一、 netTCPBinding
3、 安全模式 – Message
3.1. 客户端验证 – None
3.1.1. 获得和安装证书
3.1.2. 服务端代码
3.1.3. 客户端代码
3.1.4. 测试
3.2. 客户端验证 – Windows
3.2.1. 获得和安装证书
3.2.2. 服务端代码
3.2.3. 客户端代码
3.2.4. 测试
3.3. 客户端验证 – UserName
3.3.1. 获得和安装证书
3.3.2. 服务端代码
3.3.3. 客户端代码
3.3.4. 测试
3.3.5. 身份模拟和访问权限控制
3.4. 客户端验证:Certificate
3.4.1. 获得和安装证书
3.4.2. 服务端代码
3.4.3. 客户端代码
3.4.4. 测试
3.4.5. 证书映射到windows用户
一、 netTCPBinding
此绑定使用TCP传输协议,不具交互性,只适用于 WCF 到 WCF 的通信。
此绑定的传输安全性的实现:
l 安全模式Message
这种模式WCF中都一样,都是使用WS-*通过对SOAP消息本身进行加密、签名等等的处理来保证安全性。Message模式不依赖于传输协议。服务端需要指定服务端证书,用来加密服务端和客户端相互传送的消息。
l Transport – 客户端windows验证
使用windows security保证消息的安全,使用windows credential进行身份验证。
这种方式不需要服务端证书。
至于windows security的实现安全的原理我还不明白,这部分尚待了解。
l Transport – 客户端其他验证方式
使用TLS over TCP实现传输安全性,需要服务端证书。
一般大家对SSL比较熟悉,对TLS可能要陌生些,其实可以说TLS协议可以看作跟SSL协议后续版本。1994年,netscape为了在internet上进行安全的数据传输,开发了的SSL协议,后来标准化组织把SSL标准化了,稍作修改改名叫TLS,在一般的使用意义上,这两个协议差别不大,就是在保证消息完整性的散列算法上使用了不同的算法。
TLS over TCP 直接建立在TCP协议上,通过传输层TCP协议实现安全性。
netTCPBinding绑定是直接使用TCP协议,不走HTTP,所以不能使用IIS宿主。这部分的测试实例采用自宿主的服务端console应用,基于代码的方式。
3、 安全模式 – Message
这部分测试netTCPBinding绑定的Message安全模式的各种情况。
共用测试WCF服务类
所有测试都是用同样的服务端contract和实现这个contract的service:
[ServiceContract(Namespace = "http://chnking.com")]
public interface IGetIdentity
{
[OperationContract]
string Get(string ClientIdentity);
}
public class GetIdentity : IGetIdentity
{
public string Get(string ClientIdentity)
{
return ("服务端Identity 是'" + ServiceSecurityContext.Current. PrimaryIdentity.Name +
"'"n"r客户端Identity是 '" + ClientIdentity + "'");
}
}
代码很简单,一个contract提供了一个Get方法,接收一个string参数,返回一个string参数。在后面的测试中,客户端把客户端安全上下文的Identity发送到服务端,服务端返回服务端安全上下文的Identity给客户端。
3.1. 客户端验证 – None
这部分的测试代码: NetTcpBinding_Message_None.rar
netTCPBinding绑定的Message安全模式,客户端None验证。此时将使用服务端证书,通过WS-Trust协议建立的安全通道,原理上类似SSL或TLS的机制(但不是通过网络传输层来实现,而是通过处理SOAP中的消息)来保证消息的安全性。
这种方式的安全性:
| 完整性 |
使用服务端证书,通过WS-Trust协议建立的安全通道 |
| 保密性 |
使用服务端证书,通过WS-Trust协议建立的安全通道 |
| 服务端身份身份验证 |
服务端证书提供 |
| 客户端身份验证 |
没有 |
3.1.1. 获得和安装证书
这里用Makecert.exe工具生成证书,使用下面的命令:
makecert -sr localmachine -ss My -n CN=win2008 -sky exchange -pe -r
这是服务端证书,win2008是服务端的机器名。
如果做过前面BasicHttpBinding的测试,这个服务端证书就应该已经有了。
3.1.2. 服务端代码
internal static ServiceHost myServiceHost = null;
internal static void Main()
{
NetTcpBinding myBinding = new NetTcpBinding();
myBinding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Message;
myBinding.Security.Message.ClientCredentialType = MessageCredentialType.None;
Uri baseAddress = new Uri("net.tcp://localhost:8056/WCFService/");
myServiceHost = new ServiceHost(typeof(GetIdentity), baseAddress);
ServiceEndpoint myServiceEndpoint = myServiceHost.AddServiceEndpoint
(typeof(IGetIdentity), myBinding, "GetIdentity");
