写于2015年8月2日。
背景:Palm是流行的掌上电脑(PDA)的一种,由Palm公司发明,这种PDA上的操作系统也称为Palm,有时又称为Palm OS。
Zen of Palm(提取码gngd)包含四个部分链接:
Design Philosophies设计哲学
Design Practices设计实践
Design Validation 设计验证
Design Improvements设计完善
每部分都以谜语的形式引出话题,继而深入讨论,得出结论。
一、Design Philosophies设计哲学
谜语1:大猩猩怎么学会飞?
提示:你需要了解大猩猩的本质。
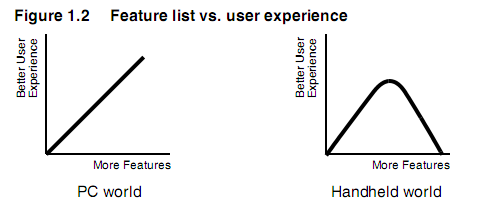
思考大猩猩和老鹰的区别。然后思考Handheld(后面用HH代替)和PC的区别。不仅仅是大小,而是使用模式和暗含的东西。
PC的本质 VS HH本质
More features are better 越多功能越好(PC)
Handhelds excel at perceived speed.(HH)
Too many features frustrate customers.
太多的功能会困扰用户。只需要提供用户需要的功能,确保这些功能能够快速上手和易用。
A handheld must be free to roam about.
做功能时,考虑性能、耗电量和电池寿命。
Handhelds must be wearable.
轻便、易于携带。
Handhelds are about the user.
更侧重与用户体验。
Inverse Usage Patterns 相反的使用模式
Handhelds are used frequently but briefly. Handhelds使用频繁,且简洁。
人们的使用更加频繁、突发性的,更像是一瞥。
PC跟HH不同的使用模式对比图
Different Design Approaches 不同的设计方法
PC 越多功能越好
HH 少而精的功能,帮助用户get the job done
所以,谜语1的答案是:只有变成老鹰才能飞。
二、Design Practices 设计实践
谜语2:如何将一座山放入一个杯子里?
提示:思考为什么要将一座山放到杯子里呢?
more-is-better PC midset VS less-is-more thinking
特征的平衡
• Pocket size
• Fast response
• Easy to use
• Low cost and high value
• Worry-free battery life
• Seamless connection with PCs
三、Design Validation设计验证
1. Focus on benefits to users
关键特征的罗列是为了强调给用户带来的好处,而不是为了展示这些技术上的特征。如500HZ、128MB、12GB听起来好像很给力,但是实际上能给用户带来什么并不清晰。
Palm就罗列了用户能获得的好处和带来这些好处的技术 。
2. 所谓天堂:最甜蜜的点
Balance features with the user experience
平衡特征和用户体验
Added features must improve the user experience. 增加功能必须基于提升用户体验。
每当要增加新功能的时候,问2个问题:
用户满意度有提升吗?
会引起用户困惑?带来硬件资源损耗么?
寻求平衡的一个方法是:
(pragmatic innovation)
• Identify the problems
• Find the simplest solution to each problem
• Get rid of everything else.
技术若不能使用户满意,那说明还未成熟。
先定位用户实际的需求,再去寻求务实的创新。
Find the real problems behind what customers ask for.找到用户声音背后的真正问题。
Don’t be afraid to respond to an answer with more questions. 不要害怕对一个答案提更多的问题。
顾客并不清楚技术的限制和可能带来的后果。如果有一个功能列表,那么每个功能都过下,思考为什么需要这个功能。
3. Ignore conventional wisdom 忽略传统经验
When you ignore convention, you must be ready to stand your ground. If your design is good and you have tested it with users to confirm that it works, then don’t let other people talk you out of it.Listen to qualified critics who make comments based on thoughtful observation.If they don’t understand your design, try to learn why not and eliminate any sources of confusion. But watch out for people who are uncomfortable simply because your idea does not conform to conventional design. These people will confuse you and pull you back to where they are—conventionality.
4. The 80/20 Rule 二八原则
专注于用户80%的时间会做的事情,忽略其他20%。关注大部分用户会做的事,不要因为一些边缘案例,增加复杂度。记住你和你的同事并非”大多数人“。
Focus on what users do 80 percent of the timeand try to ignore the other 20 percent. Accommodate what most people need to do, but don’t add complexity just to address fringe cases.Keep in mind that you and most of your coworkers are not “most people.”You use technology intensively, so you probably shouldn’t apply the 80/20 rule to your own activities. Apply the rule to what typical users do.
5. Scaling the Problems 缩小问题范围
Start with nothing, and add only essentials—one by one.
案例:记事本,只为纪事,一次只有一种字体,纯文字,无图表。适用于小屏幕、低容量、不易于输入的设备。放弃PC上类似于word处理的功能。
Decompose a large PC application into multiple handheld applications.
6. Sharing the Work
PC和HH可以协作。笨重的工作就交给PC吧。
Solutions—not Features
The right approach is to figure out how your application can accomplish precisely what the user needs to do. Look for solutions that are fast and easy to use. Try to delight the user.
7. Minimize clutter 减少混乱
减少功能,整理屏幕格局。增加易用性。
Reduce the step count for common tasks 日常操作,步奏简化
Conceal risky functions 隐藏有风险的操作(防止数据的误删除)
Include power features discreetly 谨慎添加高级功能(不能影响新手的使用。高级功能入口无需明显,高级用户自会去发掘。)
8. Intuitive 直觉
用户易上手、易用,界面要与内置的app风格一致。
Stick to the user interface guidelines 遵循用户界面规则。
利用用户对标准界面已有的了解,若我们的设计基于同样的规范,则用户学习成本大大减少。
9. Easy to Remember 易于记住
操作让人易于记住。
谜语2的解决方法:找到大山里面的钻石(抛弃石头和泥土),放入杯中。
Make the product useful and elegant: minimize clutter, reduce the step count for common tasks, conceal risky functions, and include power features discreetly. Scale your product for the handheld world. Let a companion PC application do the heavy work. Use the 80/20 rule to hone in on the most frequently used features and jettison the rest.
四、Design Improvements设计完善
谜语3:铁匠如何打造完美的马蹄铁?
提示:什么是更加完美的组合?
1. Stretching the Sweet Spot 延长甜蜜点
Pragmatic innovation lets you shift the curve and make the sweet spot larger over time.
2. Add features creatively
The feature must be added creatively and elegantly or the user experience deteriorates and the product moves out of the sweet spot.
3. Discovering New Features
4. Study other products
谜语4答案:完美是一个平衡的艺术。改变环境后,你要重新调整这个平衡。
In technology, perfection is strictly for the moment.Your “perfect” solution balances available technologies, costs, market forces, and user expectations.Whenever the surrounding forces shift, your balancing act needs to be re-balanced. Put another way:“perfection” is dynamic, not static.