最近想到一个比较好玩的,就是自定义一个相机,通过简单的图像处理算法来改变真实的世界,发现效果还真的挺好玩,所以最后简单的实现了一下。
1 实现准备
要实现这个需要用到几个重要的系统类
- Camera:已经过时,谷歌推荐使用camera2,但是camera2用起来贼麻烦,总体思路是从摄像头获取图像流,然后交给后续来处理,一般来说获取到图像流的数据之后会直接展示到SurfaceView上面进行预览,但是这样就达不到我们得目的了,我们得目的是拿到图像流之后先进行一些处理之后再展示出来,这样的话就需要用到下面讲到的SurfaceTexture了;
- SurfaceTexture:功能就是获取图像流作为OpenGL ES的纹理,可以接收来自摄像头或者视频解码的图像流,在这里的目的就是接收来自Camera的图像流,然后交给OpenGL ES进行渲染,当updateTexImage()方法被调用时就会刷新最新图像的图像流到OpenGL ES的渲染器上,纹理数据会默认绑定到GL_TEXTURE_EXTERNAL_OES 目标上,我们要做的就是在着色器中声明使用,看下官方文档怎么说
意思是着色器中得加"#extension GL_OES_EGL_image_external : require"这句声明,还有获取纹理数据得使用samplerExternalOES类型,这就导致我们写着色器得按规矩来。这样讲起来比较抽象,来看下代码,Don't bb,show me code!!!Additionally, any OpenGL ES 2.0 shader that samples from the texture must declare its use of this extension using, for example, an "#extension GL_OES_EGL_image_external : require" directive. Such shaders must also access the texture using the samplerExternalOES GLSL sampler type.
- GlSurfaceview:预览使用OpenGL ES渲染后的图像,就是最后的展示效果了,绘制和渲染和着色器加载基本上可以在这里头完成。
2 具体实现
2.1 Camera操作
/**
* 打开摄像头
*/
private void openCamera() {
try {
mCamera = getCameraInstance();
mCamera.setPreviewTexture(mSurface);
mCamera.startPreview();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 关闭摄像头
*/
private void closeCamera() {
try {
mCamera.stopPreview();
mCamera.release();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Camera getCameraInstance() {
Camera c = null;
try {
c = Camera.open(); // attempt to get a Camera instance
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// Camera is not available (in use or does not exist)
}
return c; // returns null if camera is unavailable
}
就是Camera的打开和关闭,通过Camera.open()来获取Camera对象,setPreviewTexture(mSurface)中的mSurface就是SurfaceTexture,关键是当关闭应用的时候得及时的释放Camera资源,因为不仅仅是你这个应用会用到摄像头资源。
2.2 SurfaceTexture操作
@Override
public void onSurfaceCreated(GL10 gl10, EGLConfig eglConfig) {
...
mSurface = new SurfaceTexture(mTextureID);
mSurface.setOnFrameAvailableListener(this);
...
}
/**
* 纹理配置
*/
private int createTextureID() {
int[] texture = new int[1];
int[] fbo = new int[1];
GLES20.glGenTextures(1, texture, 0);
GLES20.glBindTexture(GLES11Ext.GL_TEXTURE_EXTERNAL_OES, texture[0]);
GLES20.glTexParameterf(GLES11Ext.GL_TEXTURE_EXTERNAL_OES,
GL10.GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL10.GL_LINEAR);
GLES20.glTexParameterf(GLES11Ext.GL_TEXTURE_EXTERNAL_OES,
GL10.GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL10.GL_LINEAR);
GLES20.glTexParameteri(GLES11Ext.GL_TEXTURE_EXTERNAL_OES,
GL10.GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL10.GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
GLES20.glTexParameteri(GLES11Ext.GL_TEXTURE_EXTERNAL_OES,
GL10.GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL10.GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
GLES20.glGenBuffers(1, fbo, 0);
GLES20.glBindBuffer(GLES20.GL_FRAMEBUFFER, fbo[0]);
GLES20.glFramebufferTexture2D(GLES20.GL_FRAMEBUFFER,
GLES20.GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0, GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, texture[0], 0);
return texture[0];
}
createTextureID()进行纹理对象的一些参数配置,主要就是纹理采样的设置,得到纹理之后交给SurfaceTexture,SurfaceTexture还需要注册OnFrameAvailableListener回调
@Override
public void onFrameAvailable(SurfaceTexture surfaceTexture) {
this.requestRender();
}
@Override
public void onDrawFrame(GL10 gl10) {
...
mSurface.updateTexImage();
...
