【Android】手撸抖音小游戏潜艇大挑战
《潜水艇大挑战》是抖音上的一款小游戏,以面部识别来驱动潜艇通过障碍物,最近特别火爆,相信很多人都玩过。

一时兴起自己用Android自定义View也撸了一个,发现只要有好的创意,不用高深的技术照样可以开发出好玩的应用。开发过程现拿出来与大家分享一下。
项目地址:
https://github.com/vitaviva/ugame
基本思路
整个游戏视图可以分成三层:
- camera(相机):处理相机的preview以及人脸识别
- background(后景):处理障碍物相关逻辑
- foreground(前景):处理潜艇相关
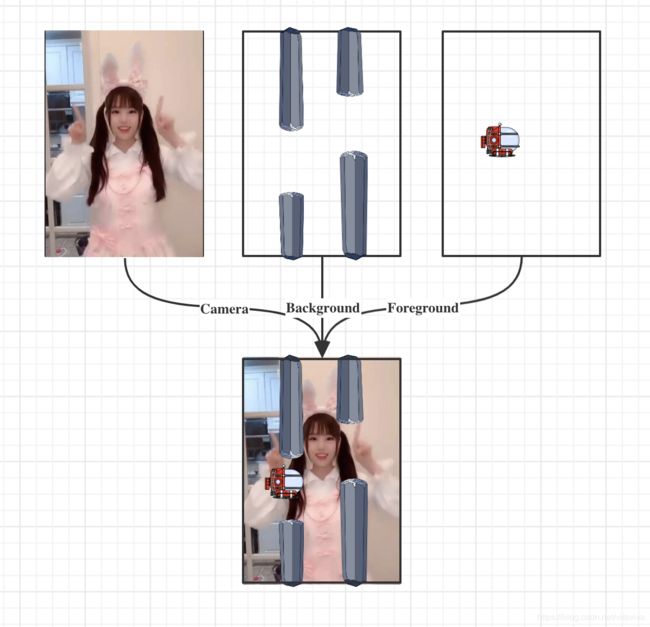
代码也是按上面三个层面组织的,游戏界面的布局可以简单理解为三层视图的叠加,然后在各层视图中完成相关工作
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextureView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
<com.my.ugame.bg.BackgroundView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
<com.my.ugame.fg.ForegroundView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
Framelayout>
开发中会涉及以下技术的使用,没有高精尖、都是大路货:
- 相机:使用Camera2完成相机的预览和人脸识别
- 自定义View:定义并控制障碍物和潜艇
- 属性动画:控制障碍物和潜艇的移动及各种动效
少啰嗦,先看东西!下面介绍各部分代码的实现。
后景(Background)
Bar
首先定义障碍物基类Bar,主要负责是将bitmap资源绘制到指定区域。由于障碍物从屏幕右侧定时刷新时的高度随机,所以其绘制区域的x、y、w、h需要动态设置
/**
* 障碍物基类
*/
sealed class Bar(context: Context) {
protected open val bmp = context.getDrawable(R.mipmap.bar)!!.toBitmap()
protected abstract val srcRect: Rect
private lateinit var dstRect: Rect
private val paint = Paint()
var h = 0F
set(value) {
field = value
dstRect = Rect(0, 0, w.toInt(), h.toInt())
}
var w = 0F
set(value) {
field = value
dstRect = Rect(0, 0, w.toInt(), h.toInt())
}
var x = 0F
set(value) {
view.x = value
field = value
}
val y
get() = view.y
internal val view by lazy {
BarView(context) {
it?.apply {
drawBitmap(
bmp,
srcRect,
dstRect,
paint
)
}
}
}
}
internal class BarView(context: Context?, private val block: (Canvas?) -> Unit) :
View(context) {
override fun onDraw(canvas: Canvas?) {
block((canvas))
}
}
障碍物分为上方和下方两种,由于使用了同一张资源,所以绘制时要区别对待,因此定义了两个子类:UpBar和DnBar
/**
* 屏幕上方障碍物
*/
class UpBar(context: Context, container: ViewGroup) : Bar(context) {
private val _srcRect by lazy(LazyThreadSafetyMode.NONE) {
Rect(0, (bmp.height * (1 - (h / container.height))).toInt(), bmp.width, bmp.height)
}
override val srcRect: Rect
get() = _srcRect
}
下方障碍物的资源旋转180度后绘制
/**
* 屏幕下方障碍物
*/
class DnBar(context: Context, container: ViewGroup) : Bar(context) {
override val bmp = super.bmp.let {
Bitmap.createBitmap(
it, 0, 0, it.width, it.height,
Matrix().apply { postRotate(-180F) }, true
)
}
private val _srcRect by lazy(LazyThreadSafetyMode.NONE) {
Rect(0, 0, bmp.width, (bmp.height * (h / container.height)).toInt())
}
override val srcRect: Rect
get() = _srcRect
}
BackgroundView
接下来创建后景的容器BackgroundView,容器用来定时地创建、并移动障碍物。
通过列表barsList管理当前所有的障碍物,onLayout中,将障碍物分别布局到屏幕上方和下方
/**
* 后景容器类
*/
class BackgroundView(context: Context, attrs: AttributeSet?) : FrameLayout(context, attrs) {
internal val barsList = mutableListOf<Bars>()
override fun onLayout(changed: Boolean, left: Int, top: Int, right: Int, bottom: Int) {
barsList.flatMap { listOf(it.up, it.down) }.forEach {
