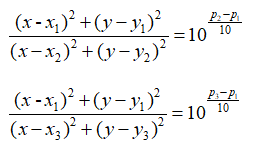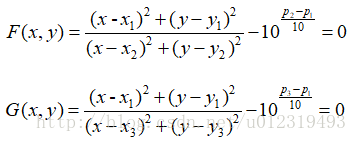C#---最速下降+牛顿迭代求二元非线性方程组
求解非线性方程组
Newton.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace NewtonIteration
{
class Newton
{
int _MaxIterativeTime = 1000000; // 最大迭代次数
double _Precision = 0.0001; // 精度
public double[] result;
double xk, yk;
double p1, p2, p3, x1, x2, x3, y1, y2, y3, c1, c2;
public Newton(double p1, double p2, double p3, double x1, double x2, double x3, double y1, double y2, double y3)
{
this.p1 = p1;
this.p2 = p2;
this.p3 = p3;
this.x1 = x1;
this.x2 = x2;
this.x3 = x3;
this.y1 = y1;
this.y2 = y2;
this.y3 = y3;
this.c1 = Math.Pow(10, (p2 - p1) / 10.0);
this.c2 = Math.Pow(10, (p3 - p1) / 10.0);
}
private double F(double x, double y)
{
return (Math.Pow(x - x1, 2) + Math.Pow(y - y1, 2)) / (Math.Pow(x - x2, 2) + Math.Pow(y - y2, 2)) - c1;
}
private double Fx(double x)
{
return 2.0 * x * (1 - c1) + 2.0 * (-x1 + c1 * x2);
}
private double Fy(double y)
{
return 2.0 * y * (1 - c1) + 2.0 * (-y1 + c1 * y2);
}
private double G(double x, double y)
{
return (Math.Pow(x - x1, 2) + Math.Pow(y - y1, 2)) / (Math.Pow(x - x3, 2) + Math.Pow(y - y3, 2)) - c2;
}
private double Gx(double x)
{
return 2.0 * x * (1 - c2) + 2.0 * (-x1 + c2 * x3);
}
private double Gy(double y)
{
return 2.0 * y * (1 - c2) + 2.0 * (-y1 + c2 * y3);
}
// 最速下降
private void ZSXJ()
{
double m = 0.0001;
for(int i=0; i<1000; i++)
{
double f = m * 2 * (F(xk, yk) * Fx(xk) + G(xk, yk) * Gx(xk));
double g = m * 2 * (F(xk, yk) * Fy(yk) + G(xk, yk) * Gy(yk));
xk -= f;
yk -= g;
double a = f * Fx(xk) + g * Fy(yk);
double b = f * Gx(xk) + g * Gy(yk);
m = (F(xk, yk) * a + G(xk, yk) * b) / (Math.Pow(a, 2) + Math.Pow(b, 2));
if (Math.Pow(F(xk, yk), 2) + Math.Pow(G(xk, yk), 2) < 0.001)
break;
}
}
public void run()
{
xk = (x1 + x2 + x3) / 3.0;
yk = (y1 + y2 + y3) / 3.0;
Console.WriteLine(xk);
Console.WriteLine(yk);
// 最速下降
ZSXJ();
Console.WriteLine(xk);
Console.WriteLine(yk);
double lastX = xk;
double lastY = yk;
// 牛顿迭代
for (int i = 0; i < _MaxIterativeTime; i++)
{
xk += (F(xk, yk) * Gy(yk) - G(xk, yk) * Fy(yk)) / (Gx(xk) * Fy(yk) - Fx(xk) * Gy(yk));
yk += (G(xk, yk) * Fx(yk) - F(xk, yk) * Gx(xk)) / (Gx(xk) * Fy(yk) - Fx(xk) * Gy(yk));
if (Math.Abs(xk - lastX) < _Precision && Math.Abs(yk - lastY) < _Precision)
break;
lastX = xk;
lastY = yk;
}
Console.WriteLine(xk);
Console.WriteLine(yk);
result = new double[2];
result[0] = xk;
result[1] = yk;
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Program.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace NewtonIteration
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double[] x = { 668565.725, 668199.829, 667936.921 };
double[] y = { 3548174.709, 3547598.824, 3548511.284 };
double[] p = { -50.13, -47.71, -47.88 };
Newton newton = new Newton(p[0], p[1], p[2], x[0], x[1], x[2], y[0], y[1], y[2]);
newton.run();
}
}
}
原理
最速下降:https://wenku.baidu.com/view/85892d3c10661ed9ad51f3b7.html
牛顿迭代:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_14ecf9fa60102wtjq.html
http://www.doc88.com/p-3137553224119.html