opencv:双目视觉 ——实现详细教程(matlabR2015b+opencv-python)
原本这个文章是打算转载别人的,在经历过各个教程都失败后(1.要不然是前后不对应,估计是随便复制一下,2.要么是讲解很不清楚,没有讲解怎么使用参数),决定自己写一下。记录一下,尽量会非常详细
0.前期准备
- 准备棋盘格
类似于这种:下载地址在这里:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1qYu0IkgbffuoCgANiQ5-Dw
必须实际打印出来哦,你用别人的标定图片怎么可能反映你自己的摄像头特征呢。
- 准备标定图片
利用opencv读取你自己的摄像头,按下s键进行截图,分别保存在left文件夹和right文件夹
| 有可能需要修改的地方: 1.folder 改为自己的路径 2.我这里的双目摄像头图像是在一个框里显示的,所以只需要capture一次,如果你的摄像头是分开的,则要两次capture 3.分辨率设置的时候,要根据自己的摄像机分辨率参数来设置,这很重要!!! |
import cv2
import time
AUTO = True # 自动拍照,或手动按s键拍照
INTERVAL = 2 # 自动拍照间隔
camera = cv2.VideoCapture(0)#也许你可能要capture两次
camera.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, 2560)#设置分辨率
camera.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, 960)#
utc = time.time()
folder = "E:/pythonlearning/opencv/screenshot/" # 拍照文件目录
def shot( frame):
global counter
leftpath = folder +"left/"+"left_" + str(counter) + ".jpg"
rightpath=folder + "right/"+ "right_" + str(counter) + ".jpg"
leftframe=frame[0:960,0:1280]#这里是为了将合在一个窗口显示的图像分为左右摄像头
rightframe=frame[0:960,1280:2560]
cv2.imwrite(leftpath, leftframe)
cv2.imwrite(rightpath, rightframe)
print("snapshot saved into: " + leftpath)
print("snapshot saved into: " + rightpath)
while True:
ret, frame = camera.read()
cv2.imshow("original", frame)
now = time.time()
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == ord("q"):
break
elif key == ord("s"):
shot( frame)
counter += 1
camera.release()
cv2.destroyWindow("original")
1.Matlab标定
matlab版本:R2015b
获取图片成功后,则要使用这些图片了
1.打开app->找到stereo calibration camera
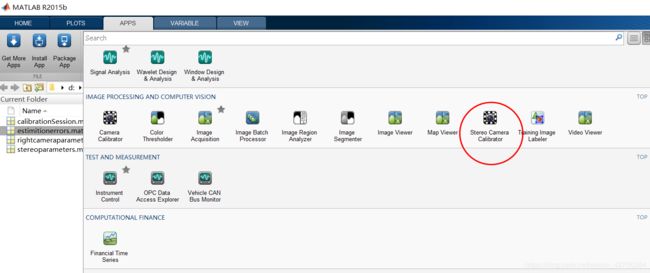
2.选定三个复选框后,add images
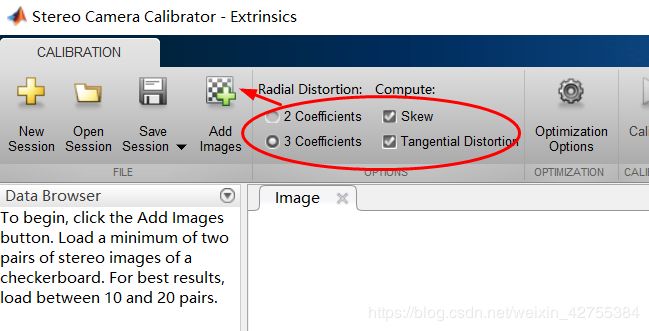
切记此处的 25是系统默认的,实际的是根据自己打印出来的方格宽度决定的。

添加图片


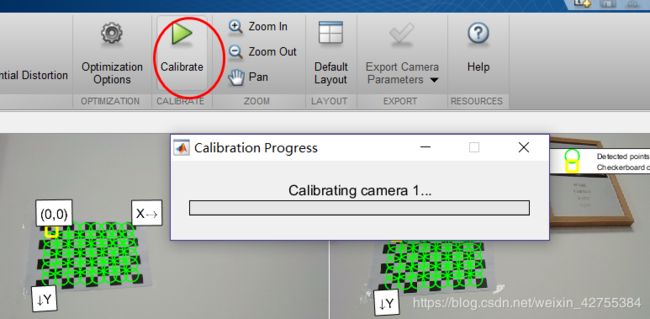


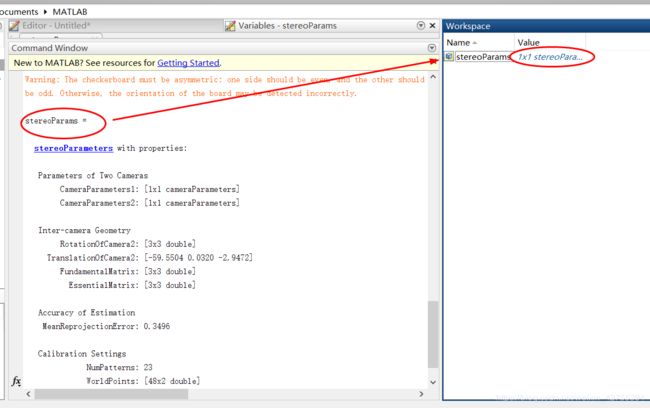
下面将会使用这些参数
2.opencv配置参数
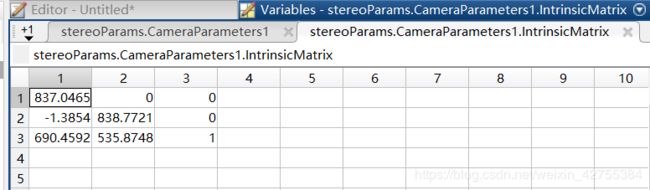
left_camera_matrix = np.array([[837.046533944197, 0., 0.],
[-1.38537933662732, 838.772077702795, 0.],
[690.459242460418, 535.874773256865, 1.]])
- 点进去radialdistortion和tangentialdistoration
RadialDistortion:径向畸变,摄像头由于光学透镜的特性使得成像存在着径向畸变,可由K1,K2,K3确定。
TangentialDistortion:切向畸变,由于装配方面的误差,传感器与光学镜头之间并非完全平行,因此成像存在切向畸变,可由两个参数P1,P2确定。
使用时,需要注意参数的排放顺序,即K1,K2,P1,P2,K3。切记不可弄错,否则后续的立体匹配会出现很大的偏差。
left_distortion = np.array([[0.0037, 0.00060366, 0.0101, 0.0013, -0.0626]])
- 同理写出右摄像头的矩阵,stereoParams.CameraParameters2中