}
在有新的一帧图像可用时就会调用onFrameAvailable()方法,这个时候就可以调用GlSurfaceview的requestRender()让OpenGL ES来刷新数据了,就是会调用到GLSurfaceView.Renderer的onDrawFrame()方法,在这里头mSurface.updateTexImage()来获取最新的图像流转换为纹理数据绑定到着色器中,在着色器中我们会对图像流进行图像处理,最后展示出来素描图像。
2.3 GLSurfaceView实现
public class CameraGLSurfaceView extends GLSurfaceView implements GLSurfaceView.Renderer, SurfaceTexture.OnFrameAvailableListener {
public CameraGLSurfaceView(Context context) {
super(context);
mContext = context;
// 创建一个2.0的context
setEGLContextClientVersion(2);
// 设置渲染器来在GLSurfaceView中进行绘制
setRenderer(this);
// 只有在用户需要进行绘制时,才会进行真正的重新渲染,配合GLSurfaceView.requestRender()使用
setRenderMode(RENDERMODE_WHEN_DIRTY);
}
/**
* CameraGLSurfaceView创建只调用一次,用来创建环境
*/
@Override
public void onSurfaceCreated(GL10 gl10, EGLConfig eglConfig) {
mTextureID = createTextureID();
mSurface = new SurfaceTexture(mTextureID);
mSurface.setOnFrameAvailableListener(this);
mDirectDrawer = new DirectDrawer(mContext, mTextureID);
}
/**
* 当物理环境发生改变的时候会进行调用,比如屏幕方向发生改变
*/
@Override
public void onSurfaceChanged(GL10 gl10, int width, int height) {
GLES20.glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
openCamera();
}
/**
* 每次重绘都会进行调用
*/
@Override
public void onDrawFrame(GL10 gl10) {
GLES20.glClearColor(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
GLES20.glClear(GLES20.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GLES20.GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
mSurface.updateTexImage();
float[] mtx = new float[16];
mSurface.getTransformMatrix(mtx);
//绘制类封装到DirectDrawer哒
mDirectDrawer.draw();
}
@Override
public void onFrameAvailable(SurfaceTexture surfaceTexture) {
Log.i(TAG, "onFrameAvailable...");
this.requestRender();
}
}
这里头就是进行一些流程化操作,前面都已经提到过了,重点在于具体的绘制类封装到DirectDrawer,DirectDrawer主要进行了着色器的加载和链接等流水化操作。
DirectDrawer.java
/**
* Author:xishuang
* Date:2017.10.26
* Des:绘制类
*/
public class DirectDrawer {
private FloatBuffer vertexBuffer, textureVerticesBuffer;
private ShortBuffer drawListBuffer;
private final int mProgram;
private int mPositionHandle;
private int mTextureCoordHandle;
/**
* 顶点坐标的绘制顺序
*/
private short drawOrder[] = {0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3};
// 每个顶点坐标需要两个数表示
private static final int COORDS_PER_VERTEX = 2;
/**
* 获取坐标值的跨度,其中每个数占用4个字节(float)
*/
private final int vertexStride = COORDS_PER_VERTEX * 4;
/**
* 顶点坐标
*/
private static float squareCoords[] = {
-1.0f, 1.0f,
-1.0f, -1.0f,
1.0f, -1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f,
};
/**
* 纹理坐标
*/
private static float textureVertices[] = {
0.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f,
1.0f, 0.0f,
0.0f, 0.0f,
};
private int texture;
public DirectDrawer(Context context, int texture) {
this.texture = texture;
//初始化需要传入着色器中的顶点坐标缓存数据
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(squareCoords.length * 4);
