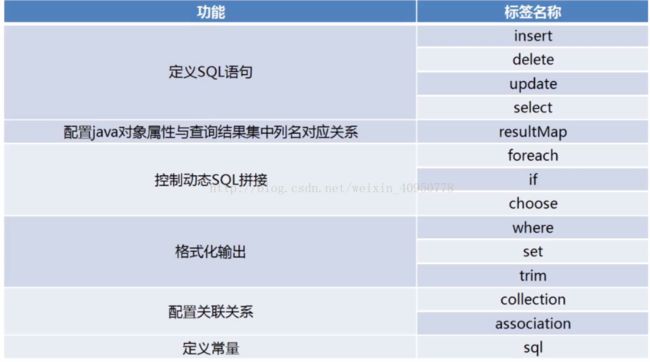
Mybatis全部标签
一、定义SQL语句
(1)select 标签的使用
属性介绍:
id :唯一的标识符.
parameterType:传给此语句的参数的全路径名或别名 例:com.test.poso.User或user
resultType :语句返回值类型或别名。注意,如果是集合,那么这里填写的
是集合的泛型,而不是集合本身(resultType 与resultMap 不能并用)
例子:
sql:
select * from user where name =#{name}
(2)insert 标签的使用
属性介绍:
id :唯一的标识符
parameterType:传给此语句的参数的全路径名或别名 例:com.test.poso.User
(3)delete 标签的使用
例:
delete from user
where id = #{id}
(4)update 标签的使用
类似于insert
二、配置对象属性与查询结果集
(1)resultMap 标签的使用
基本作用:建立SQL查询结果字段与实体属性的映射关系信息
查询的结果集转换为java对象,方便进一步操作
将结果集中的列与java对象中的属性对应起来并将值填充进去
!注意:与java对象对应的列不是数据库中表的列名,而是查询后结果集的列名
例:
标签说明:
主标签
id:该resultMap的标志
type:返回值的类名,此例中返回EStudnet类
子标签:
id:用于设置主键字段与领域模型属性的映射关系,此处主键为ID,对应id。result:用于设置普通字段与领域模型属性的映射关系
三、动态拼接SQL
(1)if 标签的使用
if标签通常用于WHERE语句中,通过判断参数值来决定是否使用某个查询条件, 他也经常用于UPDATE语句中判断是否更新某一个字段,还可以在INSERT语句中用来判断是否插入某个字段的值
例:
- <select id="getStudentListLikeName" parameterType="StudentEntity" resultMap="studentResultMap">
- SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST
- WHERE ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #{studentName}),'%')
- select>
但是此时如果studentName是null或空字符串,此语句很可能报错或查询结果为空。此时我们使用if动态sql语句先进行判断,如果值为null或等于空字符串,我们就不进行此条件的判断。
修改为:
- <select id=" getStudentListLikeName " parameterType="StudentEntity" resultMap="studentResultMap">
- SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST
- <if test="studentName!=null and studentName!='' ">
- WHERE ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #{studentName}),'%')
- if>
- select>
(2)foreach 标签的使用
foreach标签主要用于构建in条件,他可以在sql中对集合进行迭代。如下:
delete from user where id in
#{id}
我们假如说参数为---- int[] ids = {1,2,3,4,5} ----那么打印之后的SQL如下:
delete form user where id in (1,2,3,4,5)
释义:
collection :collection属性的值有三个分别是list、array、map三种,分别对应的参数类型为:List、数组、map集合,我在上面传的参数为数组,所以值为array
item : 表示在迭代过程中每一个元素的别名
index :表示在迭代过程中每次迭代到的位置(下标)
open :前缀
close :后缀
separator :分隔符,表示迭代时每个元素之间以什么分隔
我们通常可以将之用到批量删除、添加等操作中。
(3)choose 标签的使用
有时候我们并不想应用所有的条件,而只是想从多个选项中选择一个。MyBatis提供了choose 元素,按顺序判断when中的条件出否成立,如果有一个成立,则choose结束。当choose中所有when的条件都不满则时,则执行 otherwise中的sql。类似于Java 的switch 语句,choose为switch,when为case,otherwise则为default。
if是与(and)的关系,而choose是或(or)的关系。
例如下面例子,同样把所有可以限制的条件都写上,方面使用。选择条件顺序,when标签的从上到下的书写顺序:
- <select id="getStudentListChooseEntity" parameterType="StudentEntity" resultMap="studentResultMap">
- SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST
- <where>
- <choose>
- <when test="studentName!=null and studentName!='' ">
- ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #{studentName}),'%')
- when>
- <when test="studentSex!= null and studentSex!= '' ">
- AND ST.STUDENT_SEX = #{studentSex}
- when>
- <when test="studentBirthday!=null">
- AND ST.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY = #{studentBirthday}
- when>
- <when test="classEntity!=null and classEntity.classID !=null and classEntity.classID!='' ">
- AND ST.CLASS_ID = #{classEntity.classID}
- when>
- <otherwise>
- otherwise>
- choose>
- where>
- select>
四、格式化输出
(1)where
当if标签较多时,这样的组合可能会导致错误。例如,like姓名,等于指定性别等:
Xml代码
- <select id="getStudentListWhere" parameterType="StudentEntity" resultMap="studentResultMap">
- SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST
- WHERE
- <if test="studentName!=null and studentName!='' ">
- ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #{studentName}),'%')
- if>
- <if test="studentSex!= null and studentSex!= '' ">
- AND ST.STUDENT_SEX = #{studentSex}
- if>
- select>
如果上面例子,参数studentName为null或’’,则或导致此sql组合成“WHERE AND”之类的关键字多余的错误SQL。
这时我们可以使用where动态语句来解决。这个“where”标签会知道如果它包含的标签中有返回值的话,它就插入一个‘where’。此外,如果标签返回的内容是以AND 或OR 开头的,则它会剔除掉。
上面例子修改为:
Xml代码
- <select id="getStudentListWhere" parameterType="StudentEntity" resultMap="studentResultMap">
- SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST
- <where>
- <if test="studentName!=null and studentName!='' ">
- ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #{studentName}),'%')