//设置服务端证书
myServiceHost.Credentials.ServiceCertificate.SetCertificate("CN=win2008");
ServiceMetadataBehavior behavior = new ServiceMetadataBehavior();
behavior.HttpGetEnabled = true;
behavior.HttpGetUrl = new Uri("http://localhost:8057/mex");
myServiceHost.Description.Behaviors.Add(behavior);
myServiceHost.Open();
Console.WriteLine("Service started!");
Console.ReadLine();
myServiceHost.Close();
}
3.1.3. 客户端代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
NetTcpBinding myBinding = new NetTcpBinding();
myBinding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Message;
myBinding.Security.Message.ClientCredentialType = MessageCredentialType.None;
EndpointAddress ea = new EndpointAddress("net.tcp://win2008:8056/WCFService/GetIdentity");
GetIdentityClient gc = new GetIdentityClient(myBinding, ea);
//不验证服务端证书的有效性
gc.ClientCredentials.ServiceCertificate.Authentication.CertificateValidationMode =
System.ServiceModel.Security.X509CertificateValidationMode.None;
//为使用TcpTrace跟踪消息设置的TcpTrace监听端口
ClientViaBehavior myClientViaBehavior = new ClientViaBehavior
(new Uri("net.tcp://win2008:8055/WCFService/GetIdentity"));
gc.Endpoint.Behaviors.Add(myClientViaBehavior);
//执行代理类Get方法
string result = gc.Get(WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent().Name);
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadLine();
}
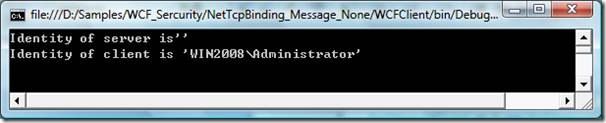
3.1.4. 测试
3.2. 客户端验证 – Windows
这部分的测试代码: NetTcpBinding_Message_Windows.rar
netTCPBinding绑定的Message安全模式,客户端Windows验证。此时将使用服务端证书,通过WS-Trust协议建立的安全通道,原理上类似SSL或TLS的机制(但不是通过网络传输层来实现,而是通过处理SOAP中的消息)来保证消息的安全性。
这种方式的安全性:
| 完整性 |
使用服务端证书,通过WS-Trust协议建立的安全通道 |
| 保密性 |
使用服务端证书,通过WS-Trust协议建立的安全通道 |
| 服务端身份身份验证 |
服务端证书提供 |
| 客户端身份验证 |
Windows身份验证 |
3.2.1. 获得和安装证书
这里用Makecert.exe工具生成证书,使用下面的命令:
makecert -sr localmachine -ss My -n CN=win2008 -sky exchange -pe -r
这是服务端证书,win2008是服务端的机器名。
如果做过前面BasicHttpBinding的测试,这个服务端证书就应该已经有了。
3.2.2. 服务端代码
internal static ServiceHost myServiceHost = null;
internal static void Main()
{
NetTcpBinding myBinding = new NetTcpBinding();
myBinding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Message;
myBinding.Security.Message.ClientCredentialType = MessageCredentialType.Windows;
Uri baseAddress = new Uri("net.tcp://localhost:8056/WCFService/");
myServiceHost = new ServiceHost(typeof(GetIdentity), baseAddress);
ServiceEndpoint myServiceEndpoint = myServiceHost.AddServiceEndpoint
(typeof(IGetIdentity), myBinding, "GetIdentity");
//设置服务端证书
myServiceHost.Credentials.ServiceCertificate.SetCertificate("CN=win2008");
ServiceMetadataBehavior behavior = new ServiceMetadataBehavior();
behavior.HttpGetEnabled = true;