bb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
vertexBuffer = bb.asFloatBuffer();
vertexBuffer.put(squareCoords);
vertexBuffer.position(0);
//初始化需要传入着色器中的顶点绘制顺序缓存数据
ByteBuffer dlb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(drawOrder.length * 2);
dlb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
drawListBuffer = dlb.asShortBuffer();
drawListBuffer.put(drawOrder);
drawListBuffer.position(0);
//初始化需要传入着色器中的纹理坐标缓存数据
ByteBuffer bb2 = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(textureVertices.length * 4);
bb2.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
textureVerticesBuffer = bb2.asFloatBuffer();
textureVerticesBuffer.put(textureVertices);
textureVerticesBuffer.position(0);
//从文件中加载和编译顶点着色器
String vertex = LoadShaderUtil.readShaderFromRawResource(context, R.raw.vertexshader);
int vertexShader = loadShader(GLES20.GL_VERTEX_SHADER, vertex);
//从文件中加载和编译片元着色器
//String fra = LoadShaderUtil.readShaderFromRawResource(context, R.raw.fragmentsketchshader);
String fra = LoadShaderUtil.readShaderFromRawResource(context, R.raw.fragmentcameoshader);
int fragmentShader = loadShader(GLES20.GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER, fra);
mProgram = GLES20.glCreateProgram(); // 创建program
GLES20.glAttachShader(mProgram, vertexShader); // 绑定顶点着色器shader到program
GLES20.glAttachShader(mProgram, fragmentShader); // 绑定片元着色器shader到program
GLES20.glLinkProgram(mProgram); // 链接program
}
public void draw() {
// 使用program
GLES20.glUseProgram(mProgram);
GLES20.glActiveTexture(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE0);
GLES20.glBindTexture(GLES11Ext.GL_TEXTURE_EXTERNAL_OES, texture);
// 获取顶点着色器中的顶点引用对象
mPositionHandle = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(mProgram, "vPosition");
// 启用顶点引用对象
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(mPositionHandle);
// 顶点缓存数据绑定到顶点引用对象
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(mPositionHandle, COORDS_PER_VERTEX, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, vertexStride, vertexBuffer);
// 获取顶点着色器中的纹理坐标引用对象
mTextureCoordHandle = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(mProgram, "inputTextureCoordinate");
// 纹理坐标引用对象
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(mTextureCoordHandle);
// 纹理坐标的缓存数据绑定到纹理坐标引用对象
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(mTextureCoordHandle, COORDS_PER_VERTEX, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, vertexStride, textureVerticesBuffer);
// 正式渲染
GLES20.glDrawElements(GLES20.GL_TRIANGLES, drawOrder.length, GLES20.GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT, drawListBuffer);
// 禁用
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(mPositionHandle);
GLES20.glDisableVertexAttribArray(mTextureCoordHandle);
}
private int loadShader(int type, String shaderCode) {