- if>
- <if test="studentSex!= null and studentSex!= '' ">
- AND ST.STUDENT_SEX = #{studentSex}
- if>
- where>
- select>
(2)set
当在update语句中使用if标签时,如果前面的if没有执行,则或导致逗号多余错误。使用set标签可以将动态的配置SET 关键字,和剔除追加到条件末尾的任何不相关的逗号。
没有使用if标签时,如果有一个参数为null,都会导致错误,如下示例:
Xml代码
- <update id="updateStudent" parameterType="StudentEntity">
- UPDATE STUDENT_TBL
- SET STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_NAME = #{studentName},
- STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_SEX = #{studentSex},
- STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY = #{studentBirthday},
- STUDENT_TBL.CLASS_ID = #{classEntity.classID}
- WHERE STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_ID = #{studentID};
- update>
使用set+if标签修改后,如果某项为null则不进行更新,而是保持数据库原值。如下示例:
Xml代码
- <update id="updateStudent" parameterType="StudentEntity">
- UPDATE STUDENT_TBL
- <set>
- <if test="studentName!=null and studentName!='' ">
- STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_NAME = #{studentName},
- if>
- <if test="studentSex!=null and studentSex!='' ">
- STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_SEX = #{studentSex},
- if>
- <if test="studentBirthday!=null ">
- STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY = #{studentBirthday},
- if>
- <if test="classEntity!=null and classEntity.classID!=null and classEntity.classID!='' ">
- STUDENT_TBL.CLASS_ID = #{classEntity.classID}
- if>
- set>
- WHERE STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_ID = #{studentID};
- update>
(3)trim
trim是更灵活的去处多余关键字的标签,他可以实践where和set的效果。
where例子的等效trim语句:
- <select id="getStudentListWhere" parameterType="StudentEntity" resultMap="studentResultMap">
- SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST
- <trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND|OR">
- <if test="studentName!=null and studentName!='' ">
- ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #{studentName}),'%')
- if>
- <if test="studentSex!= null and studentSex!= '' ">
- AND ST.STUDENT_SEX = #{studentSex}
- if>
- trim>
- select>
set例子的等效trim语句:
Xml代码
- <update id="updateStudent" parameterType="StudentEntity">
- UPDATE STUDENT_TBL
- <trim prefix="SET" suffixOverrides=",">
- <if test="studentName!=null and studentName!='' ">
- STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_NAME = #{studentName},
- if>
- <if test="studentSex!=null and studentSex!='' ">
- STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_SEX = #{studentSex},
- if>
- <if test="studentBirthday!=null ">
- STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY = #{studentBirthday},
- if>
- <if test="classEntity!=null and classEntity.classID!=null and classEntity.classID!='' ">
- STUDENT_TBL.CLASS_ID = #{classEntity.classID}
- if>
- trim>
- WHERE STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_ID = #{studentID};
- update>
五、配置关联关系
(1)collection
一对一
association通常用来映射一对一的关系,例如,有个类user,对应的实体类如下:(getter,setter方法省略)
private String id;//主键 private String userName;//用户姓名
有个类Article,对应的实体类如下:
private String id;//主键 private String articleTitle;//文章标题 private String articleContent;//文章内容
如果我想查询一个用户的时候,也查到他写的一篇文章,可以怎样写呢?在类user加入一个属性article
private String id;//主键 private String userName;//用户姓名 private Article article;//新增的文章属性
2、mapper.xml 我在user类的mapper.xml这样配置
//这里把user的id传过去 select="test.mybatis.dao.articleMapper.selectArticleByUserId" />//test.mybatis.dao.articleMapper为命名空间
同时,我的article对应的xml这样写:
12 (当然,这里还有查询user表的语句,省略)3 4 5
同时,在article对应的xml有这样的select语句:
(2)association
一对多
实体类增加对应属性
private String id;//主键 private String userName;//用户姓名 private ListarticleList;
userMapper.xml这样配置
以下省略,类同,Mybatis会把结果封装成List类型。 //这里把user的id传过去 select="test.mybatis.dao.articleMapper.selectArticleListByUserId" />
三、如果我还想通过Article表另一张表,比如文章中有个fk_id,也可以像上面这样重复配置,把fk_id当做与另一张表关联的参数,那时就可以通过用户查到文章,查到文章关联的另一张表了。
六、SQL标签
更多用于写sql语句的一部分,写在配置文件中的常量
七、include标签
用于引用常量