behavior.HttpGetUrl = new Uri("http://localhost:8057/mex");
myServiceHost.Description.Behaviors.Add(behavior);
myServiceHost.Open();
Console.WriteLine("Service started!");
Console.ReadLine();
myServiceHost.Close();
}
3.2.3. 客户端代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
NetTcpBinding myBinding = new NetTcpBinding();
myBinding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Message;
myBinding.Security.Message.ClientCredentialType = MessageCredentialType.Windows;
EndpointAddress ea = new EndpointAddress("net.tcp://win2008:8056/WCFService/GetIdentity");
GetIdentityClient gc = new GetIdentityClient(myBinding, ea);
//不验证服务端证书的有效性
gc.ClientCredentials.ServiceCertificate.Authentication.CertificateValidationMode =
System.ServiceModel.Security.X509CertificateValidationMode.None;
//为使用TcpTrace跟踪消息设置的TcpTrace监听端口
ClientViaBehavior myClientViaBehavior = new ClientViaBehavior
(new Uri("net.tcp://win2008:8055/WCFService/GetIdentity"));
gc.Endpoint.Behaviors.Add(myClientViaBehavior);
//执行代理类Get方法
string result = gc.Get(WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent().Name);
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadLine();
}
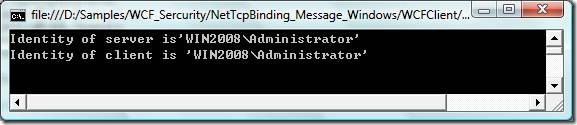
3.2.4. 测试
可以看出,客户端windows身份被传送到服务端。
3.3. 客户端验证 – UserName
这部分的测试代码: NetTcpBinding_Message_UserName.rar
netTCPBinding绑定的Message安全模式,客户端使用UserName验证。此时将使用服务端证书,通过WS-Trust协议建立的安全通道,原理上类似SSL或TLS的机制(但不是通过网络传输层来实现,而是通过处理SOAP中的消息)来保证消息的安全性。
这种方式的安全性:
| 完整性 |
使用服务端证书,通过WS-Trust协议建立的安全通道 |
| 保密性 |
使用服务端证书,通过WS-Trust协议建立的安全通道 |
| 服务端身份身份验证 |
服务端证书提供 |
| 客户端身份验证 |
客户端提供的用户名和密码 |
3.3.1. 获得和安装证书
这里用Makecert.exe工具生成证书,使用下面的命令:
makecert -sr localmachine -ss My -n CN=win2008 -sky exchange -pe -r
这是服务端证书,win2008是服务端的机器名。
如果做过前面BasicHttpBinding的测试,这个服务端证书就应该已经有了。
3.3.2. 服务端代码
Contract和Services部分的代码:
[ServiceContract(Namespace = "http://chnking.com")]
public interface IGetIdentity
{
[OperationContract]
string Get(string ClientIdentity);
}
public class GetIdentity : IGetIdentity
{
[PrincipalPermission(SecurityAction.Demand, Role = "admin")]
public string Get(string ClientIdentity)
{
IPrincipal myWindowsPrincipal = (IPrincipal)Thread.CurrentPrincipal;
return ("Identity of server is'" + myWindowsPrincipal.Identity.Name +
"'"n"rIdentity of client is '" + ClientIdentity + "'");
}
}
这部分代码跟前面的测试例子一样,只是为了测试服务端模拟身份后的权限控制在Get方法前增加了了如下的控制访问的attribute:
[PrincipalPermission(SecurityAction.Demand, Role = "admin")]
表示只有运行方法的当前线程安全上下文的identity属于admin角色时才有权限访问这个方法。
服务宿主部分的代码:
internal class MyServiceHost
{
internal static ServiceHost myServiceHost = null;
internal static void Main()
{
NetTcpBinding myBinding = new NetTcpBinding();
