Apriori算法,MATLAB代码实现
Apriori算法简介:
想必大家都知道apriori算法的原理吧,最著名的关联规则发现方法R.Agrawal提出的Apriori算法。
- 1 Apriori 算法的基本思想
- 2 Apriori算法的基本思想是通过对数据库的多次扫描来计算项集的支持度,发现的频繁项集从而生成关联规则。Apriori算法对数据集进行多次扫描。第一次扫描得到频繁1-项集的集合
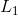 ,第k(k>1)次扫描的结果
,第k(k>1)次扫描的结果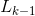 来产生候选k-项集的集合
来产生候选k-项集的集合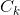 ,然后在扫描的过程中确定
,然后在扫描的过程中确定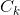 中元素的支持度,最后在每一次扫描结束时计算频繁k-项集的集合
中元素的支持度,最后在每一次扫描结束时计算频繁k-项集的集合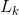 ,算法在当候选k-项集的集合
,算法在当候选k-项集的集合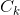 为空时结束。
为空时结束。 - Apriori算法产生频繁项集的过程
- 产生频繁项集的过程主要分为连接和剪枝两步:
(1)连接步。为找到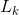 (k>=2),通过
(k>=2),通过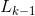 与自身作连接产生候选k-项集的集合
与自身作连接产生候选k-项集的集合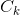 。设
。设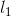 和
和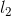 是
是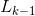 中的项集。记
中的项集。记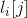 表示
表示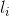 的第j个项。Apriori算法假定事务或项集中的项按字典次序排序;对于(k-1)项集
的第j个项。Apriori算法假定事务或项集中的项按字典次序排序;对于(k-1)项集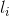 ,对应的项排序为
,对应的项排序为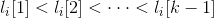 。如果
。如果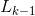 的元素
的元素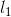 和
和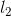 的前(k-2)个对应项相等,则
的前(k-2)个对应项相等,则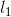 和
和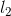 。即如果
。即如果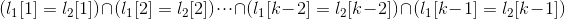 时,
时, 和
和 可连接。条件
可连接。条件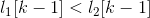 可以保证不产生重复,而按照
可以保证不产生重复,而按照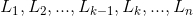 次序寻找频繁项集可以避免对事务数据库中不可能发生的项集所进行的搜索和统计工作。连接
次序寻找频繁项集可以避免对事务数据库中不可能发生的项集所进行的搜索和统计工作。连接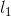 和
和 产生的结果项集为(
产生的结果项集为(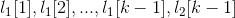 )。
)。
(2)剪枝步。由Apriori算法的性质可知,频繁k-项集的任何子集必须是频繁项集。由连接生成的集合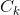 需要进行验证,去除不满足支持度的非频繁k-项集。
需要进行验证,去除不满足支持度的非频繁k-项集。
- 产生频繁项集的过程主要分为连接和剪枝两步:
- Apriori算法的主要步骤
(1)扫描全部数据,产生候选1-项集的集合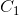 .
.
