Android官方文档—User Interface(Dialogs)
对话框
对话框是一个小窗口,提示用户做出决定或输入其他信息。对话框不会填满屏幕,通常用于需要用户在继续操作之前执行操作的模态事件。
对话框设计
有关如何设计对话框的信息(包括语言建议),请阅读“对话框设计指南”。
Dialog类是对话框的基类,但您应该避免直接实例化Dialog。而是使用以下子类之一:
AlertDialog
一个对话框,可以显示标题,最多三个按钮,可选项列表或自定义布局。
DatePickerDialog or TimePickerDialog
具有预定义UI的对话框,允许用户选择日期或时间。
避免使用ProgressDialog
Android包含另一个名为ProgressDialog的对话框类,它显示带有进度条的对话框。但是,如果您需要指示加载或不确定进度,则应遵循Progress&Activity的设计指南,并在布局中使用ProgressBar。
这些类定义对话框的样式和结构,但您应该使用DialogFragment作为对话框的容器。 DialogFragment类提供了创建对话框和管理其外观所需的所有控件,而不是调用Dialog对象上的方法。
使用DialogFragment管理对话框可确保它正确处理生命周期事件,例如用户按下“返回”按钮或旋转屏幕时。 DialogFragment类还允许您将对话框的UI重用为更大UI中的可嵌入组件,就像传统的Fragment一样(例如,当您希望对话UI在大屏幕和小屏幕上以不同方式显示时)。
本指南的以下部分描述了如何将DialogFragment与AlertDialog对象结合使用。如果您想创建日期或时间选择器,您应该阅读选择器指南。
注意:由于DialogFragment类最初是使用Android 3.0(API级别11)添加的,因此本文档介绍了如何使用随支持库提供的DialogFragment类。通过将此库添加到您的应用程序,您可以在运行Android 1.6或更高版本的设备上使用DialogFragment和各种其他API。如果您的应用程序支持的最低版本是API级别11或更高版本,那么您可以使用DialogFragment的框架版本,但请注意,本文档中的链接适用于支持库API。使用支持库时,请确保导入android.support.v4.app.DialogFragment类而不是android.app.DialogFragment。
创建对话框片段
您可以通过扩展DialogFragment并在onCreateDialog()回调方法中创建AlertDialog来完成各种对话框设计 - 包括自定义布局和Dialogs设计指南中描述的那些。
例如,这是一个在DialogFragment中管理的基本AlertDialog:
public class FireMissilesDialogFragment extends DialogFragment {
@Override
public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// Use the Builder class for convenient dialog construction
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity());
builder.setMessage(R.string.dialog_fire_missiles)
.setPositiveButton(R.string.fire, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) {
// FIRE ZE MISSILES!
}
})
.setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) {
// User cancelled the dialog
}
});
// Create the AlertDialog object and return it
return builder.create();
}
} 图1.带有消息和两个操作按钮的对话框。
图1.带有消息和两个操作按钮的对话框。
现在,当您创建此类的实例并在该对象上调用show()时,对话框将如图1所示。
下一节将介绍有关使用AlertDialog.Builder API创建对话框的更多信息。
根据对话框的复杂程度,您可以在DialogFragment中实现各种其他回调方法,包括所有基本的片段生命周期方法。
建立警报对话框
AlertDialog类允许您构建各种对话框设计,并且通常是您需要的唯一对话框类。如图2所示,警报对话框有三个区域:
1.Title
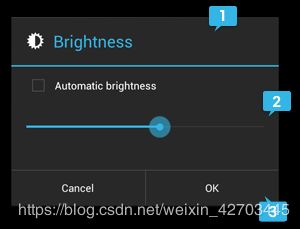 图2.对话框的布局。
图2.对话框的布局。
这是可选的,仅当内容区域被详细消息,列表或自定义布局占用时才应使用。如果您需要声明一个简单的消息或问题(例如图1中的对话框),则不需要标题。
2.Content area
这可以显示消息,列表或其他自定义布局。
3.Action buttons
对话框中的操作按钮不应超过三个。
AlertDialog.Builder类提供的API允许您使用这些类型的内容创建AlertDialog,包括自定义布局。
要构建AlertDialog:
// 1. Instantiate an AlertDialog.Builder with its constructor
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity());
// 2. Chain together various setter methods to set the dialog characteristics
builder.setMessage(R.string.dialog_message)
.setTitle(R.string.dialog_title);
// 3. Get the AlertDialog from create()
AlertDialog dialog = builder.create();以下主题说明如何使用AlertDialog.Builder类定义各种对话框属性。
添加按钮
要添加如图2中的操作按钮,请调用setPositiveButton()和setNegativeButton()方法:
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity());
// Add the buttons
builder.setPositiveButton(R.string.ok, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) {
// User clicked OK button
}
});
builder.setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) {
// User cancelled the dialog
}
});
// Set other dialog properties
...