myBinding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Message;
myBinding.Security.Message.ClientCredentialType = MessageCredentialType.UserName;
Uri baseAddress = new Uri("net.tcp://localhost:8056/WCFService/");
myServiceHost = new ServiceHost(typeof(GetIdentity), baseAddress);
ServiceEndpoint myServiceEndpoint = myServiceHost.AddServiceEndpoint
(typeof(IGetIdentity), myBinding, "GetIdentity");
//设置服务端证书
myServiceHost.Credentials.ServiceCertificate.SetCertificate("CN=win2008");
//默认服务端PrincipalPermissionMode为UseWindowsGroups,将Thread.CurrentPrincipal设置为WindowsPrincipal
//一般是windows验证时映射到windows用户。
//本例需要自己设置Thread.CurrentPrincipal,故此处设置为None
myServiceHost.Authorization.PrincipalPermissionMode = PrincipalPermissionMode.None;
//设置客户端username在服务端验证模式为Custom
myServiceHost.Credentials.UserNameAuthentication.UserNamePasswordValidationMode =
System.ServiceModel.Security.UserNamePasswordValidationMode.Custom;
myServiceHost.Credentials.UserNameAuthentication.CustomUserNamePasswordValidator = new customUserNamePasswordValidator();
ServiceMetadataBehavior behavior = new ServiceMetadataBehavior();
behavior.HttpGetEnabled = true;
behavior.HttpGetUrl = new Uri("http://localhost:8057/mex");
myServiceHost.Description.Behaviors.Add(behavior);
myServiceHost.Open();
Console.WriteLine("Service started!");
Console.ReadLine();
myServiceHost.Close();
}
}
public class customUserNamePasswordValidator : System.IdentityModel.Selectors.UserNamePasswordValidator
{
public override void Validate(string username, string password)
{
if (username == "chnking" && password == "jjz666")
{
string[] roles = { "admin", "operator" };
Thread.CurrentPrincipal = new GenericPrincipal(new GenericIdentity("chnking", "Custom"), roles);
}
else
{
throw(new SecurityTokenException("用户名或密码无效!"));
}
}
}
这部分代码有几处需要说明:
客户端使用UserName验证方式,在服务端可以使用对客户端发送来的UserName的验证方式有三种:
Windows:用windows的帐号和密码验证客户端送来的UserName。
MembershipProvider:提供基于已配置的MembershipProvider的密码验证。
Custom:由自定义的从UserNamePasswordValidator继承来的类验证用户名和密码。
本例中选用自定义验证,并新建了一个从UserNamePasswordValidator继承来的类customUserNamePasswordValidator来验证客户端用户名和口令。
验证了用户正确后,新建一个跟此用户对应的GenericPrincipal,包括这个用户的Identity,这里叫做”chnking”,和这个identity所属的角色,这里这个用户同时属于"admin", "operator"。还把这个用户的GenericPrincipal赋给了Thread.CurrentPrincipal,使本线程往下的运行上下文切换到这个定制的GenericPrincipal。
还有一点,服务端的PrincipalPermissionMode默认是UseWindowsGroups,这表示将Thread.CurrentPrincipal设置为WindowsPrincipal,一般是windows验证时映射到windows用户。本例需要自己设置Thread.CurrentPrincipal,故此处设置为None,否则,到了执行服务端services代码时,Thread.CurrentPrincipal将为空。
3.3.3. 客户端代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
NetTcpBinding myBinding = new NetTcpBinding();
myBinding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Message;