(2)根据最小支持度,由候1-选项集的集合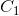 产生频繁1-项集的集合
产生频繁1-项集的集合 。
。
(3)对k>1,重复执行步骤(4)(5)(6)。
(4)由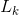 执行连接和剪枝操作,产生候选(k+1)-项集集合
执行连接和剪枝操作,产生候选(k+1)-项集集合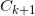 。
。
(5)根据最小支持度,由候选(k+1)-项集的集合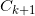 ,产生频繁(k+1)-项集集合
,产生频繁(k+1)-项集集合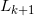 。
。
(6)若L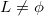 ,则k=k+1,跳往步骤(4);否则,跳往步骤(7)。
,则k=k+1,跳往步骤(4);否则,跳往步骤(7)。
(7)根据最小置信度,由频繁项集产生强关联规则,结束。 - Apriori算法描述
输入:数据库D,最小支持度阈值min_sup。
输出:D中的频繁项集L。
(1)Begin
(2) =1-频繁项集;
=1-频繁项集;
(3)for(k=1;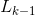 )
) ;k++)do begin
;k++)do begin
(4) =Apriori_gen(
=Apriori_gen(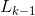 );{调用函数Apriori_gen(
);{调用函数Apriori_gen(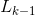 )}通过频繁项集(k-1)-项集产生候选项k-项集}
)}通过频繁项集(k-1)-项集产生候选项k-项集}
(5)for 所有数据集 do begin{扫描D用于计数}
do begin{扫描D用于计数}
(6) =subset(
=subset(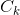 ,t);{用subset找出该事物中候选的所有子集}
,t);{用subset找出该事物中候选的所有子集}
(7)for 所有候选集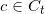 do
do
(8)c.count++;
(9)end
(10)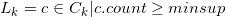
(11)end
(12)end
(13)Return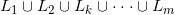 {形成频繁集集合}
{形成频繁集集合} MATLAB实现Apriori算法的过程:
算法一:扫描数据库生成布尔矩阵后,对这个布尔矩阵进行操作,通过Apriori的连接步剪枝步找到其候选项集,然后把候选项集生成候选项集向量,比如数据库中的事务集有5个项,5个事务:事务矩阵T
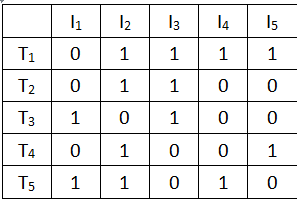
这就是生成的布尔矩阵,其中T代表的是事务,I代表的是项(属性),怎样扫描这个事务矩阵呢?这个算法中是用候选项集向量匹配事务矩阵中的每一行,比如候选2-项集为{ }那么它的候选2-项集的向量为s=[0 1 1 0 0],为了求出此候选集的支持度,直接用s分别和事务矩阵的每行做内积,即sum=s./T(i,:),i为T的行数,第i行
}那么它的候选2-项集的向量为s=[0 1 1 0 0],为了求出此候选集的支持度,直接用s分别和事务矩阵的每行做内积,即sum=s./T(i,:),i为T的行数,第i行如果 sum==2 则此候选项集的支持度计数+1
这样就求出了此候选项集的支持度了。
Apriori.m
function Apriori(T, minSup)
M = size(T,1);%事务数
N = size(T,2);%属性数
C=cell(1,N);
STCount=sum(T)/M;%候选集的支持度
for r=1:N
C{r}=r;
end
L=C(STCount>minSup);%把count里面的>=MST的值找出来
LL=L;
ICount=sum(T,2);%T矩阵的各行之和
k=1;%频繁项集的项?
disp(numel(L));
% Initialize Counter
k=1;%频繁项集的项数
B=[];
BB=reshape(cell2mat(L),1,numel(L));
% Iterations
while ~isempty(L)%可以直接用这个isempty()函数来判空。while循环是生成频繁项集的大循环41-87行,由L{k}-->L{k+1}变化
C={};
%L={};
u=0;
for r=1:numel(L)
for i=r:(numel(L)-1)
x1=L{r};
x2=L{i+1};
if k==1
c=0;
else
y1=x1;
y2=x2;
y1(k)=[];
y2(k)=[];
c = sum(y1==y2);%求两个候选集的交集
end
if (c==k-1)%判断1.交集长度是否为1,2.判断交集c和x1前le-1相同的个数是否le-1
NEW=x1;
NEW(k+1)=x2(k);
sub_set=subset(NEW);%求NEW的子集
%生成该候选项的所有K-1项子集
len=length(sub_set);
%判断这些K-1项自己是否都为频繁的
p=1; n=0;
while(p && n1;%计数子集属于频繁项集的个数
if k==1
p=in(sub_set{n},BB);%in函数判断NEW子集是否属于L频繁项集
else
p=in(sub_set{n},B);%in函数判断NEW子集是否属于L频繁项集
end
end
if n==len%如果计数n和len相等,则其子集全部属于频繁项集
u=u+1;
%候选k项集
C{u}=NEW;%把这个符合条件的NEW集归于C候选集合
end
else
break;
end
end