val w = it.view.measuredWidth
val h = it.view.measuredHeight
when (it) {
is UpBar -> it.view.layout(0, 0, w, h)
else -> it.view.layout(0, height - h, w, height)
}
}
}
提供两个方法start和stop,控制游戏的开始和结束:
- 游戏结束时,要求所有障碍物停止移动。
- 游戏开始后会通过
Timer,定时刷新障碍物
/**
* 游戏结束,停止所有障碍物的移动
*/
@UiThread
fun stop() {
_timer.cancel()
_anims.forEach { it.cancel() }
_anims.clear()
}
/**
* 定时刷新障碍物:
* 1. 创建
* 2. 添加到视图
* 3. 移动
*/
@UiThread
fun start() {
_clearBars()
Timer().also { _timer = it }.schedule(object : TimerTask() {
override fun run() {
post {
_createBars(context, barsList.lastOrNull()).let {
_addBars(it)
_moveBars(it)
}
}
}
}, FIRST_APPEAR_DELAY_MILLIS, BAR_APPEAR_INTERVAL_MILLIS
)
}
/**
* 游戏重启时,清空障碍物
*/
private fun _clearBars() {
barsList.clear()
removeAllViews()
}
刷新障碍物
障碍物的刷新经历三个步骤:
- 创建:上下两个为一组创建障碍物
- 添加:将对象添加到
barsList,同时将View添加到容器 - 移动:通过属性动画从右侧移动到左侧,并在移出屏幕后删除
创建障碍物时会为其设置随机高度,随机不能太过,要以前一个障碍物为基础进行适当调整,保证随机的同时兼具连贯性
/**
* 创建障碍物(上下两个为一组)
*/
private fun _createBars(context: Context, pre: Bars?) = run {
val up = UpBar(context, this).apply {
h = pre?.let {
val step = when {
it.up.h >= height - _gap - _step -> -_step
it.up.h <= _step -> _step
_random.nextBoolean() -> _step
else -> -_step
}
it.up.h + step
} ?: _barHeight
w = _barWidth
}
val down = DnBar(context, this).apply {
h = height - up.h - _gap
w = _barWidth
}
Bars(up, down)
}
/**
* 添加到屏幕
*/
private fun _addBars(bars: Bars) {
barsList.add(bars)
bars.asArray().forEach {
addView(
it.view,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams(
it.w.toInt(),
it.h.toInt()
)
)
}
}
/**
* 使用属性动画移动障碍物
*/
private fun _moveBars(bars: Bars) {
_anims.add(
ValueAnimator.ofFloat(width.toFloat(), -_barWidth)
.apply {
addUpdateListener {
bars.asArray().forEach { bar ->
bar.x = it.animatedValue as Float
if (bar.x + bar.w <= 0) {
post { removeView(bar.view) }
}
}
}
duration = BAR_MOVE_DURATION_MILLIS
interpolator = LinearInterpolator()
start()
})
}
}
前景(Foreground)
Boat
定会潜艇类Boat,创建自定义View,并提供方法移动到指定坐标
/**
* 潜艇类
*/
class Boat(context: Context) {
internal val view by lazy { BoatView(context) }
val h
get() = view.height.toFloat()
val w
get() = view.width.toFloat()
val x
get() = view.x
val y
get() = view.y
/**
* 移动到指定坐标
*/
fun moveTo(x: Int, y: Int) {
view.smoothMoveTo(x, y)
}
}
BoatView
自定义View中完成以下几个事情
- 通过两个资源定时切换,实现探照灯闪烁的效果
- 通过
OverScroller让移动过程更加顺滑 - 通过一个
Rotation Animation,让潜艇在移动时可以调转角度,更加灵动
internal class BoatView(context: Context?) : AppCompatImageView(context) {
private val _scroller by lazy { OverScroller(context) }
private val _res = arrayOf(
R.mipmap.boat_000,
R.mipmap.boat_002
)
private var _rotationAnimator: ObjectAnimator? = null
private var _cnt = 0
set(value) {
field = if (value > 1) 0 else value
}
init {
scaleType = ScaleType.FIT_CENTER
_startFlashing()
}
private fun _startFlashing() {
postDelayed({
setImageResource(_res[_cnt++])