myBinding.Security.Message.ClientCredentialType = MessageCredentialType.UserName;
EndpointAddress ea = new EndpointAddress("net.tcp://jinjz2008:8056/WCFService/GetIdentity");
GetIdentityClient gc = new GetIdentityClient(myBinding, ea);
//不验证服务端证书的有效性
gc.ClientCredentials.ServiceCertificate.Authentication.CertificateValidationMode =
System.ServiceModel.Security.X509CertificateValidationMode.None;
//提供UserName客户端用户凭据
gc.ClientCredentials.UserName.UserName = "chnking";
gc.ClientCredentials.UserName.Password = "jjz666";
//为使用TcpTrace跟踪消息设置的TcpTrace监听端口
ClientViaBehavior myClientViaBehavior = new ClientViaBehavior
(new Uri("net.tcp://jinjz2008:8055/WCFService/GetIdentity"));
gc.Endpoint.Behaviors.Add(myClientViaBehavior);
//执行代理类Get方法
string result = gc.Get(WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent().Name);
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadLine();
}
客户端没有太多需要特别说明的。设置客户端验证方式为UserName后用以下代码提供用户名和口令:
//提供UserName客户端用户凭据
gc.ClientCredentials.UserName.UserName = "chnking";
gc.ClientCredentials.UserName.Password = "jjz666";
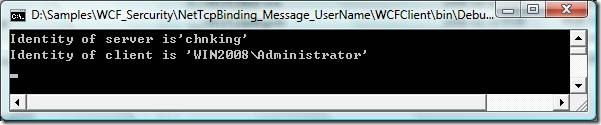
3.3.4. 测试
可以看出,客户端的chnking身份被传送到服务端。并且,有权限执行服务端的Get方法。
3.3.5. 身份模拟和访问权限控制
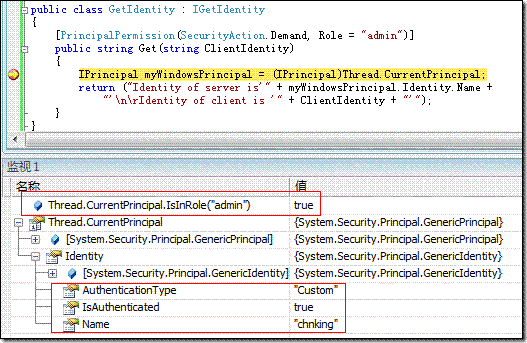
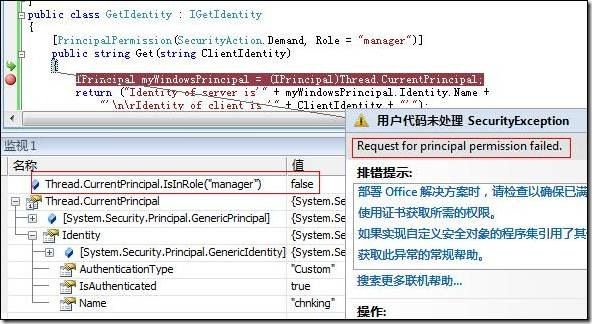
如果在服务端的Get方法中设置一个断点,如下图:
可以看到当代码运行到Get方法中时,当前线程的Principal就是在customUserNamePasswordValidator定制类中赋给的chnking,并且这个chnking属于admin角色。
如果把Get的权限改一下,改成只有叫”manager”的角色可以方法此方法:
[PrincipalPermission(SecurityAction.Demand, Role = " manager ")]
public string Get(string ClientIdentity)
再看运行结果:
Chning不属于”manager”角色,也就没有执行Get方法的权限。
3.4. 客户端验证:Certificate
这部分的测试代码: NetTcpBinding_Message_Certificate.rar
netTCPBinding绑定的Message安全模式,客户端Certificate验证,此时将使用服务端证书,通过WS-Trust协议建立的安全通道,原理上类似SSL或TLS的机制(但不是通过网络传输层来实现,而是通过处理SOAP中的消息)来保证消息的安全性。
这种方式的安全性:
| 完整性 |
使用服务端证书,通过WS-Trust协议建立的安全通道 |
| 保密性 |
使用服务端证书,通过WS-Trust协议建立的安全通道 |
| 服务端身份身份验证 |
服务端证书提供 |
| 客户端身份验证 |
客户端证书提供 |
3.4.1. 获得和安装证书
同时客户端验证设置为Certificate,就需要提供客户端证书以验证客户端身份。
所有这里需要在服务端和客户端分别安装证书。
这里用Makecert.exe工具生成证书,使用下面的命令:
makecert -sr localmachine -ss My -n CN=win2008 -sky exchange -pe -r
这是服务端证书,win2008是服务端的机器名。
如果做过前面BasicHttpBinding的测试,这个服务端证书就应该已经有了。
makecert -sr currentuser -ss My -n CN=TestClient -sky exchange -pe -r
这是客户端证书。
3.4.2. 服务端代码
internal static ServiceHost myServiceHost = null;
internal static void Main()
{
NetTcpBinding myBinding = new NetTcpBinding();
myBinding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Message;
myBinding.Security.Message.ClientCredentialType = MessageCredentialType.Certificate;
Uri baseAddress = new Uri("net.tcp://localhost:8056/WCFService/");