// Create the AlertDialog
AlertDialog dialog = builder.create();set ... Button()方法需要按钮的标题(由字符串资源提供)和DialogInterface.OnClickListener,它定义用户按下按钮时要执行的操作。
您可以添加三个不同的操作按钮:
Positive
您应该使用它来接受并继续操作(“确定”操作)。
Negative
您应该使用它来取消操作。
Neutral
当用户可能不想继续操作时,您应该使用此功能,但不一定要取消。它出现在正负按钮之间。例如,行动可能是“稍后提醒我”。
 图3.包含标题和列表的对话框。
图3.包含标题和列表的对话框。
您只能将每种按钮类型中的一种添加到AlertDialog中。也就是说,你不能有一个以上的“肯定”按钮。
添加列表
AlertDialog API提供三种列表:
- 传统的单选列表
- 持久性单选列表(单选按钮)
- 持久性多选列表(复选框)
要创建类似于图3中的单选列表,请使用setItems()方法:
@Override
public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity());
builder.setTitle(R.string.pick_color)
.setItems(R.array.colors_array, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// The 'which' argument contains the index position
// of the selected item
}
});
return builder.create();
}由于列表出现在对话框的内容区域中,因此对话框不能同时显示消息和列表,您应该使用setTitle()为对话框设置标题。要指定列表的项目,请调用setItems(),传递数组。或者,您可以使用setAdapter()指定列表。这允许您使用ListAdapter使用动态数据(例如从数据库)备份列表。
如果选择使用ListAdapter备份列表,请始终使用Loader以便异步加载内容。在使用适配器和装载程序指南构建布局中进一步描述了这一点。
注意:默认情况下,触摸列表项会取消对话框,除非您使用以下持久性选项列表之一。
 图4.多项选择项列表。
图4.多项选择项列表。
添加持久性多项选择或单项选择列表
要添加多项选项(复选框)或单项选项(单选按钮)的列表,请分别使用setMultiChoiceItems()或setSingleChoiceItems()方法。
例如,以下是如何创建多选列表,如图4所示,将选定项保存在ArrayList中:
@Override
public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
mSelectedItems = new ArrayList(); // Where we track the selected items
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity());
// Set the dialog title
builder.setTitle(R.string.pick_toppings)
// Specify the list array, the items to be selected by default (null for none),
// and the listener through which to receive callbacks when items are selected
.setMultiChoiceItems(R.array.toppings, null,
new DialogInterface.OnMultiChoiceClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which,
boolean isChecked) {
if (isChecked) {
// If the user checked the item, add it to the selected items
mSelectedItems.add(which);
} else if (mSelectedItems.contains(which)) {
// Else, if the item is already in the array, remove it
mSelectedItems.remove(Integer.valueOf(which));
}
}
})
// Set the action buttons
.setPositiveButton(R.string.ok, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) {
// User clicked OK, so save the mSelectedItems results somewhere
// or return them to the component that opened the dialog
...
}
})
.setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) {
...
}
});
return builder.create();
}虽然传统列表和带单选按钮的列表都提供“单选”操作,但如果要保留用户的选择,则应使用setSingleChoiceItems()。也就是说,如果稍后再次打开对话框应该指示用户当前的选择,那么您将创建一个带有单选按钮的列表。
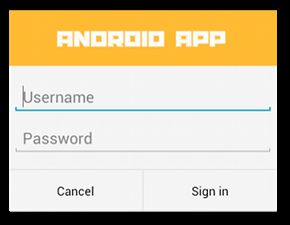 图5.自定义对话框布局。
图5.自定义对话框布局。
创建自定义布局
如果要在对话框中使用自定义布局,请通过调用AlertDialog.Builder对象上的setView()创建布局并将其添加到AlertDialog。
默认情况下,自定义布局填充对话框窗口,但您仍然可以使用AlertDialog.Builder方法添加按钮和标题。
例如,这是图5中对话框的布局文件:
res/layout/dialog_signin.xml
提示:默认情况下,当您将EditText元素设置为使用“textPassword”输入类型时,字体系列将设置为等宽字体,因此您应将其字体系列更改为“sans-serif”,以便两个文本字段都使用匹配的字体样式。
要在DialogFragment中扩充布局,请使用getLayoutInflater()获取LayoutInflater并调用inflate(),其中第一个参数是布局资源ID,第二个参数是布局的父视图。然后,您可以调用setView()将布局放在对话框中。
@Override
public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity());
// Get the layout inflater
LayoutInflater inflater = getActivity().getLayoutInflater();
// Inflate and set the layout for the dialog
// Pass null as the parent view because its going in the dialog layout
builder.setView(inflater.inflate(R.layout.dialog_signin, null))
// Add action buttons
.setPositiveButton(R.string.signin, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) {
// sign in the user ...
