基于Python的Webserver开发之文档分页
相关webService的简介、原理、使用、流程图
本文主要是利用python包spyne实现web server
在实现之前需要安装三个包:spyne,suds,zeep
pip3 install spyne
pip3 install suds-jurko
pip3 install zeep注:这里不要pip install suds 这样安装完成后,suds对应的Client是python2版本的,与python3不兼容,导致报错。
Web Service 之 Python -- spyne学习
Server部分:
from spyne import Application, rpc, ServiceBase
from spyne import Integer, Unicode, Array, ComplexModel, Iterable, String
from spyne.protocol.soap import Soap11 #如果支持soap的协议需要用到Soap11
from spyne.server.wsgi import WsgiApplication #可以创建一个wsgi服务器,做测试用
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
from spyne.protocol.json import JsonDocument #如果开发传入传出为Json需要用到JsonDocument
class Person(ComplexModel):
name = Unicode
age = Integer
class HelloWorldService(ServiceBase):
@rpc(Unicode, Integer, _returns=Iterable(Unicode))
def say_hello(self, name, times):
for i in range(times):
yield "Hello %s, It's the %s time to meet you." % (name, i + 1)
@rpc(Array(Person), _returns=Iterable(Unicode))
def say_hello_1(self, persons):
print('-------say_hello_1()--------')
if not persons:
yield 'None'
for person in persons:
print('name is : %s, age is %s.' % (person.name, person.age))
yield 'name is : %s, age is %s.' % (person.name, person.age)
#定义API的输入输出类型
application = Application([HelloWorldService],
'spyne.examples.hello',
in_protocol=Soap11(validator='lxml'),
out_protocol=Soap11())
wsgi_application = WsgiApplication(application)
if __name__ == '__main__':
import logging
host = '127.0.0.1'
port = 8000
logging.info("listening to http://127.0.0.1:8000")
logging.info("wsdl is at: http://localhost:8000/?wsdl")
server = make_server(host, port, wsgi_application)
server.serve_forever()Client部分:
#!/usr/bin/python
# coding:utf-8
from suds.client import Client
host = '127.0.0.1'
port = 8000
client = Client('http://%s:%s/?wsdl' % (host, port))
# print(client)
persons = client.service.say_hello('zhangsan', 2)
print(persons)
print('-' * 20)
person = {}
person['name'] = 'zhangsan'
person['age'] = 23
persons = client.factory.create('PersonArray')
persons.Person.append(person)
persons.Person.append(person)
# print(persons)
person = client.service.say_hello_1(persons)
print(person)返回结果:
(stringArray){
string[] =
"Hello zhangsan, It's the 1 time to meet you.",
"Hello zhangsan, It's the 2 time to meet you.",
}
--------------------
(stringArray){
string[] =
"name is : zhangsan, age is 23.",
"name is : zhangsan, age is 23.",
}zeep——这里也是起一个测试作用
from zeep import Client
ip = '127.0.0.1'
port = 8000
client = Client("http://%s:%s/?wsdl" % (ip, port))
# print(client.wsdl.dump())
### say_hello
factory = client.type_factory("ns0")
r = client.service.say_hello('zhangsan', 3)
print(r)
## say_hello_1
factory = client.type_factory("ns0")
person = factory.Person(name='zhangsan', age=23)
persons = factory.PersonArray([person, person])
r = client.service.say_hello_1(persons)
print(r)返回结果:
["Hello zhangsan, It's the 1 time to meet you.", "Hello zhangsan, It's the 2 time to meet you.", "Hello zhangsan, It's the 3 time to meet you."]
['name is : zhangsan, age is 23.', 'name is : zhangsan, age is 23.']根据上面的学习,框架是固定的,主要是根据需求定义自己的视图函数,这里写一个简单的文档分页功能:
Server部分:
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
"""
@author:ZSW
@file:server_partnew.py
@time:2020/04/16
"""
#https://blog.csdn.net/shangguanyunluo123/article/details/79070064
#https://www.cnblogs.com/Evan-fanfan/p/10325447.html
from spyne import Application, rpc, ServiceBase
from spyne import Integer, Unicode, Array, ComplexModel, Iterable, String
from spyne.protocol.soap import Soap11 #如果支持soap的协议需要用到Soap11
from spyne.server.wsgi import WsgiApplication #可以创建一个wsgi服务器,做测试用
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
from spyne.protocol.json import JsonDocument #如果开发传入传出为Json需要用到JsonDocument
import csv
import pandas as pd
import json
#创建一个服务
class splitPageService(ServiceBase):
#传入参数Unicode, Integer,由之前定义的
@rpc(Integer, Integer, _returns=Unicode)
#具体实现的视图函数 pagesize为每页多少条数据 pagenumber为第几页
def splitPage(self, pagesize, pagenumber):
excel_data = pd.read_excel("laws.xlsx")
data_df = pd.DataFrame(excel_data)
start = (pagenumber - 1) * pagesize
end = pagenumber * pagesize
df = data_df.loc[start:end]
result = df.to_dict(orient='records')
return json.dumps(result, ensure_ascii=False)
# for res in result:
# print(res)
# yield json.dumps(res,ensure_ascii=False)
# yield str(res)
#定义API的输入输出类型
application = Application([splitPageService],
'spyne.examples.hello',
in_protocol=Soap11(validator='lxml'),
out_protocol=Soap11()
)
# application = Application([splitPageService],
# 'spyne.examples.hello',
# in_protocol=JsonDocument(validator='soft'),
# out_protocol=JsonDocument()
# )
wsgi_application = WsgiApplication(application)
if __name__ == '__main__':
import logging
host = '127.0.0.1'
port = 8091
logging.info("listening to http://127.0.0.1:8091")
logging.info("wsdl is at: http://localhost:8091/?wsdl")
server = make_server(host, port, wsgi_application)
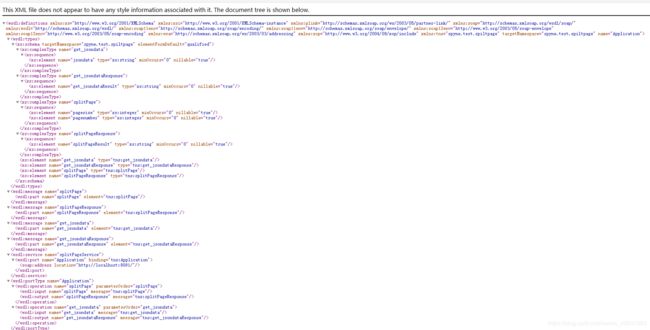
server.serve_forever()服务端创建成功并启动,通过浏览器输入 http://localhost:8091/?wsdl,可看到接口wsdl,如下图示:
Client部分:对server部分进行测试
from suds.client import Client
host = '127.0.0.1'
port = 8091
client = Client('http://%s:%s/?wsdl' % (host, port))
# print(client)
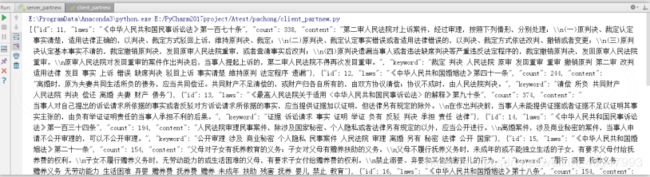
res = client.service.splitPage(10, 2) #设置每页10条,查看第2页数据
print(res)返回结果:
参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/shangguanyunluo123/article/details/79070064
https://www.cnblogs.com/Evan-fanfan/p/10325447.html