myServiceHost = new ServiceHost(typeof(GetIdentity), baseAddress);
ServiceEndpoint myServiceEndpoint = myServiceHost.AddServiceEndpoint
(typeof(IGetIdentity), myBinding, "GetIdentity");
//设置服务端证书
myServiceHost.Credentials.ServiceCertificate.SetCertificate("CN=win2008");
//设置不验证客户端证书的有效性
myServiceHost.Credentials.ClientCertificate.Authentication.CertificateValidationMode =
System.ServiceModel.Security.X509CertificateValidationMode.None;
ServiceMetadataBehavior behavior = new ServiceMetadataBehavior();
behavior.HttpGetEnabled = true;
behavior.HttpGetUrl = new Uri("http://localhost:8057/mex");
myServiceHost.Description.Behaviors.Add(behavior);
myServiceHost.Open();
Console.WriteLine("Service started!");
Console.ReadLine();
myServiceHost.Close();
}
3.4.3. 客户端代码
static void Main(string[] args)
{
NetTcpBinding myBinding = new NetTcpBinding();
myBinding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Message;
myBinding.Security.Message.ClientCredentialType = MessageCredentialType.Certificate;
EndpointAddress ea = new EndpointAddress("net.tcp://win2008:8056/WCFService/GetIdentity");
GetIdentityClient gc = new GetIdentityClient(myBinding, ea);
//设置客户端证书
gc.ClientCredentials.ClientCertificate.SetCertificate("CN=TestClient",
StoreLocation.CurrentUser, StoreName.My);
//设置不验证服务端证书有效性
gc.ClientCredentials.ServiceCertificate.Authentication.CertificateValidationMode =
System.ServiceModel.Security.X509CertificateValidationMode.None;
//为使用TcpTrace跟踪消息设置的TcpTrace监听端口
ClientViaBehavior myClientViaBehavior = new ClientViaBehavior
(new Uri("net.tcp://win2008:8055/WCFService/GetIdentity"));
gc.Endpoint.Behaviors.Add(myClientViaBehavior);
//执行代理类Get方法
string result = gc.Get(WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent().Name);
Console.WriteLine(result);
Console.ReadLine();
}
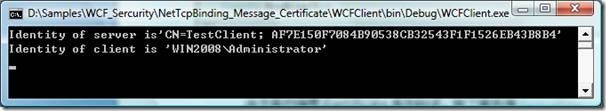
3.4.4. 测试
由于客户端是Certificate身份验证,到了服务端 ServiceSecurityContext.Current. PrimaryIdentity.Name获得的是证书的subject name和证书指纹。
3.4.5. 证书映射到windows用户
有时需要把客户端证书映射为服务端的windows用户,这样可以使用windows权限控制客户端在服务端的权限。
在本例的情况,可以设置客户端证书跟服务端windows用户的映射,首先在服务端的代码或配置文件中设置允许客户端证书到服务端windows用户的映射。
代码中将客户端验证MapClientCertificateToWindowsAccount设为True:
myServiceHost.Credentials.ClientCertificate.Authentication.MapClientCertificateToWindowsAccount = true;
配置文件中将服务端Behavior的客户端证书验证MapClientCertificateToWindowsAccount设为True:
<serviceBehaviors>
<behavior>
<serviceCredentials>
<clientCertificate>
<authentication certificateValidationMode="None" mapClientCertificateToWindowsAccount="True" />
clientCertificate>
serviceCredentials>
behavior>
serviceBehaviors>
然后在服务端设置映射,在操作系统上把客户端的证书与windows用户作映射,这必须是要在安装了Active Directory的服务器上做。
具体步骤参考文章:Map certificates to user accounts