缓存机制不佳
参考资料
1.MyBatis框架的学习(二)——MyBatis架构与入门https://blog.csdn.net/yerenyuan_pku/article/details/71699515
2.Mybatis源码分析(一)- Configuration配置文件详解https://blog.csdn.net/einarzhang/article/details/53022820
3.MyBatis 源码分析系列https://www.cnblogs.com/hayasi/category/920416.html
4.《mybatis技术内幕》徐郡明
待续。。。。