right_camera_matrix = np.array([[829.904768800558, 0., 0.],
[0.449308928342319, 831.157653465328, 0.],
[728.582976346643, 550.936706268738, 1.]])
right_distortion = np.array([[0.00607433417962732, -0.0112160302647384, 0.0104597000277839 ,0.00265721874066941,-0.0262959511445746]])
- 外部数据:(相机二相对于相机一的旋转变量与平移变量)
| 此处必须提醒,有些教程会有OM,然后再转成R,可能以前matlab这样,但是现在matlab直接提供R了,则不需要你自己再去转换了,直接用就好 |
R = np.array([[1., 0.0039, -0.0038],
[-0.0039, 1., 0.],
[0.0038, 0., 1.]])#旋转向量
T = np.array([-59.5777,0.032,-2.9472]) # 平移关系向量TranslationOfCamera2
此段完成代码为
import numpy as np
import cv2
left_camera_matrix = np.array([[837.046533944197, 0., 0.],
[-1.38537933662732, 838.772077702795, 0.],
[690.459242460418, 535.874773256865, 1.]]) #CameraParameters1.IntrinsicMatrix
left_distortion = np.array([[0.00372605723623423, 0.000603658659694726, 0.0100736540032466, 0.00134603874266809, -0.0625795789344168]])
right_camera_matrix = np.array([[829.904768800558, 0., 0.],
[0.449308928342319, 831.157653465328, 0.],
[728.582976346643, 550.936706268738, 1.]])
right_distortion = np.array([[0.00607433417962732, -0.0112160302647384, 0.0104597000277839 ,0.00265721874066941,-0.0262959511445746]])
R = np.array([[1., 0.0039, -0.0038],
[-0.0039, 1., 0.],
[0.0038, 0., 1.]])#旋转向量
T = np.array([-59.5777,0.032,-2.9472]) # 平移关系向量TranslationOfCamera2
size = (1280, 960) # 图像尺寸
# 进行立体更正
R1, R2, P1, P2, Q, validPixROI1, validPixROI2 = cv2.stereoRectify(left_camera_matrix, left_distortion,
right_camera_matrix, right_distortion, size, R,
T)
# 计算更正map
left_map1, left_map2 = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(left_camera_matrix, left_distortion, R1, P1, size, cv2.CV_16SC2)
right_map1, right_map2 = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(right_camera_matrix, right_distortion, R2, P2, size, cv2.CV_16SC2)
3.opencv生成深度图
| 请务必按照你实际相机的像素参数进行设置,否则一定会报错!!! |
import numpy as np
import cv2
left_camera_matrix = np.array([[837.046533944197, 0., 0.],
[-1.38537933662732, 838.772077702795, 0.],
[690.459242460418, 535.874773256865, 1.]]) #CameraParameters1.IntrinsicMatrix
left_distortion = np.array([[0.00372605723623423, 0.000603658659694726, 0.0100736540032466, 0.00134603874266809, -0.0625795789344168]])
right_camera_matrix = np.array([[829.904768800558, 0., 0.],
[0.449308928342319, 831.157653465328, 0.],
[728.582976346643, 550.936706268738, 1.]])