_startFlashing()
}, 500)
}
override fun computeScroll() {
super.computeScroll()
if (_scroller.computeScrollOffset()) {
x = _scroller.currX.toFloat()
y = _scroller.currY.toFloat()
// Keep on drawing until the animation has finished.
postInvalidateOnAnimation()
}
}
/**
* 移动更加顺换
*/
internal fun smoothMoveTo(x: Int, y: Int) {
if (!_scroller.isFinished) _scroller.abortAnimation()
_rotationAnimator?.let { if (it.isRunning) it.cancel() }
val curX = this.x.toInt()
val curY = this.y.toInt()
val dx = (x - curX)
val dy = (y - curY)
_scroller.startScroll(curX, curY, dx, dy, 250)
_rotationAnimator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(
this,
"rotation",
rotation,
Math.toDegrees(atan((dy / 100.toDouble()))).toFloat()
).apply {
duration = 100
start()
}
postInvalidateOnAnimation()
}
}
ForegroundView
- 通过
boat成员持有潜艇对象,并对其进行控制 - 实现
CameraHelper.FaceDetectListener根据人脸识别的回调,移动潜艇到指定位置 - 游戏开始时,创建潜艇并做开场动画
/**
* 前景容器类
*/
class ForegroundView(context: Context, attrs: AttributeSet?) : FrameLayout(context, attrs),
CameraHelper.FaceDetectListener {
private var _isStop: Boolean = false
internal var boat: Boat? = null
/**
* 游戏停止,潜艇不再移动
*/
@MainThread
fun stop() {
_isStop = true
}
/**
* 接受人脸识别的回调,移动位置
*/
override fun onFaceDetect(faces: Array<Face>, facesRect: ArrayList<RectF>) {
if (_isStop) return
if (facesRect.isNotEmpty()) {
boat?.run {
val face = facesRect.first()
val x = (face.left - _widthOffset).toInt()
val y = (face.top + _heightOffset).toInt()
moveTo(x, y)
}
_face = facesRect.first()
}
}
}
开场动画
游戏开始时,将潜艇通过动画移动到起始位置,即y轴的二分之一处
/**
* 游戏开始时通过动画进入
*/
@MainThread
fun start() {
_isStop = false
if (boat == null) {
boat = Boat(context).also {
post {
addView(it.view, _width, _width)
AnimatorSet().apply {
play(
ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(
it.view,
"y",
0F,
this@ForegroundView.height / 2f
)
).with(
ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(it.view, "rotation", 0F, 360F)
)
doOnEnd { _ -> it.view.rotation = 0F }
duration = 1000
}.start()
}
}
}
}
相机(Camera)
相机部分主要有TextureView和CameraHelper组成。TextureView提供给Camera承载preview;工具类CameraHelper主要完成以下功能:
- 开启相机:通过
CameraManger代开摄像头 - 摄像头切换:切换前后置摄像头,
- 预览:获取Camera提供的可预览尺寸,并适配
TextureView显示 - 人脸识别:检测人脸位置,进行
TestureView上的坐标变换
适配PreviewSize
相机硬件提供的可预览尺寸与屏幕实际尺寸(即TextureView尺寸)可能不一致,所以需要在相机初始化时,选取最合适的PreviewSize,避免TextureView上发生画面拉伸等异常
class CameraHelper(val mActivity: Activity, private val mTextureView: TextureView) {
private lateinit var mCameraManager: CameraManager
private var mCameraDevice: CameraDevice? = null
private var mCameraCaptureSession: CameraCaptureSession? = null
private var canExchangeCamera = false //是否可以切换摄像头
private var mFaceDetectMatrix = Matrix() //人脸检测坐标转换矩阵
private var mFacesRect = ArrayList<RectF>() //保存人脸坐标信息
private var mFaceDetectListener: FaceDetectListener? = null //人脸检测回调
