ELFK日志平台入门2---Elasticseach集群搭建
ELFK日志平台入门1---架构设计
ELFK日志平台入门2---Elasticseach集群搭建
ELFK日志平台入门3---Kibana搭建
ELFK日志平台入门4---Kafka集群搭建
ELFK日志平台入门5---Logstash+Filebeat集群搭建
这个章节我们介绍下Elasticseach集群搭建以及Elasticseach-head的搭建。
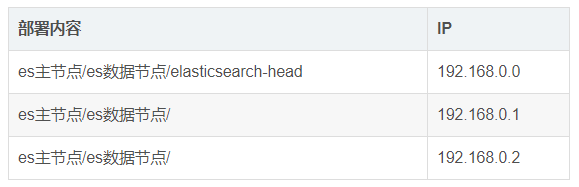
1、环境准备
注:以下操作系统均为centos7+为例
资源规划:
环境配置(全部服务器配置):
- 全部关闭防火墙和selinux:
# systemctl stop firewalld && systemctl disable firewalld
# sed -i 's/=enforcing/=disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config && setenforce 0- 修改最大文件描述符限制:
# vim /etc/security/limits.conf
* soft nofile 65536
* hard nofile 131072
* soft nproc 2048
* hard nproc 4096- 修改内存权限大小:
# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
vm.max_map_count=655360
# sysctl -p- 安装Java环境:
# yum install -y java-1.8.0-openjdk*2、Elasticsearch集群部署
- 上传ELKF、Kafka相关安装包,目录:/app/elk(可自定义):
[root@iZuf6dxdji7ys1e6mfapcfZ elk]# ls
elasticsearch-6.2.4.tar.gz filebeat-6.2.4-linux-x86_64.tar.gz kibana-6.2.4-linux-x86_64.tar.gz node-v8.11.3-linux-x64.tar.xz
elasticsearch-head-master.zip kafka_2.11-1.0.0.tgz logstash-6.2.4.tar.gz phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64.tar.bz2
[root@iZuf6dxdji7ys1e6mfapcfZ elk]# pwd
/app/elk
- 创建用户elk:
# useradd elk- 安装Elasticsearch:
# cd /app/elk
# tar zxf elasticsearch-6.2.4.tar.gz && mv elasticsearch-6.2.4 /usr/local/elasticsearch
# mkdir /usr/local/elasticsearch/data
# chown -R elk:elk /usr/local/elasticsearch
- 修改Elasticsearch配置 :
# vim /usr/local/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: elk #集群名,同一集群必须相同
node.name: elk-0 #指定节点主机名(注:每台主机不同)
node.master: true #允许成为主节点
node.data: true #允许成为数据节点
path.data: /usr/local/elasticsearch/data #数据存放路径
path.logs: /usr/local/elasticsearch/logs #日志路径
bootstrap.memory_lock: false #关闭锁定内存,设置为true会报错
network.host: 192.168.0.0 #监听ip(注:每台主机不同)
http.port: 9200 #http端口
transport.tcp.port: 9300
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.0.0", "192.168.0.1", "192.168.0.2"] #初始主机列表
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2 # n/2+1
http.enabled: true #使用http协议对外提供服务
http.cors.enabled: true #允许head插件访问es
http.cors.allow-origin: "*" #跨域解决这里会遇到一个问题 bootstrap.memory_lock: true:
# vim /etc/security/limits.conf
baoshan soft memlock unlimited
baoshan hard memlock unlimited
# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
vm.swappiness=0
# reboot
- 启动Elasticsearch:
# su - elk -c "/usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch -d"
# tail -f /usr/local/elasticsearch/logs/elk.log #查看日志,是否正常启动- 查看Elasticsearch集群健康状态:
# curl '192.168.0.0:9200/_cluster/health?pretty'
{
"cluster_name" : "elk",
"status" : "green",
"timed_out" : false,
"number_of_nodes" : 3,
"number_of_data_nodes" : 3,
"active_primary_shards" : 0,
"active_shards" : 0,
"relocating_shards" : 0,
"initializing_shards" : 0,
"unassigned_shards" : 0,
"delayed_unassigned_shards" : 0,
"number_of_pending_tasks" : 0,
"number_of_in_flight_fetch" : 0,
"task_max_waiting_in_queue_millis" : 0,
"active_shards_percent_as_number" : 100.0
}
# curl '192.168.0.1:9200/_cluster/health?pretty'
# curl '192.168.0.2:9200/_cluster/health?pretty' #返回结果与上面一致则成功
- 配置Elasticsearch服务:
# vim /etc/sysconfig/elasticsearch
################################
# Elasticsearch
################################
# Elasticsearch home directory
#ES_HOME=/usr/share/elasticsearch
ES_HOME=/usr/local/elasticsearch
# Elasticsearch Java path
#JAVA_HOME=
JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk
CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar:$JAVA_HOME/jre/lib
# Elasticsearch configuration directory
#ES_PATH_CONF=/etc/elasticsearch
ES_PATH_CONF=/usr/local/elasticsearch/config
# Elasticsearch PID directory
#PID_DIR=/var/run/elasticsearch
PID_DIR=/usr/local/elasticsearch/run
# Additional Java OPTS
#ES_JAVA_OPTS=
# Configure restart on package upgrade (true, every other setting will lead to not restarting)
#RESTART_ON_UPGRADE=true
################################
# Elasticsearch service
################################
# SysV init.d
#
# The number of seconds to wait before checking if Elasticsearch started successfully as a daemon process
ES_STARTUP_SLEEP_TIME=5
################################
# System properties
################################
# Specifies the maximum file descriptor number that can be opened by this process
# When using Systemd, this setting is ignored and the LimitNOFILE defined in
# /usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service takes precedence
#MAX_OPEN_FILES=65535
# The maximum number of bytes of memory that may be locked into RAM
# Set to "unlimited" if you use the 'bootstrap.memory_lock: true' option
# in elasticsearch.yml.
# When using systemd, LimitMEMLOCK must be set in a unit file such as
# /etc/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service.d/override.conf.
#MAX_LOCKED_MEMORY=unlimited
# Maximum number of VMA (Virtual Memory Areas) a process can own
# When using Systemd, this setting is ignored and the 'vm.max_map_count'
# property is set at boot time in /usr/lib/sysctl.d/elasticsearch.conf
#MAX_MAP_COUNT=262144
配置服务文件:
# vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service
[Unit]
Description=Elasticsearch
Documentation=http://www.elastic.co
Wants=network-online.target
After=network-online.target
[Service]
RuntimeDirectory=elasticsearch
PrivateTmp=true
Environment=ES_HOME=/usr/local/elasticsearch
Environment=ES_PATH_CONF=/usr/local/elasticsearch/config
Environment=PID_DIR=/usr/local/elasticsearch/run
EnvironmentFile=-/etc/sysconfig/elasticsearch
WorkingDirectory=/usr/local/elasticsearch
User=elk
Group=elk
ExecStart=/usr/local/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch -p ${PID_DIR}/elasticsearch.pid --quiet
# StandardOutput is configured to redirect to journalctl since
# some error messages may be logged in standard output before
# elasticsearch logging system is initialized. Elasticsearch
# stores its logs in /var/log/elasticsearch and does not use
# journalctl by default. If you also want to enable journalctl
# logging, you can simply remove the "quiet" option from ExecStart.
StandardOutput=journal
StandardError=inherit
# Specifies the maximum file descriptor number that can be opened by this process
LimitNOFILE=65535
# Specifies the maximum number of processes
LimitNPROC=4096
# Specifies the maximum size of virtual memory
LimitAS=infinity
# Specifies the maximum file size
LimitFSIZE=infinity
# Disable timeout logic and wait until process is stopped
TimeoutStopSec=0
# SIGTERM signal is used to stop the Java process
KillSignal=SIGTERM
# Send the signal only to the JVM rather than its control group
KillMode=process
# Java process is never killed
SendSIGKILL=no
# When a JVM receives a SIGTERM signal it exits with code 143
SuccessExitStatus=143
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
# Built for packages-6.7.1 (packages)
管理服务:
# chmod +x /usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service
# mkdir /usr/local/elasticsearch/run
# touch /usr/local/elasticsearch/run/elasticsearch.pid && chown -R elk:elk /usr/local/elasticsearch
# systemctl daemon-reload
# systemctl enable elasticsearch
# systemctl start elasticsearch #先kill之前的elasticsearch进程
# yum install -y bash-completion && source /etc/profile #命令自动补全
2、Elasticsearch-head部署
Ealsticsearch只是后端提供各种api,那么怎么直观的使用它呢?Elasticsearch-head是一款专门针对于Elasticsearch的客户端工具。下面介绍安装流程:
- 因为Elasticsearch-head是node.js开发,需先安装node.js:
# cd /app/elk
# tar -Jxf node-v8.11.3-linux-x64.tar.xz && mvnode-v8.11.3-linux-x64/ /usr/local/node
# vim /etc/profile
export NODE_HOME=/usr/local/node
export PATH=$NODE_HOME/bin:$PATH
export NODE_PATH=$NODE_HOME/lib/node_modules:$PATH
# source /etc/profile
# node -v
v8.11.3 #出现node版本即为成功
- 安装相关插件:
# cd /app/elk
# unzip elasticsearch-head-master.zip && mv elasticsearch-head-master/ /usr/local/elasticsearch-head
# npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org
# cnpm install -g grunt-cli
# cnpm install -g grunt
# cnpm install grunt-contrib-clean
# cnpm install grunt-contrib-concat
# cnpm install grunt-contrib-watch
# cnpm install grunt-contrib-connect
# cnpm install grunt-contrib-copy
# cnpm install grunt-contrib-jasmine #若报错就再执行一遍
- 环境配置 :
# vim /usr/local/elasticsearch-head/Gruntfile.js
connect: {
server: {
options: {
hostname: '0.0.0.0', #增加hostname
port: 9100,
base: '.',
keepalive: true
}
}
}
- 启动Elasticsearch-head:
# cd /usr/local/elasticsearch-head
# nohup grunt server &
- 浏览器访问 (未创建索引里面无数据):
至此,Elasticsearch集群已经搭建完成,后面继续介绍相关组件搭建。