语义分割代码阅读---评价指标mIoU的计算
1. 语义分割IoU的定义
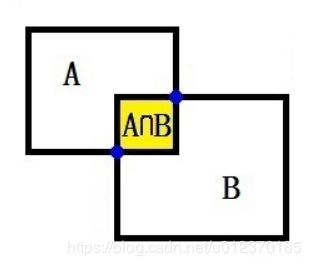
传统意义上的IoU(Intersection over Union,交并比)
直观表示:
语义分割中的IoU
在语义分割的问题中,这两个集合为真实值(ground truth)和预测值(predicted segmentation)。
这个比例可以变形为正真数(intersection)比上真正、假负、假正(并集)之和。在每个类上计算IoU,之后平均。
![]()
语义分割中的MIoU
Mean Intersection over Union(MIoU,均交并比):为语义分割的标准度量。其计算所有类别交集和并集之比的平均值.
2. 某个类别的IoU的计算
对于pascal数据集来说, 对于21个类别, 分别求IOU:
对于某一个类别的IOU计算公式如下:
直观理解:
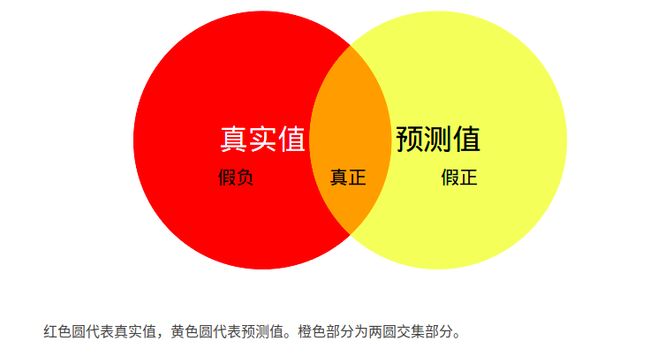
MIoU:计算两圆交集(橙色部分)与两圆并集(红色+橙色+黄色)之间的比例,理想情况下两圆重合,比例为1。
扩展提示:
TP(真正): 预测正确, 预测结果是正类, 真实是正类
FP(假正): 预测错误, 预测结果是正类, 真实是负类
FN(假负): 预测错误, 预测结果是负类, 真实是正类TN(真负): 预测正确, 预测结果是负类, 真实是负类 #跟类别1无关,所以不包含在并集中
(本例中, 正类:是类别1, 负类:不是类别1)扩展阅读:
准确率和召回率
3. mIoU的计算
对于每个类别计算出的IoU求和取平均
步骤一 先求出混淆矩阵
步骤二 再求MIoU
混淆矩阵的每一行再加上每一列,最后减去对角线上的值
import numpy as np
class IOUMetric:
"""
Class to calculate mean-iou using fast_hist method
"""
def __init__(self, num_classes):
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.hist = np.zeros((num_classes, num_classes))
def _fast_hist(self, label_pred, label_true):
# 找出标签中需要计算的类别,去掉了背景
mask = (label_true >= 0) & (label_true < self.num_classes)
# # np.bincount计算了从0到n**2-1这n**2个数中每个数出现的次数,返回值形状(n, n)
hist = np.bincount(
self.num_classes * label_true[mask].astype(int) +
label_pred[mask], minlength=self.num_classes ** 2).reshape(self.num_classes, self.num_classes)
return hist
# 输入:预测值和真实值
# 语义分割的任务是为每个像素点分配一个label
def ev aluate(self, predictions, gts):
for lp, lt in zip(predictions, gts):
assert len(lp.flatten()) == len(lt.flatten())
self.hist += self._fast_hist(lp.flatten(), lt.flatten())
# miou
iou = np.diag(self.hist) / (self.hist.sum(axis=1) + self.hist.sum(axis=0) - np.diag(self.hist))
miou = np.nanmean(iou)
# -----------------其他指标------------------------------
# mean acc
acc = np.diag(self.hist).sum() / self.hist.sum()
acc_cls = np.nanmean(np.diag(self.hist) / self.hist.sum(axis=1))
freq = self.hist.sum(axis=1) / self.hist.sum()
fwavacc = (freq[freq > 0] * iou[freq > 0]).sum()
return acc, acc_cls, iou, miou, fwavacc
项目中的代码:
class Evaluator(object):
def __init__(self, num_class):
self.num_class = num_class
self.confusion_matrix = np.zeros((self.num_class,)*2)#21*21的矩阵,行代表ground truth类别,列代表preds的类别,值代表
'''
正确的像素占总像素的比例
'''
def Pixel_Accuracy(self):
Acc = np.diag(self.confusion_matrix).sum() / self.confusion_matrix.sum()
return Acc
'''
分别计算每个类分类正确的概率
'''
def Pixel_Accuracy_Class(self):
Acc = np.diag(self.confusion_matrix) / self.confusion_matrix.sum(axis=1)
Acc = np.nanmean(Acc)
return Acc
'''
Mean Intersection over Union(MIoU,均交并比):为语义分割的标准度量。其计算两个集合的交集和并集之比.