private lateinit var mPreviewSize: Size
/**
* 初始化
*/
private fun initCameraInfo() {
mCameraManager = mActivity.getSystemService(Context.CAMERA_SERVICE) as CameraManager
val cameraIdList = mCameraManager.cameraIdList
if (cameraIdList.isEmpty()) {
mActivity.toast("没有可用相机")
return
}
//获取摄像头方向
mCameraSensorOrientation =
mCameraCharacteristics.get(CameraCharacteristics.SENSOR_ORIENTATION)!!
//获取StreamConfigurationMap,它是管理摄像头支持的所有输出格式和尺寸
val configurationMap =
mCameraCharacteristics.get(CameraCharacteristics.SCALER_STREAM_CONFIGURATION_MAP)!!
val previewSize = configurationMap.getOutputSizes(SurfaceTexture::class.java) //预览尺寸
// 当屏幕为垂直的时候需要把宽高值进行调换,保证宽大于高
mPreviewSize = getBestSize(
mTextureView.height,
mTextureView.width,
previewSize.toList()
)
//根据preview的size设置TextureView
mTextureView.surfaceTexture.setDefaultBufferSize(mPreviewSize.width, mPreviewSize.height)
mTextureView.setAspectRatio(mPreviewSize.height, mPreviewSize.width)
}
选取preview尺寸的原则与TextureView的长宽比尽量一致,且面积尽量接近。
private fun getBestSize(
targetWidth: Int,
targetHeight: Int,
sizeList: List<Size>
): Size {
val bigEnough = ArrayList<Size>() //比指定宽高大的Size列表
val notBigEnough = ArrayList<Size>() //比指定宽高小的Size列表
for (size in sizeList) {
//宽高比 == 目标值宽高比
if (size.width == size.height * targetWidth / targetHeight
) {
if (size.width >= targetWidth && size.height >= targetHeight)
bigEnough.add(size)
else
notBigEnough.add(size)
}
}
//选择bigEnough中最小的值 或 notBigEnough中最大的值
return when {
bigEnough.size > 0 -> Collections.min(bigEnough, CompareSizesByArea())
notBigEnough.size > 0 -> Collections.max(notBigEnough, CompareSizesByArea())
else -> sizeList[0]
}
initFaceDetect()
}
initFaceDetect()用来进行人脸的Matrix初始化,后文介绍
人脸识别
为相机预览,创建一个CameraCaptureSession对象,会话通过CameraCaptureSession.CaptureCallback返回TotalCaptureResult,通过参数可以让其中包括人脸识别的相关信息
/**
* 创建预览会话
*/
private fun createCaptureSession(cameraDevice: CameraDevice) {
// 为相机预览,创建一个CameraCaptureSession对象
cameraDevice.createCaptureSession(
arrayListOf(surface),
object : CameraCaptureSession.StateCallback() {
override fun onConfigured(session: CameraCaptureSession) {
mCameraCaptureSession = session
session.setRepeatingRequest(
captureRequestBuilder.build(),
mCaptureCallBack,
mCameraHandler
)
}
},
mCameraHandler
)
}
private val mCaptureCallBack = object : CameraCaptureSession.CaptureCallback() {
override fun onCaptureCompleted(
session: CameraCaptureSession,
request: CaptureRequest,
result: TotalCaptureResult
) {
super.onCaptureCompleted(session, request, result)
if (mFaceDetectMode != CaptureRequest.STATISTICS_FACE_DETECT_MODE_OFF)
handleFaces(result)
}
}
通过mFaceDetectMatrix对人脸信息进行矩阵变化,确定人脸坐标以使其准确应用到TextureView。
/**
* 处理人脸信息
*/
private fun handleFaces(result: TotalCaptureResult) {
val faces = result.get(CaptureResult.STATISTICS_FACES)!!