right_distortion = np.array([[0.00607433417962732, -0.0112160302647384, 0.0104597000277839 ,0.00265721874066941,-0.0262959511445746]])
R = np.array([[1., 0.0039, -0.0038],
[-0.0039, 1., 0.],
[0.0038, 0., 1.]])#旋转向量
T = np.array([-59.5777,0.032,-2.9472]) # 平移关系向量TranslationOfCamera2
size = (1280, 960) # 图像尺寸
# 进行立体更正
R1, R2, P1, P2, Q, validPixROI1, validPixROI2 = cv2.stereoRectify(left_camera_matrix, left_distortion,
right_camera_matrix, right_distortion, size, R,
T)
# 计算更正map
left_map1, left_map2 = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(left_camera_matrix, left_distortion, R1, P1, size, cv2.CV_16SC2)
right_map1, right_map2 = cv2.initUndistortRectifyMap(right_camera_matrix, right_distortion, R2, P2, size, cv2.CV_16SC2)
# ToDO 问题可能出在此处,读取的摄像头并不大,导致
cv2.namedWindow("left")
cv2.namedWindow("right")
cv2.namedWindow("depth")
cv2.moveWindow("left", 0, 0)
cv2.moveWindow("right", 600, 0)
cv2.createTrackbar("num", "depth", 0, 10, lambda x: None)
cv2.createTrackbar("blockSize", "depth", 5, 255, lambda x: None)
camera = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
camera.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, 2560)#1920,1280
camera.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, 960)#1080,720
# camera2 = cv2.VideoCapture(1)
# 添加点击事件,打印当前点的距离
def callbackFunc(e, x, y, f, p):
if e == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
print (threeD[y][x])
cv2.setMouseCallback("depth", callbackFunc, None)
while True:
ret, frame= camera.read()
# ret2, frame2 = camera2.read()
if not ret :
print('can\'t open camera or camera has been opened' )
break
frame1=frame[0:960,0:1280]
frame2=frame[0:960,1280:2560]
# 根据更正map对图片进行重构
img1_rectified = cv2.remap(frame1, left_map1, left_map2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
img2_rectified = cv2.remap(frame2, right_map1, right_map2, cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
# 将图片置为灰度图,为StereoBM作准备
imgL = cv2.cvtColor(img1_rectified, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
imgR = cv2.cvtColor(img2_rectified, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 两个trackbar用来调节不同的参数查看效果
num = cv2.getTrackbarPos("num", "depth")
blockSize = cv2.getTrackbarPos("blockSize", "depth")
if blockSize % 2 == 0:
blockSize += 1
if blockSize < 5:
blockSize = 5
# 根据Block Maching方法生成差异图(opencv里也提供了SGBM/Semi-Global Block Matching算法,有兴趣可以试试)
stereo = cv2.StereoBM_create(numDisparities=16*num, blockSize=blockSize)
disparity = stereo.compute(imgL, imgR)
disp = cv2.normalize(disparity, disparity, alpha=0, beta=255, norm_type=cv2.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv2.CV_8U)
# 将图片扩展至3d空间中,其z方向的值则为当前的距离
threeD = cv2.reprojectImageTo3D(disparity.astype(np.float32)/16., Q)
cv2.imshow("left", img1_rectified)
cv2.imshow("right", img2_rectified)
cv2.imshow("depth", disp)
key = cv2.waitKey(1)
if key == ord("q"):
break
elif key == ord("s"):
cv2.imwrite("E:/pythonlearning/opencv/screenshot/BM_left.jpg", imgL)
cv2.imwrite("E:/pythonlearning/opencv/screenshot/BM_right.jpg", imgR)
cv2.imwrite("E:/pythonlearning/opencv/screenshot/BM_depth.jpg", disp)
camera.release()
# camera2.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()