在语义分割的问题中,这两个集合为真实值(ground truth)和预测值(predicted segmentation)。
这个比例可以变形为正真数(intersection)比上真正、假负、假正(并集)之和。在每个类上计算IoU,之后平均。
对于21个类别,分别求IOU:
例如,对于类别1的IOU定义如下:
(1)统计在ground truth中属于类别1的像素数
(2)统计在预测结果中每个类别1的像素数
(1) + (2)就是二者的并集像素数(类比于两块区域的面积加和, 注:二者交集部分的面积加重复了)
再减去二者的交集(既在ground truth集合中又在预测结果集合中的像素),得到的就是二者的并集(所有跟类别1有关系的像素:包括TP,FP,FN)
扩展提示:
TP(真正): 预测正确, 预测结果是正类, 真实是正类
FP(假正): 预测错误, 预测结果是正类, 真实是负类
FN(假负): 预测错误, 预测结果是负类, 真实是正类
TN(真负): 预测正确, 预测结果是负类, 真实是负类 #跟类别1无关,所以不包含在并集中
(本例中, 正类:是类别1, 负类:不是类别1)
mIoU:
对于每个类别计算出的IoU求和取平均
'''
def Mean_Intersection_over_Union(self):
MIoU = np.diag(self.confusion_matrix) / (
np.sum(self.confusion_matrix, axis=1) + np.sum(self.confusion_matrix, axis=0) -
np.diag(self.confusion_matrix))
MIoU = np.nanmean(MIoU) #跳过0值求mean,shape:[21]
return MIoU
def Class_IOU(self):
MIoU = np.diag(self.confusion_matrix) / (
np.sum(self.confusion_matrix, axis=1) + np.sum(self.confusion_matrix, axis=0) -
np.diag(self.confusion_matrix))
return MIoU
def Frequency_Weighted_Intersection_over_Union(self):
freq = np.sum(self.confusion_matrix, axis=1) / np.sum(self.confusion_matrix)
iu = np.diag(self.confusion_matrix) / (
np.sum(self.confusion_matrix, axis=1) + np.sum(self.confusion_matrix, axis=0) -
np.diag(self.confusion_matrix))
FWIoU = (freq[freq > 0] * iu[freq > 0]).sum()
return FWIoU
'''
参数的传入:
evaluator = Evaluate(4) #只需传入类别数4
evaluator.add_batch(target, preb) #target:[batch_size, 512, 512] , preb:[batch_size, 512, 512]
在add_batch中统计这个epoch中所有图片的预测结果和ground truth的对应情况, 累计成confusion矩阵(便于之后求mean)
参数列表对应:
gt_image: target 图片的真实标签 [batch_size, 512, 512]
per_image: preb 网络生成的图片的预测标签 [batch_size, 512, 512]
parameters:
mask: ground truth中所有正确(值在[0, classe_num])的像素label的mask---为了保证ground truth中的标签值都在合理的范围[0, 20]
label: 为了计算混淆矩阵, 混淆矩阵中一共有num_class*num_class个数, 所以label中的数值也是在0与num_class**2之间. [batch_size, 512, 512]
cout(reshape): 记录了每个类别对应的像素个数,行代表真实类别,列代表预测的类别,count矩阵中(x, y)位置的元素代表该张图片中真实类别为x,被预测为y的像素个数
np.bincount: https://blog.csdn.net/xlinsist/article/details/51346523
confusion_matrix: 对角线上的值的和代表分类正确的像素点个数(preb与target一致),对角线之外的其他值的和代表所有分类错误的像素的个数
'''
# 计算混淆矩阵
def _generate_matrix(self, gt_image, pre_image):
mask = (gt_image >= 0) & (gt_image < self.num_class)#ground truth中所有正确(值在[0, classe_num])的像素label的mask
label = self.num_class * gt_image[mask].astype('int') + pre_image[mask]
# np.bincount计算了从0到n**2-1这n**2个数中每个数出现的次数,返回值形状(n, n)
count = np.bincount(label, minlength=self.num_class**2)
confusion_matrix = count.reshape(self.num_class, self.num_class)#21 * 21(for pascal)
return confusion_matrix
# --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
def add_batch(self, gt_image, pre_image):
assert gt_image.shape == pre_image.shape
tmp = self._generate_matrix(gt_image, pre_image)
#矩阵相加是各个元素对应相加,即21*21的矩阵进行pixel-wise加和
self.confusion_matrix += self._generate_matrix(gt_image, pre_image)
def reset(self):
self.confusion_matrix = np.zeros((self.num_class,) * 2)其中, 利用计算出来的混淆矩阵计算MIoU的方法如下:
'''
confusion_matrix是一个[num_classes,num_classes]的矩阵,
confusion_matrix矩阵中(x, y)位置的元素代表该张图片中真实类别为x,被预测为y的像素个数
第一个MIoU: [bach_size, 类别数]:对角线/(混淆矩阵各行加和+各列加和-对角线)
第二个MIoU: [1, 类别数]
'''
def Mean_Intersection_over_Union(self):
MIoU = np.diag(self.confusion_matrix) / (
np.sum(self.confusion_matrix, axis=1) +
np.sum(self.confusion_matrix, axis=0) -
np.diag(self.confusion_matrix))
MIoU = np.nanmean(MIoU) #跳过0值求mean,shape:[1, 21]
return MIoU后面是用fake数据帮助理解,可忽略:
其中a:预测值, b: ground truth
>>> b
array([[0, 0, 0, 2],
[0, 0, 2, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 1, 2]])
>>> a
array([[0, 0, 0, 2],
[0, 0, 2, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 2],
[1, 0, 1, 2]])
>>> label = 3 * b[mask] + a[mask]
>>> count = numpy.bincount(label)
>>> count
array([6, 0, 1, 0, 6, 0, 0, 0, 3])
>>> count = count.reshape(3, 3)
>>> numpy.sum(count, axis=1)
array([7, 6, 3])
>>> numpy.sum(count, axis=0)
array([6, 6, 4])
>>> numpy.sum(count, axis=1) + numpy.sum(count, axis=0)
array([13, 12, 7])
>>> numpy.sum(count, axis=1) + numpy.sum(count, axis=0) - numpy.diag(count)
array([7, 6, 4])
参考链接: https://blog.csdn.net/baidu_27643275/article/details/90445422