mFacesRect.clear()
for (face in faces) {
val bounds = face.bounds
val left = bounds.left
val top = bounds.top
val right = bounds.right
val bottom = bounds.bottom
val rawFaceRect =
RectF(left.toFloat(), top.toFloat(), right.toFloat(), bottom.toFloat())
mFaceDetectMatrix.mapRect(rawFaceRect)
var resultFaceRect = if (mCameraFacing == CaptureRequest.LENS_FACING_FRONT) {
rawFaceRect
} else {
RectF(
rawFaceRect.left,
rawFaceRect.top - mPreviewSize.width,
rawFaceRect.right,
rawFaceRect.bottom - mPreviewSize.width
)
}
mFacesRect.add(resultFaceRect)
}
mActivity.runOnUiThread {
mFaceDetectListener?.onFaceDetect(faces, mFacesRect)
}
}
最后,在UI线程将包含人脸坐标的Rect通过回调传出:
mActivity.runOnUiThread {
mFaceDetectListener?.onFaceDetect(faces, mFacesRect)
}
FaceDetectMatrix
mFaceDetectMatrix是在获取PreviewSize之后创建的
/**
* 初始化人脸检测相关信息
*/
private fun initFaceDetect() {
val faceDetectModes =
mCameraCharacteristics.get(CameraCharacteristics.STATISTICS_INFO_AVAILABLE_FACE_DETECT_MODES) //人脸检测的模式
mFaceDetectMode = when {
faceDetectModes!!.contains(CaptureRequest.STATISTICS_FACE_DETECT_MODE_FULL) -> CaptureRequest.STATISTICS_FACE_DETECT_MODE_FULL
faceDetectModes!!.contains(CaptureRequest.STATISTICS_FACE_DETECT_MODE_SIMPLE) -> CaptureRequest.STATISTICS_FACE_DETECT_MODE_FULL
else -> CaptureRequest.STATISTICS_FACE_DETECT_MODE_OFF
}
if (mFaceDetectMode == CaptureRequest.STATISTICS_FACE_DETECT_MODE_OFF) {
mActivity.toast("相机硬件不支持人脸检测")
return
}
val activeArraySizeRect =
mCameraCharacteristics.get(CameraCharacteristics.SENSOR_INFO_ACTIVE_ARRAY_SIZE)!! //获取成像区域
val scaledWidth = mPreviewSize.width / activeArraySizeRect.width().toFloat()
val scaledHeight = mPreviewSize.height / activeArraySizeRect.height().toFloat()
val mirror = mCameraFacing == CameraCharacteristics.LENS_FACING_FRONT
mFaceDetectMatrix.setRotate(mCameraSensorOrientation.toFloat())
mFaceDetectMatrix.postScale(if (mirror) -scaledHeight else scaledHeight, scaledWidth)// 注意交换width和height的位置!
