BiGAN 简介与代码实战
1.介绍
在AAEGan(AAEGan 简介与代码实战)中,图片经过编码端可以被提取出隐变量z,隐变量z通过解码端可以被生成图片,其实这里面就有一种对称美,我们今天的猪脚BiGan也是有对称美。更加详细的内容可以参见论文: ADVERSARIAL FEATURE LEARNING
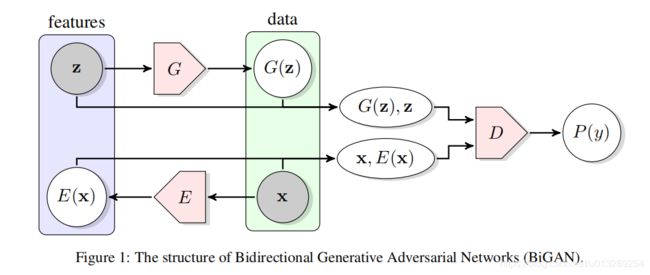
2.模型结构
整个结构包括三部分:Encode网络,G网络,D网络。
Encode网络,提取原始图片的隐变量
G网络,将噪声生成图片
D网络,判断这个配对(原始图片和隐变量 生成图片和噪声)是来自encoder还是decoder
3.模型特点
bigan的全称是Bidirectional GAN,中文翻译是“双向Gan”,对于配对“原始图片和隐变量 ”原始图片是已知的,隐变量 是学习噪声,对于配对“生成图片和噪声”,噪声是已知的,生成图片是学习原始图片,这就是一个双向学习过程。
4.代码实现keras
class BIGAN():
def __init__(self):
self.img_rows = 28
self.img_cols = 28
self.channels = 1
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.latent_dim = 100
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
# Build and compile the discriminator
self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator()
self.discriminator.compile(loss=['binary_crossentropy'],
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
self.generator = self.build_generator()
# Build the encoder
self.encoder = self.build_encoder()
# The part of the bigan that trains the discriminator and encoder
self.discriminator.trainable = False
# Generate image from sampled noise
z = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim, ))
img_ = self.generator(z)
# Encode image
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
z_ = self.encoder(img)
# Latent -> img is fake, and img -> latent is valid
fake = self.discriminator([z, img_])
valid = self.discriminator([z_, img])
# Set up and compile the combined model
# Trains generator to fool the discriminator
self.bigan_generator = Model([z, img], [fake, valid])
self.bigan_generator.compile(loss=['binary_crossentropy', 'binary_crossentropy'],
optimizer=optimizer)
def build_encoder(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Flatten(input_shape=self.img_shape))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(self.latent_dim))
model.summary()
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
z = model(img)
return Model(img, z)
def build_generator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(512, input_dim=self.latent_dim))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(np.prod(self.img_shape), activation='tanh'))
model.add(Reshape(self.img_shape))
model.summary()
z = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
gen_img = model(z)
return Model(z, gen_img)
def build_discriminator(self):
z = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim, ))
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
d_in = concatenate([z, Flatten()(img)])
model = Dense(1024)(d_in)
model = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(model)
model = Dropout(0.5)(model)
model = Dense(1024)(model)
model = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(model)
model = Dropout(0.5)(model)
model = Dense(1024)(model)
model = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(model)
model = Dropout(0.5)(model)
validity = Dense(1, activation="sigmoid")(model)
return Model([z, img], validity)
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X_train, _), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Rescale -1 to 1
X_train = (X_train.astype(np.float32) - 127.5) / 127.5
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Sample noise and generate img
z = np.random.normal(size=(batch_size, self.latent_dim))
imgs_ = self.generator.predict(z)
# Select a random batch of images and encode
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs = X_train[idx]
z_ = self.encoder.predict(imgs)
# Train the discriminator (img -> z is valid, z -> img is fake)
d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch([z_, imgs], valid)
d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch([z, imgs_], fake)
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# ---------------------
# Train Generator
# ---------------------
# Train the generator (z -> img is valid and img -> z is is invalid)
g_loss = self.bigan_generator.train_on_batch([z, imgs], [valid, fake])
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D loss: %f, acc: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[1], g_loss[0]))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
self.sample_interval(epoch)
def sample_interval(self, epoch):
r, c = 5, 5
z = np.random.normal(size=(25, self.latent_dim))
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(z)
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt, :,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/mnist_%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()