}
})
.setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) {
LoginDialogFragment.this.getDialog().cancel();
}
});
return builder.create();
}提示:如果需要自定义对话框,则可以将“活动”显示为对话框,而不是使用“对话框API”。只需创建一个活动并将其主题设置为
清单元素中的Theme.Holo.Dialog: 这样。活动现在显示在对话窗口而不是全屏。
将事件传递回Dialog的宿主
当用户触摸对话框的某个操作按钮或从其列表中选择一个项目时,DialogFragment可能会自行执行必要的操作,但通常您需要将事件传递给打开对话框的活动或片段。为此,请为每种类型的单击事件定义一个带有方法的接口。然后在主机组件中实现该接口,该接口将从对话框接收操作事件。
例如,这是一个DialogFragment,它定义了一个接口,通过该接口将事件传递回主机活动:
public class NoticeDialogFragment extends DialogFragment {
/* The activity that creates an instance of this dialog fragment must
* implement this interface in order to receive event callbacks.
* Each method passes the DialogFragment in case the host needs to query it. */
public interface NoticeDialogListener {
public void onDialogPositiveClick(DialogFragment dialog);
public void onDialogNegativeClick(DialogFragment dialog);
}
// Use this instance of the interface to deliver action events
NoticeDialogListener mListener;
// Override the Fragment.onAttach() method to instantiate the NoticeDialogListener
@Override
public void onAttach(Activity activity) {
super.onAttach(activity);
// Verify that the host activity implements the callback interface
try {
// Instantiate the NoticeDialogListener so we can send events to the host
mListener = (NoticeDialogListener) activity;
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
// The activity doesn't implement the interface, throw exception
throw new ClassCastException(activity.toString()
+ " must implement NoticeDialogListener");
}
}
...
}托管对话框的活动使用对话框片段的构造函数创建对话框的实例,并通过NoticeDialogListener接口的实现接收对话框的事件:
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity
implements NoticeDialogFragment.NoticeDialogListener{
...
public void showNoticeDialog() {
// Create an instance of the dialog fragment and show it
DialogFragment dialog = new NoticeDialogFragment();
dialog.show(getSupportFragmentManager(), "NoticeDialogFragment");
}
// The dialog fragment receives a reference to this Activity through the
// Fragment.onAttach() callback, which it uses to call the following methods
// defined by the NoticeDialogFragment.NoticeDialogListener interface
@Override
public void onDialogPositiveClick(DialogFragment dialog) {
// User touched the dialog's positive button
...
}
@Override
public void onDialogNegativeClick(DialogFragment dialog) {
// User touched the dialog's negative button
...
}
}由于host活动实现了NoticeDialogListener(由上面显示的onAttach()回调方法强制执行),因此对话框片段可以使用接口回调方法将click事件传递给activity:
public class NoticeDialogFragment extends DialogFragment {
...