end
L={};
w=0;
for r=1:numel(C)
SS=zeros(N,1);
SS(C{r})=1;
Sup=sum(T*SS==k+1)/M;
if Sup > minSup
w=w+1;
L{w}=C{r};
end
end
B=reshape(cell2mat(L),k+1,numel(L));
disp(numel(L));%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
clear C;
k=k+1;
end
end BooleMatrix.m把数据转化为布尔矩阵,注意读入的数据一定是每行数据的个数一致
function [ B ] = BooleMatrix(A)
%UNTITLED Summary of this function goes here
% Detailed explanation goes here
M=size(A,1);
N=size(A,2);
B=zeros(M,119);
for i=1:M
for j=1:N
B(i,A(i,j))=1;
end
end
end
in.m判断候选项集的子集是否频繁项集
function [re]=Copy_of_in(a,b)
re=0;
b=b';
m=size(b,1);
n=length(a);
if(sum(all(b == repmat(a,size(b,1),1),2))==1)
re=1;
end
end Main.m主函数,运行这个文件就可以
function Main()
load mushroom.mat;
MushroomBooleMatrix=BooleMatrix(mushroom);
minSup = 0.2;
Apriori(MushroomBooleMatrix,minSup);
endsubset.m求出候选项集的子集
function [a]=subset(b)
%对于含有k个元素的集合,生成该集合的所有k-1项子集
%生成过程,用全集分别减去某一个元素就可以得到一个K-1项子集
m=length(b);
a{1}=b(2:m);
for i=2:m
NEW=b;
NEW(i)=[];
a{i}=NEW;
end
end 算法二:这个算法和上个算法不同之处在于,这个算法求支持度时是把候选项集所对应的事务矩阵的列找出来进行求“与”操作,比如某候选2-项集为{![]() },则取出这两列的事务矩阵进行相”与”操作,即:[11011]&[11100]=[1 1 0 0 0]则此候选2-项集的支持度计数为2;其他类此!代码如下:
},则取出这两列的事务矩阵进行相”与”操作,即:[11011]&[11100]=[1 1 0 0 0]则此候选2-项集的支持度计数为2;其他类此!代码如下:
Apriori找频繁项集的函数
function Apriori(T, minSup)
M = size(T,1);%事务数
% Number of attributes in the dataset
N = size(T,2);%属性数
% Find frequent item sets of size 1 (list of all items with minSup)
L={};
for i = 1:N
S = sum(T(:,i))/M;
if S >= minSup
L = [L; i];
end
end
LL=L;
%Find frequent item sets of size >=2 and from those identify rules with minConf
% Initialize Counter
disp(numel(LL));%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Initialize Counter
k=1;%频繁项集的项数
% Iterations
while ~isempty(LL)%可以直接用这个isempty()函数来判空。while循环是生成频繁项集的大循环41-87行,由L{k}-->L{k+1}变化
C={};
L={};
w=0;
for r=1:numel(LL)
for i=r:(numel(LL)-1)
Ecount=0;
for j=1:(k-1)
if(LL{r}(j)==LL{i+1}(j))
Ecount=Ecount+1;
else
break;
end
end
if(Ecount==(k-1))
w=w+1;
NEW=LL{r};
NEW(k+1)=LL{i+1}(k);
C{w}=NEW;
else
break;
end
end
end
w=0;
for r=1:numel(C)
S=T(:,C{r});
[~, x]=size(S);
SS=ones(M,1);
for i=1:x
SS=SS&(S(:,i));
end
Sup=sum(SS)/M;
if Sup >= minSup
w=w+1;
L{w}=C{r};
end
end
LL=L;
disp(numel(LL));%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Increment Counter
k=k+1;
end
endBooleMatrix.m生成布尔矩阵
function [ B ] = BooleMatrix(A)
%UNTITLED Summary of this function goes here
% Detailed explanation goes here
M=size(A,1);
N=size(A,2);
B=zeros(M,N);
for i=1:M
for j=1:N
B(i,A(i,j))=1;
end
end
end
Main.m主函数,执行此函数就可以
%%%看内存
% % % % % profile on -memory
% % % % % myprog
% % % % % profile viewer
function Main()
load mushroom.mat;
MushroomBooleMatrix=BooleMatrix(mushroom);
minSup = 0.2;
Apriori(MushroomBooleMatrix,minSup);
end