coreboot学习5:启动流程跟踪之ramstage阶段主干分析
ramstage阶段涉及比较多的操作,比如枚举板子上的外围设备,分配资源(PCI),使能设备。本文根据该阶段的主干函数流程做分析,细节方面不涉及。理顺这个主干,从全局上把控大致流程。
romstage阶段执行完毕,在arch_prog_run函数中,使用jmp指令跳转到ramstge的入口地址。代码如下:
__asm__ volatile (
#ifdef __x86_64__
"jmp *%%rdi\n"
#else
"jmp *%%edi\n"
#endif
:: "D"(prog_entry(prog))
);
之后就是ramstage阶段的运行了。主体代码在src\lib\hardwaremain.c中,主函数为main。该文件使用启动状态结构体(struct boot_state)定义了所有要执行的函数。定义如下:
struct boot_state {
const char *name;
boot_state_t id;
u8 post_code;
struct boot_phase phases[2];
boot_state_t (*run_state)(void *arg);
void *arg;
int complete : 1;
#if CONFIG_HAVE_MONOTONIC_TIMER
struct boot_state_times times;
#endif
};
#define BS_INIT(state_, run_func_) \
{ \
.name = #state_, \
.id = state_, \
.post_code = POST_ ## state_, \
.phases = { { NULL, 0 }, { NULL, 0 } }, \
.run_state = run_func_, \
.arg = NULL, \
.complete = 0, \
}
#define BS_INIT_ENTRY(state_, run_func_) \
[state_] = BS_INIT(state_, run_func_)
// 此结构体定义ramstage依次执行的函数
// 前一函数结束后会返回下一阶段要执行的函数id
static struct boot_state boot_states[] = {
BS_INIT_ENTRY(BS_PRE_DEVICE, bs_pre_device),
BS_INIT_ENTRY(BS_DEV_INIT_CHIPS, bs_dev_init_chips),
BS_INIT_ENTRY(BS_DEV_ENUMERATE, bs_dev_enumerate),
BS_INIT_ENTRY(BS_DEV_RESOURCES, bs_dev_resources),
BS_INIT_ENTRY(BS_DEV_ENABLE, bs_dev_enable),
BS_INIT_ENTRY(BS_DEV_INIT, bs_dev_init),
BS_INIT_ENTRY(BS_POST_DEVICE, bs_post_device),
BS_INIT_ENTRY(BS_OS_RESUME_CHECK, bs_os_resume_check),
BS_INIT_ENTRY(BS_OS_RESUME, bs_os_resume),
BS_INIT_ENTRY(BS_WRITE_TABLES, bs_write_tables),
BS_INIT_ENTRY(BS_PAYLOAD_LOAD, bs_payload_load),
BS_INIT_ENTRY(BS_PAYLOAD_BOOT, bs_payload_boot),
};
每个函数运行结束后,都会返回下一次要执行的函数ID,这样就可以顺序地执行每个小阶段的函数。其实现是在最关键的函数:bs_walk_state_machine():
static void bs_walk_state_machine(void)
{
while (1) {
static int cnt = 1;
struct boot_state *state;
boot_state_t next_id;
// 拿到一个state
state = &boot_states[current_phase.state_id];
if (state->complete) {
printk(BIOS_EMERG, "BS: %s state already executed.\n",
state->name);
break;
}
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_DEBUG_BOOT_STATE))
printk(BIOS_DEBUG, "BS: Entering %s state.\n",
state->name);
bs_run_timers(0);
bs_sample_time(state);
bs_call_callbacks(state, current_phase.seq);
/* Update the current sequence so that any calls to block the
* current state from the run_state() function will place a
* block on the correct phase. */
current_phase.seq = BS_ON_EXIT;
bs_sample_time(state);
ll_printk("%s() state %d start==============================\n", __func__, state->id);
post_code(state->post_code);
// 真正调用boot_states定义好的函数
// 函数返回后,得到下一次要执行的id
next_id = state->run_state(state->arg);