@Override
public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// Build the dialog and set up the button click handlers
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity());
builder.setMessage(R.string.dialog_fire_missiles)
.setPositiveButton(R.string.fire, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) {
// Send the positive button event back to the host activity
mListener.onDialogPositiveClick(NoticeDialogFragment.this);
}
})
.setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) {
// Send the negative button event back to the host activity
mListener.onDialogNegativeClick(NoticeDialogFragment.this);
}
});
return builder.create();
}
}显示对话框
当您想要显示对话框时,创建DialogFragment的实例并调用show(),传递FragmentManager和对话框片段的标记名称。
您可以通过从FragmentActivity调用getSupportFragmentManager()或从Fragment调用getFragmentManager()来获取FragmentManager。例如:
public void confirmFireMissiles() {
DialogFragment newFragment = new FireMissilesDialogFragment();
newFragment.show(getSupportFragmentManager(), "missiles");
}第二个参数“missiles”是一个唯一的标记名称,系统在必要时用它来保存和恢复片段状态。标签还允许您通过调用findFragmentByTag()来获取片段的句柄。
显示对话框全屏或嵌入式片段
您可能有一个UI设计,在这种UI设计中,您希望UI在某些情况下显示为对话框,但在其他情况下则显示为全屏或嵌入式片段(可能取决于设备是大屏幕还是小屏幕)。 DialogFragment类为您提供了这种灵活性,因为它仍然可以作为可嵌入的片段。
但是,在这种情况下,您无法使用AlertDialog.Builder或其他Dialog对象来构建对话框。如果希望DialogFragment可嵌入,则必须在布局中定义对话框的UI,然后在onCreateView()回调中加载布局。
这是一个示例DialogFragment,可以显示为对话框或可嵌入的片段(使用名为purchase_items.xml的布局):
public class CustomDialogFragment extends DialogFragment {
/** The system calls this to get the DialogFragment's layout, regardless
of whether it's being displayed as a dialog or an embedded fragment. */
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// Inflate the layout to use as dialog or embedded fragment
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.purchase_items, container, false);
}
/** The system calls this only when creating the layout in a dialog. */
@Override
public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// The only reason you might override this method when using onCreateView() is
// to modify any dialog characteristics. For example, the dialog includes a
// title by default, but your custom layout might not need it. So here you can
// remove the dialog title, but you must call the superclass to get the Dialog.
Dialog dialog = super.onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState);
dialog.requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
return dialog;
}
}这里有一些代码根据屏幕大小决定是将片段显示为对话框还是全屏UI:
public void showDialog() {
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
CustomDialogFragment newFragment = new CustomDialogFragment();
if (mIsLargeLayout) {
// The device is using a large layout, so show the fragment as a dialog
newFragment.show(fragmentManager, "dialog");
} else {
// The device is smaller, so show the fragment fullscreen
FragmentTransaction transaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
// For a little polish, specify a transition animation
transaction.setTransition(FragmentTransaction.TRANSIT_FRAGMENT_OPEN);
// To make it fullscreen, use the 'content' root view as the container
// for the fragment, which is always the root view for the activity
transaction.add(android.R.id.content, newFragment)
.addToBackStack(null).commit();
}
}有关执行片段事务的更多信息,请参阅片段指南。
在此示例中,mIsLargeLayout布尔值指定当前设备是否应使用应用程序的大型布局设计(因此将此片段显示为对话框,而不是全屏)。设置此类布尔值的最佳方法是使用不同屏幕大小的备用资源值声明bool资源值。例如,以下是两种不同屏幕尺寸的bool资源版本:
res/values/bools.xml
false
res/values-large/bools.xml
true
然后,您可以在活动的onCreate()方法中初始化mIsLargeLayout值:
boolean mIsLargeLayout;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mIsLargeLayout = getResources().getBoolean(R.bool.large_layout);
}在大屏幕上将对象显示为对话框
在小屏幕上,您可以通过在大屏幕上将“活动”显示为对话框来完成相同的结果,而不是在小屏幕上将对话框显示为全屏UI。您选择哪种方法取决于您的应用程序设计,但当您的应用程序已经设计为小屏幕并且您希望通过将短期活动显示为对话框来改善平板电脑体验时,将对象显示为对话框通常很有用。
要仅在大屏幕上将活动显示为对话框,请将Theme.Holo.DialogWhenLarge主题应用于
有关使用主题设置活动样式的更多信息,请参阅样式和主题指南。
解除对话框
当用户触摸使用AlertDialog.Builder创建的任何操作按钮时,系统会为您解除对话框。
当用户触摸对话框列表中的项目时,系统也会关闭对话框,除非列表使用单选按钮或复选框。否则,您可以通过调用DialogFragment上的dismiss()来手动关闭对话框。
如果您需要在对话框消失时执行某些操作,可以在DialogFragment中实现onDismiss()方法。
您也可以取消对话框。这是一个特殊事件,表示用户在未完成任务的情况下明确地离开了对话框。如果用户按下“返回”按钮,触摸对话框区域外的屏幕,或者在对话框中显式调用cancel()(例如响应对话框中的“取消”按钮),则会发生这种情况。
如上例所示,您可以通过在DialogFragment类中实现onCancel()来响应cancel事件。
注意:系统在调用onCancel()回调的每个事件上调用onDismiss()。但是,如果调用Dialog.dismiss()或DialogFragment.dismiss(),系统将调用onDismiss()但不调用onCancel()。因此,当用户按下对话框中的“正”按钮时,通常应调用dismiss(),以便从视图中删除对话框。
