SpringBoot 开发手册
一、SpringBoot介绍及目录结构
Springboot使用”习惯优于配置”。可以以jar包形式运行。内嵌tomcat、Jetty无需war部署。Spring提供了一系列的starter pom来简化maven依赖加载,简化maven配置。Spring Boot会根据在类路径中的jar包、类,为jar包里的类自动配置Bean,这样会极大地减少我们要使用的配置。
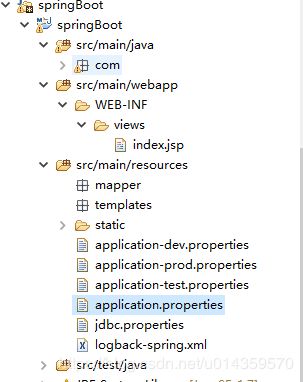
- src/main/java:主程序入口 TinyContractApplication,可以通过直接运行该类来 启动 Spring Boot应用
- src/main/resources:配置目录,该目录用来存放应用的一些配置信息,比如应用名、服务端口、数据库配置等。由于我们应用了Web模块,因此产生了 static目录与templates目录,前者用于存放静态资源,如图片、CSS、JavaScript等;后者用于存放Web页面的模板文件。application.properties 用来保存数据库链接信息等应用程序数据
- src/test:单元测试目录,生成的 TinyContractApplicationTests 通过 JUnit4实现,可以直接用运行 Spring Boot应用的测试。
spring boot对静态资源的默认扫描路径是:
classpath:/static
classpath:/public
classpath:/resources
classpath:/META-INF/resources
spring boot默认配置的动态页面路径:
classpath:/templates
二、构建工程
1、创建一个Maven Project 或者 一组Maven Module
maven相关命名说明
1、Group:一般为逆向域名格式,例:com.sw.buis
2、Artifact:唯一标识,一般为项目名称。 具体maven相关信息,可自行搜索,这里只简单阐述,例:sw-dec-front
2、在 pom.xml 文件中添加如下依赖:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
1.5.6.RELEASE
UTF-8
UTF-8
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
true
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
true
3、springboot多环境配置
创建 src/main/resources 源文件目录创建三个配置文件:
application-dev.properties:用于开发环境
application-test.properties:用于测试环境
application-prod.properties:用于生产环境
我们可以在这个三个配置文件中设置不同的信息,application.properties 配置公共的信息。
在 application.properties 中配置:
# 指定环境为dev
spring.profiles.active=dev
表示激活 application-dev.properties 文件配置, springboot 会加载使用 application.properties 和 application-dev.properties 配置文件的信息。
在不同环境下,可能加载不同的bean时,可利用@Profile注解来动态激活。
@Profile("dev")//支持数组:@Profile({"dev","test"})
@Configuration
public class ProfileBean {}
4、配置日志
1)、配置 logback(官方推荐使用)
src/main/resources 为classpath:
spring boot 默认会加载 classpath:logback-spring.xml 或者 classpath:logback-spring.groovy。
如需要自定义文件名称,在 application.properties 中配置 logging.config 选项即可。
${PATTERN}
${TEST_FILE_PATH}
${TEST_FILE_PATH}/info.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log
100
${PATTERN}
${PRO_FILE_PATH}
${PRO_FILE_PATH}/warn.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log
100
${PATTERN}
其中,springProfile 标签的 name 属性对应 application.properties 中的 spring.profiles.active=dev 的配置。
即 spring.profiles.active 的值可以看作是日志配置文件中对应的 springProfile 是否生效的开关。
5、打包部署
由于SpringBoot内置了tomcat可以打包成jar ,因为内置tomcat 可以使用 java -jar xx.jar ,或者使用tomcat 运行。
//使用@SpringBootApplication指定这是一个SpringBoot 应用程序
@SpringBootApplication
//使用@ComponentScan("com.*") 扫描注入
@ComponentScan("com.*")
public class SpringbootApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder application) {
return application.sources(SpringbootApplication.class);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}
三、SpringBoot注解
1、@SpringBootApplication
使用@SpringBootApplication指定这是一个SpringBoot 应用程序。Spring Boot 还会自动扫描 @SpringBootApplication 所在类的同级包以及下级包里的 Bean ,所以入口类建议就配置在 grounpID + arctifactID 组合的包名下(这里为 cn.wmyskxz.springboot 包)
SpringBoot项目的Bean装配默认规则是根据Application类所在的包位置从上往下扫描! “Application类”是指SpringBoot项目入口类。如果Application类所在的包为:io.github.gefangshuai.app,则只会扫描io.github.gefangshuai.app包及其所有子包。@SpringBootApplication会默认扫描,如需特殊扫描再使用 @ComponentScan("com.*") 、 @MapperScan 和 @Mapper。
@SpringBootApplication由以下3个注解组成:
@SpringBootConfiguration 实际上就是@Configuration注解,表明这个类是一个配置类
@EnableAutoConfiguration则表示让Spring Boot根据类路径中的jar包依赖为当前项目进行自动配置
@ComponentScan会扫描当前包及其子包下被@Component,@Controller,@Service,@Repository等注解标记的类并纳 入到spring容器中进行管理。
2、@Controller 和 @RestController
@RestController = @Controller + @ResponseBody 默认返回json格式。
@Controller 返回View 界面。
3、@RequestMapping
处理请求地址映射的注解,可用于类或方法上。常用属性:
value: 指定请求的实际地址,指定的地址可以是URI Template 模式;
method: 指定请求的method类型, GET、POST、PUT、DELETE等;
consumes: 指定处理请求的提交内容类型(Content-Type),
例如application/json, text/html;
produces: 指定返回的内容类型,仅当request请求头中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回;
4、@RequestBody 和 @ResponseBody
@RequestBody注解允许request的参数在reqeust体中,常常结合前端POST请求,进行前后端交互。
@ResponseBody注解支持将的参数在reqeust体中,通常返回json格式给前端。
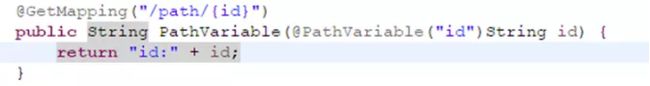
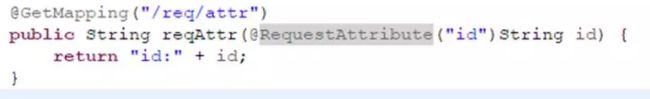
5、@PathVariable、@RequestParam、@RequestAttribute
@RequestParam 用来接收URL中的参数get请求,如/param?id=001
// required=false表示不传的话,会给参数赋值为null,required=true就是必须要有
@RequestAttribute用于访问由过滤器或拦截器创建的、预先存在的请求属性,效果等同与request.getAttrbute()。
6、@Component、@Service、@Repository
@Component 最普通的组件,可以被注入到spring容器进行管理
@Repository 作用于持久层
@Service 作用于业务逻辑层
7、@ComponentScan("com.*")
@ComponentScan是组件扫描注解,用来扫描@Controller @Service @Repository这类,主要就是定义扫描的路径从中找出 标志了需要装配的类到Spring容器中
@ComponentScan等价于
8、@MapperScan({"com.kfit.demo","com.kfit.user"}) 和 @Mapper 作用一样
@Mapper需要在每个Mapper 的接口类上加 ,
@MapperScan 只需要就接口类扫描即可,就不用每个 Mapper 接口上加@Mapper通过使用@MapperScan可以指定要扫描 的Mapper类的包的路径,可替代下面代码
@Bean
public MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer() {
MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer = new MapperScannerConfigurer();
//获取之前注入的beanName为sqlSessionFactory的对象
mapperScannerConfigurer.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName("sqlSessionFactory");
//指定xml配置文件的路径
mapperScannerConfigurer.setBasePackage("com.buis.demo.spi.dao");
return mapperScannerConfigurer;
}9、@Configuration 和@Bean
@Configuration相当于xml 中的
一般@Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages = "xxx") 一起使用。
@Bean相当于xml 中的
@Bean的作用是注册bean对象,那么完全可以使用@Component、@Controller、@Service、@Ripository、@Component 等注解注册bean,当然需要配置@ComponentScan注解进行自动扫描。
10、@EnableXXX注解
@EnableXXX 注解一般都是开启某些注解功能的注解。
11、利用@PropertySource注解既可以引入配置文件。
可使用@PropertySources设置数组,引入多个文件。使用上面注解系统会自动加载。
12、@PostConstruct和@PreConstruct
1.@PostConstruct说明
被@PostConstruct修饰的方法会在服务器加载Servlet的时候运行,并且只会被服务器调用一次,类似于Serclet的inti()方法。被@PostConstruct修饰的方法会在构造函数之后,init()方法之前运行。
2.@PreConstruct说明
被@PreConstruct修饰的方法会在服务器卸载Servlet的时候运行,并且只会被服务器调用一次,类似于Servlet的destroy()方法。被@PreConstruct修饰的方法会在destroy()方法之后运行,在Servlet被彻底卸载之前。
13、@Profile
在不同环境下,可能加载不同的bean时,可利用@Profile注解来动态激活。
@Profile("dev")//支持数组:@Profile({"dev","test"})
@Configuration
public class ProfileBean {}
14、@WebFilter
过滤器Filter,@WebFilter时Servlet3.0新增的注解,通过此注解,启动启动时会自动扫描自动注册。
四、常规属性配置
1、中文不做特殊处理会乱码
处理方式为继续在application.properties中添加如下代码:
server.tomcat.uri-encoding=UTF-8
spring.http.encoding.charset=UTF-8
spring.http.encoding.enabled=true
spring.http.encoding.force=true
spring.messages.encoding=UTF-8
2、访问路径配置:
默认访问路径是http://localhost:8080,我将之改为http://localhost:8081/helloboot
application.properties文件中添加如下代码:
# 应用上下文路径
server.context-path=/helloboot
# 端口号
server.port=8081