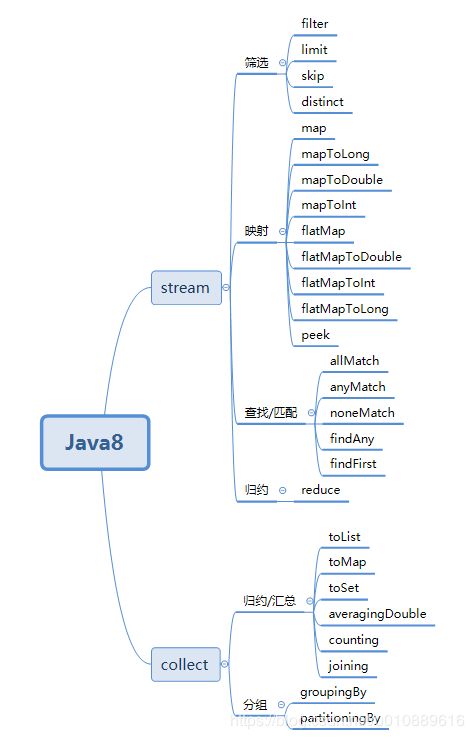
Java8 stream编程示例
最近在使用Java8编程,流式编程效率非常高,代码也比较简洁针对stream/parallelStream的常用方法foreach、filter、anyMatch、allMatch、Map、flatMap、reduce、limit、skip、distinct、summaryStatistics写了Demo示例,方便上手使用
下面Demo主要有两个类,一个是Student实体类,一个是StreamTest测试类,使用Junit写的单元测试
Github代码链接:https://github.com/HelloKittyNII/Code/blob/master/basic/java8/src/main/java/com/nii/java8/test/StreamTest.java
Student实体,每个学生定义了四个属性
package com.nii.java8.model;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* @Description 学生实体
* @Author wzj
* @Date 2020/1/11 21:31
**/
public class Student implements Serializable {
/**
* 序列号
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7544685819102239171L;
/**
* 学生编号
*/
private int id;
/**
* 姓名
*/
private String name;
/**
* 个子是否高
*/
private boolean isHigh;
/**
* 学生成绩
*/
private Double mathScore;
public Student(int id, String name, boolean isHigh, Double mathScore) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.isHigh = isHigh;
this.mathScore = mathScore;
}
public Student() {
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Double getMathScore() {
return mathScore;
}
public void setMathScore(Double mathScore) {
this.mathScore = mathScore;
}
public boolean isHigh() {
return isHigh;
}
public void setHigh(boolean high) {
isHigh = high;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", isHigh=" + isHigh +
", mathScore=" + mathScore +
'}';
}
}
StreamTest测试类
package com.nii.java8.test;
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
import com.nii.java8.model.Student;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* @Description java8流测试类
* @Author wzj
* @Date 2020/1/11 21:30
**/
public class StreamTest {
/**
* 学生列表
*/
private List studentList = null;
@Before
public void before() {
studentList = Lists.newArrayList(new Student(21, "张三", false, 89.1),
new Student(1, "李四", true, 90.0),
new Student(2, "赵六", true, 60.0),
new Student(25, "张八", false, 60.0));
}
/**
* 生成流
*/
@Test
public void generalTest() {
//1、第一种方式通过列表生成
List stringList = Lists.newArrayList("aa", "bb", "cc");
System.out.println(stringList.stream().count());
//2、第二种方式通过数组生成
List strings = Arrays.asList("aa", "bb");
System.out.println(strings.stream().count());
}
/**
* 遍历 foreach
*/
@Test
public void foreachTest() {
List stringList = Lists.newArrayList("aa", "bb", "cc");
stringList.stream().forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
}
/**
* 过滤 filter match
*/
@Test
public void filterTest() {
//过滤大于80分学生
List students = studentList.stream().filter(student -> student.getMathScore() > 80.0).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(students);
//过滤身高
List student2 = studentList.stream().filter(Student::isHigh).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(student2);
//匹配是不是所有名字都叫张三
boolean allMatch = studentList.stream().allMatch(student -> Objects.equals("张三", student.getName()));
System.out.println(allMatch);
//匹配是不是有叫张三
boolean anyMatch = studentList.stream().anyMatch(student -> Objects.equals("张三", student.getName()));
System.out.println(anyMatch);
//找到名字叫张三的学生
Student student1 = studentList.stream().filter(student -> Objects.equals("张三", student.getName())).findAny().orElse(null);
System.out.println(student1);
}
/**
* map distinct flatMap reduce
*/
@Test
public void mapTest() {
//获取分数列表,去重
List scoreList = studentList.stream().map(Student::getMathScore).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(scoreList);
//转成map,如果key重复,取第一个
Map collectMap = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Student::getMathScore,
student -> student, (stu1, stu2) -> stu1));
System.out.println(collectMap);
//flatMap 对map数据组合
List stringList = Lists.newArrayList("china", "good");
List collect = stringList.stream().flatMap(s -> Arrays.stream(s.split(""))).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);
//reduce 对列表数据分组处理
Double sumScore = studentList.stream().map(Student::getMathScore).reduce((score1, score2) -> score1 + score2).orElse(0.0);
System.out.println(sumScore);
}
/**
* sorted limit skip
*/
@Test
public void sortTest() {
//通过id排序,逆序
List sortedList =
studentList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Student::getId).reversed()).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(sortedList);
//获取前两名学生成绩
List top2Student =
studentList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Student::getMathScore).reversed()).limit(2).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(top2Student);
//取第二名学生
List secondStudent =
studentList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Student::getMathScore).reversed()).limit(2).skip(1).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(secondStudent);
}
/**
* 并行流测试
* 适用于每个线程数据独立
*/
@Test
public void parallelTest() {
studentList.parallelStream().forEach(student -> System.out.println(student + Thread.currentThread().getName()));
}
/**
* 统计测试
* 主要用于int、double、long类型
*/
@Test
public void statTest() {
DoubleSummaryStatistics statistics = studentList.stream().mapToDouble(Student::getMathScore).summaryStatistics();
System.out.println("最大值 " + statistics.getMax());
System.out.println("平均值 " + statistics.getAverage());
}
/**
* 分组 group by 测试
*/
@Test
public void groupByTest() {
Map> listMap = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Student::getMathScore));
System.out.println(listMap);
Map> booleanListMap = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(Student::isHigh));
System.out.println(booleanListMap);
}
/**
* peek map
*/
@Test
public void peekAndMapTest() {
//只需要访问获取内部元素,打印
List stringList1 = Lists.newArrayList("11", "22", "33");
stringList1.stream().peek(System.out::print).collect(Collectors.toList());
List stringList2 = Lists.newArrayList("11", "22", "33");
//支持自定义返回值,将字符串转换为数字
List mapResultList = stringList2.stream().map(s -> Integer.valueOf(s)).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(mapResultList);
//可以看到返回值还是List
List peekResultList = stringList2.stream().peek(s -> Integer.valueOf(s)).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(peekResultList);
}
/**
* 收集器测试
*/
@Test
public void collectTest(){
Stack collect1 = studentList.stream().collect(Collectors.toCollection(Stack::new));
System.out.println(collect1);
}
}