// 根据着色器得类型创建着色器对象
// GLES20.GL_VERTEX_SHADER 顶点着色器
// GLES20.GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER 片元着色器
int shader = GLES20.glCreateShader(type);
// 着色器源码加载和编译
GLES20.glShaderSource(shader, shaderCode);
GLES20.glCompileShader(shader);
return shader;
}
}
尽量注释得清晰了,纹理坐标对应着顶点坐标,顶点的颜色就是通过纹理坐标来获取图像流中的纹理颜色数据,主要讲一下顶点坐标绘制一个矩形。
/**
* 顶点坐标
*/
private static float squareCoords[] = {
-1.0f, 1.0f,
-1.0f, -1.0f,
1.0f, -1.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f,
};
/**
* 顶点坐标的绘制顺序
*/
private short drawOrder[] = {0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3};
顶点坐标有4个顶点,然后drawOrder按照4个顶点的索引来绘制两个三角形产生一个矩形。顶点的绘制顺序就是{0, 1, 2}:(-1.0,1.0)->(-1.0,-1.0)->(1.0,-1.0)然后{0, 2, 3}:(-1.0,1.0)->(1.0,-1.0)->(1.0,1.0)
3 渲染着色器实现图像处理
前面的一切操作就是为了给渲染管线提供图像流数据作为纹理,具体的图像处理操作是在片元着色器中完成的。
3.1 顶点着色器
vertexshader.sh
//顶点着色器
attribute vec4 vPosition;
attribute vec2 inputTextureCoordinate;
varying vec2 textureCoordinate;
void main(){
gl_Position = vPosition;
textureCoordinate = inputTextureCoordinate;
}
顶点着色器的工作很简单,就是接收来自我们代码里传过来的顶点坐标数据和纹理坐标数据,然后把这些数据交给渲染管线处理后交给片元着色器,所以重点还是在于片元着色器,片元着色器相当于对每个像素进行处理。
3.2 片元着色器
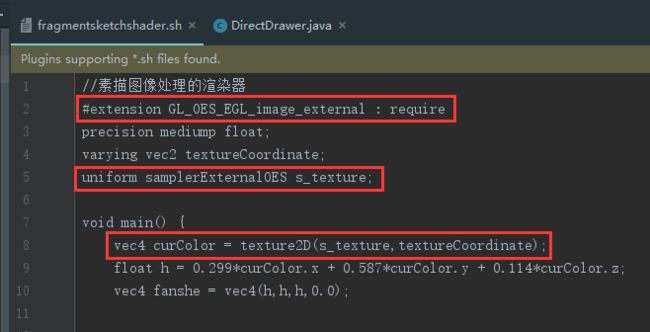
fragmentsketchshader.sh
//素描图像处理的渲染器
#extension GL_OES_EGL_image_external : require
precision mediump float;
varying vec2 textureCoordinate;
uniform samplerExternalOES s_texture;
void main() {
vec4 curColor = texture2D(s_texture,textureCoordinate);
//1、去色(黑白化)
float h = 0.299*curColor.x + 0.587*curColor.y + 0.114*curColor.z;
vec4 fanshe = vec4(h,h,h,0.0);
//2、获取该纹理附近的上下左右的纹理并求其去色,补色
vec4 sample0,sample1,sample2,sample3;
float h0,h1,h2,h3;
float fstep=0.0015;
sample0=texture2D(s_texture,vec2(textureCoordinate.x-fstep,textureCoordinate.y-fstep));
sample1=texture2D(s_texture,vec2(textureCoordinate.x+fstep,textureCoordinate.y-fstep));
sample2=texture2D(s_texture,vec2(textureCoordinate.x+fstep,textureCoordinate.y+fstep));
sample3=texture2D(s_texture,vec2(textureCoordinate.x-fstep,textureCoordinate.y+fstep));
//这附近的4个纹理值同样得进行去色(黑白化)
h0 = 0.299*sample0.x + 0.587*sample0.y + 0.114*sample0.z;
h1 = 0.299*sample1.x + 0.587*sample1.y + 0.114*sample1.z;
h2 = 0.299*sample2.x + 0.587*sample2.y + 0.114*sample2.z;
h3 = 0.299*sample3.x + 0.587*sample3.y + 0.114*sample3.z;
//反相,得到每个像素的补色
sample0 = vec4(1.0-h0,1.0-h0,1.0-h0,0.0);
sample1 = vec4(1.0-h1,1.0-h1,1.0-h1,0.0);
sample2 = vec4(1.0-h2,1.0-h2,1.0-h2,0.0);
sample3 = vec4(1.0-h3,1.0-h3,1.0-h3,0.0);
//3、对反相颜色值进行均值模糊
vec4 color=(sample0+sample1+sample2+sample3) / 4.0;
//4、颜色减淡,将第1步中的像素和第3步得到的像素值进行计算
vec3 endColor = fanshe.rgb+(fanshe.rgb*color.rgb)/(1.0-color.rgb);
//最终获取的颜色
gl_FragColor = vec4(endColor,0.0);
}
对每个像素点都进行了同样得图像处理算法,这个算法参考自Android图片素描效果,只是我这里用的是均值模糊,而不是高斯模糊,因为高斯模糊实现起来复杂,用最简单的方式实现这个素描的效果。
当然如果片元着色器使用不同的处理算法,就可以得到你想要的效果。
github Demo地址:SketchCamera