mFaceDetectMatrix.postTranslate(
mPreviewSize.height.toFloat(),
mPreviewSize.width.toFloat()
)
}
控制类(GameController)
三大视图层组装完毕,最后需要一个总控类,对游戏进行逻辑控制
GameController
主要完成以下工作:
- 控制游戏的开启/停止
- 计算游戏的当前得分
- 检测潜艇的碰撞
- 对外(
Activity或者Fragment等)提供游戏状态监听的接口
初始化
游戏开始时进行相机的初始化,创建GameHelper类并建立setFaceDetectListener回调到ForegroundView
class GameController(
private val activity: AppCompatActivity,
private val textureView: AutoFitTextureView,
private val bg: BackgroundView,
private val fg: ForegroundView
) {
private var camera2HelperFace: CameraHelper? = null
/**
* 相机初始化
*/
private fun initCamera() {
cameraHelper ?: run {
cameraHelper = CameraHelper(activity, textureView).apply {
setFaceDetectListener(object : CameraHelper.FaceDetectListener {
override fun onFaceDetect(faces: Array<Face>, facesRect: ArrayList<RectF>) {
if (facesRect.isNotEmpty()) {
fg.onFaceDetect(faces, facesRect)
}
}
})
}
}
}
游戏状态
定义GameState,对外提供状态的监听。目前支持三种状态
- Start:游戏开始
- Over:游戏结束
- Score:游戏得分
sealed class GameState(open val score: Long) {
object Start : GameState(0)
data class Over(override val score: Long) : GameState(score)
data class Score(override val score: Long) : GameState(score)
}
可以在stop、start的时候,更新状态
/**
* 游戏状态
*/
private val _state = MutableLiveData<GameState>()
internal val gameState: LiveData<GameState>
get() = _state
/**
* 游戏停止
*/
fun stop() {
bg.stop()
fg.stop()
_state.value = GameState.Over(_score)
_score = 0L
}
/**
* 游戏再开
*/
fun start() {
initCamera()
fg.start()
bg.start()
_state.value = GameState.Start
handler.postDelayed({
startScoring()
}, FIRST_APPEAR_DELAY_MILLIS)
}
计算得分
游戏启动时通过startScoring开始计算得分并通过GameState上报。
目前的规则设置很简单,存活时间即游戏得分
/**
* 开始计分
*/
private fun startScoring() {
handler.postDelayed(
{
fg.boat?.run {
bg.barsList.flatMap { listOf(it.up, it.down) }
.forEach { bar ->
if (isCollision(
bar.x, bar.y, bar.w, bar.h,
this.x, this.y, this.w, this.h
)
) {
stop()
return@postDelayed
}
}
}
_score++
_state.value = GameState.Score(_score)
startScoring()
}, 100
)
}
检测碰撞
isCollision根据潜艇和障碍物当前位置,计算是否发生了碰撞,发生碰撞则GameOver
/**
* 碰撞检测
*/
private fun isCollision(
x1: Float,
y1: Float,
w1: Float,
h1: Float,
x2: Float,
y2: Float,
w2: Float,
h2: Float
): Boolean {
if (x1 > x2 + w2 || x1 + w1 < x2 || y1 > y2 + h2 || y1 + h1 < y2) {
return false
}
return true
}
Activity
Activity的工作简单:
- 权限申请:动态申请Camera权限
- 监听游戏状态:创建
GameController,并监听GameState状态
private fun startGame() {
PermissionUtils.checkPermission(this, Runnable {
gameController.start()
gameController.gameState.observe(this, Observer {
when (it) {
is GameState.Start ->
score.text = "DANGER\nAHEAD"
is GameState.Score ->
score.text = "${it.score / 10f} m"
is GameState.Over ->
AlertDialog.Builder(this)
.setMessage("游戏结束!成功推进 ${it.score / 10f} 米! ")
.setNegativeButton("结束游戏") { _: DialogInterface, _: Int ->
finish()
}.setCancelable(false)
.setPositiveButton("再来一把") { _: DialogInterface, _: Int ->
gameController.start()
}.show()
}
})
})
}
最后
项目结构很清晰,用到的大都是常规技术,即使是新入坑Android的同学看起来也不费力。在现有基础上还可以通过添加BGM、增加障碍物种类等,进一步提高游戏性。喜欢的话留个star鼓励一下作者吧 ^^
https://github.com/vitaviva/ugame