逻辑回归-梯度下降法 python实现
机器学习的基本框架:
模型(model)、目标(cost function)、优化算法
Step1:对于一个问题,需要首先建立一个模型,如回归或分类模型;
step2:通过最小分类误差、最大似然或最大后验概率建立模型的代价函数;
step3:最优化问题求解
a.如果优化函数存在解析解,则可以通过一般的求值方法-对代价函数求导,找到倒数为0的点,即是最大值或者最小孩子;
b.如果上述方法求优化函数导数比较复杂,可利用迭代算法也求解。
对于回归问题:
(1)模型
可选择的模型有线性回归和LR回归。
(2)目标-cost function
线性回归模型:
LR回归模型:
线性回归的假设前提是y服从正态分布,LR回归的假设前提是y服从二项分布(y非零即1)。
(3)算法-最优化算法
梯度下降法、牛顿法等;
Python代码:
LRgradAscent.py
from numpy import *
def loadData(filepath):
dataMat= []
labels = []
fr = open(filepath)
for line in fr.readlines():
str = line.strip().split('\t')
dataMat.append([1.0,float(str[0]),float(str[1])])
labels.append(int(str[2]))
return mat(dataMat), mat(labels).transpose()
def sigmoid(inX):
return 1.0/(1+exp(-inX))
def gradAscent(dataMatrix,labelsMatrix):
n,m = shape(dataMatrix)
weights = ones((m,1))
step = 0.001
iter = 500
for k in range(iter):
value = sigmoid(dataMatrix*weights)
chazhi = labelsMatrix - value
grad = dataMatrix.transpose()*chazhi
weights = weights + step * grad
return weights
def plotBestFit(weights,filepath):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# illustrate the samples
dataMatrix,labelsMatrix = loadData(filepath)
n,m = shape(dataMatrix)
xcord1 = []; ycord1 = [] #store the coordination of sample having label 1
xcord2 = []; ycord2 = []
for i in range(n):
if int(labelsMatrix[i]) == 1:
xcord1.append(dataMatrix[i,1])
ycord1.append(dataMatrix[i,2])
else:
xcord2.append(dataMatrix[i,1])
ycord2.append(dataMatrix[i,2])
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.scatter(xcord1,ycord1,s = 30,c = 'red',marker = 's')
ax.scatter(xcord2,ycord2,s = 30,c = 'green')
#illustrate the classifying line
min_x = min(dataMatrix[:,1])[0,0]
max_x = max(dataMatrix[:,2])[0,0]
y_min_x = (-weights[0] - weights[1] * min_x) / weights[2]
y_max_x = (-weights[0] - weights[1] * max_x) / weights[2] #here, sigmoid(wx = 0) so wo + w1*x1 + w2*x2 = 0
plt.plot([min_x,max_x],[y_min_x[0,0],y_max_x[0,0]],'-g')
plt.show()测试程序:
import LRgradAscent
import pdb
filename = 'testSet.txt'
dataMat, labelsMat = LRgradAscent.loadData(filename)
weights = LRgradAscent.gradAscent(dataMat,labelsMat)
LRgradAscent.plotBestFit(weights,filename)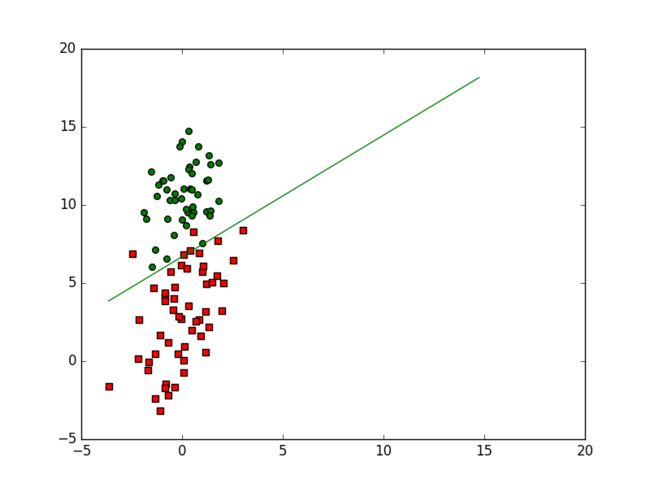
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09/article/details/20319673