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_DEBUG_BOOT_STATE))
printk(BIOS_DEBUG, "BS: Exiting %s state.\n",
state->name);
bs_sample_time(state);
bs_call_callbacks(state, current_phase.seq);
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_DEBUG_BOOT_STATE))
printk(BIOS_DEBUG,
"----------------------------------------\n");
/* Update the current phase with new state id and sequence. */
current_phase.state_id = next_id;
current_phase.seq = BS_ON_ENTRY;
bs_sample_time(state);
bs_report_time(state);
state->complete = 1;
}
}
可以看到,首先从boot_states拿到一个结构体(根据current_phase结构,此时获取到的实际上是第一个要执行的,即BS_PRE_DEVICE的结构体),然后调用该结构的run_state函数指针(比如第一个状态即为bs_pre_device函数),该函数返回的是下一状态ID,赋值给next_id,再更改current_phase中的值。不断的循环,直到结束。——事实上,coreboot最终的状态将会是payload,而payload之后,就是操作系统了,这些不再是coreboot管控范围了。因此,这个函数虽然由while(1)不断循环执行,实质上到payload后即结束了。
关于启动的状态过程,在头文件src\include\bootstate.h的注释讲得十分清楚,摘录如下:
/*
* The boot state machine provides a mechanism for calls to be made through-
* out the main boot process. The boot process is separated into discrete
* states. Upon a state's entry and exit and callbacks can be made. For
* example:
*
* Enter State
* +
* |
* V
* +-----------------+
* | Entry callbacks |
* +-----------------+
* | State Actions |
* +-----------------+
* | Exit callbacks |
* +-------+---------+
* |
* V
* Next State
*
* Below is the current flow from top to bottom:
*
* start
* |
* BS_PRE_DEVICE
* |
* BS_DEV_INIT_CHIPS
* |
* BS_DEV_ENUMERATE
* |
* BS_DEV_RESOURCES
* |
* BS_DEV_ENABLE
* |
* BS_DEV_INIT
* |
* BS_POST_DEVICE
* |
* BS_OS_RESUME_CHECK -------- BS_OS_RESUME
* | |
* BS_WRITE_TABLES os handoff
* |
* BS_PAYLOAD_LOAD
* |
* BS_PAYLOAD_BOOT
* |
* payload run
*
* Brief description of states:
* BS_PRE_DEVICE - before any device tree actions take place
* BS_DEV_INIT_CHIPS - init all chips in device tree
* BS_DEV_ENUMERATE - device tree probing
* BS_DEV_RESOURCES - device tree resource allocation and assignment
* BS_DEV_ENABLE - device tree enabling/disabling of devices
* BS_DEV_INIT - device tree device initialization
* BS_POST_DEVICE - all device tree actions performed
* BS_OS_RESUME_CHECK - check for OS resume
* BS_OS_RESUME - resume to OS
* BS_WRITE_TABLES - write coreboot tables
* BS_PAYLOAD_LOAD - Load payload into memory
* BS_PAYLOAD_BOOT - Boot to payload
*/
typedef enum {
BS_PRE_DEVICE,
BS_DEV_INIT_CHIPS,
BS_DEV_ENUMERATE,
BS_DEV_RESOURCES,
BS_DEV_ENABLE,
BS_DEV_INIT,
BS_POST_DEVICE,
BS_OS_RESUME_CHECK,
BS_OS_RESUME,
BS_WRITE_TABLES,
BS_PAYLOAD_LOAD,
BS_PAYLOAD_BOOT,
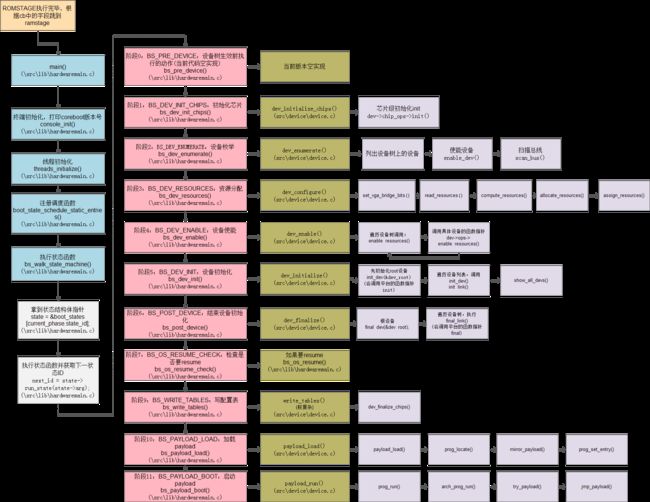
} boot_state_t;总体流程图如下:
注:
由于coreboot方面资料较少,笔者第一次尝试分析代码,还有众多未能参透的地方,难免出错。任何问题,欢迎一起交流学习。
李迟 2016.3.16 周三 夜