WGAN-GP生成对抗网络及mnist数据集的生成python(tensorflow)代码实现
一、WGAN-GP的理论基础
1、GAN生成对抗网络是2014年由Ian Goodfellow首先提出,主要用于生成类的任务。目前在超分辨率重建、图片修复等方面运用火热。
具体理论讲解可见:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/27295635
论文地址:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1406.2661
2、Wasserstein针对GAN网络难以训练的缺点,提出了WGAN的方法。GAN网络中用JS散度来衡量两个数据分布距离,在WGAN网络中使用Wasserstein距离来表示两个分布的距离。使用WGAN使网络训练更加容易,也一定程度上消除了模式坍塌的可能性(model collapse),生成图片效果得到了较大的提升。
具体理论讲解可见:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/25071913
论文地址:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1701.07875.pdf
3、WGAN-GP,实际操作上就是在WGAN的基础上增加梯度的惩罚项,但是训练效果相比于WGAN更加好。
具体理论讲解可见:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/49827134
论文地址:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.00028
二、WGAN-GP的代码实现
1、使用WGAN-GP实现mnist的生成,对于初学GAN网络的人来说是一个不错的选择,因为mnist数据集得来容易,并且网络相对来说较小。硬件要求也不高,可以使用CPU来进行训练。
2、GAN网络包括两个网络,一个是G生成网络,用于生成图片,另一个是D网络,用于判别图片真假;在训练策略上,每个训练循环里,先训练五次D网络,再训练一次G网络。
3、训练效果
1epoch训练之后
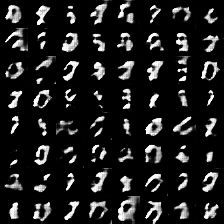
8epoch训练之后

25epoch训练之后
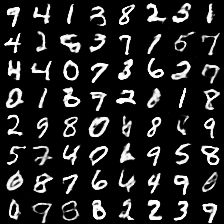
3、以下就是mnist数据集的生成代码:
#coding:utf-8
import os
import numpy as np
import scipy.misc #用于保存图片
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
def conv2d(name, tensor,ksize, out_dim, stddev=0.01, stride=2, padding='SAME'):
with tf.variable_scope(name):
w = tf.get_variable('w', [ksize, ksize, tensor.get_shape()[-1],out_dim], dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(stddev=stddev))
var = tf.nn.conv2d(tensor,w,[1,stride, stride,1],padding=padding)
b = tf.get_variable('b', [out_dim], 'float32',initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.01))
return tf.nn.bias_add(var, b)
def deconv2d(name, tensor, ksize, outshape, stddev=0.01, stride=2, padding='SAME'):
with tf.variable_scope(name):
w = tf.get_variable('w', [ksize, ksize, outshape[-1], tensor.get_shape()[-1]], dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(stddev=stddev))
var = tf.nn.conv2d_transpose(tensor, w, outshape, strides=[1, stride, stride, 1], padding=padding)
b = tf.get_variable('b', [outshape[-1]], 'float32', initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.01))
return tf.nn.bias_add(var, b)
def fully_connected(name,value, output_shape):
with tf.variable_scope(name, reuse=None):
shape = value.get_shape().as_list()
w = tf.get_variable('w', [shape[1], output_shape], dtype=tf.float32,
initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(stddev=0.01))
b = tf.get_variable('b', [output_shape], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.0))
return tf.matmul(value, w) + b
def relu(name, tensor):
return tf.nn.relu(tensor, name)
def lrelu(name,x, leak=0.2):
return tf.maximum(x, leak * x, name=name)
DEPTH = 28
OUTPUT_SIZE = 28
batch_size = 64
def Discriminator(name,inputs,reuse):
with tf.variable_scope(name, reuse=reuse):
output = tf.reshape(inputs, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
output1 = conv2d('d_conv_1', output, ksize=5, out_dim=DEPTH)
output2 = lrelu('d_lrelu_1', output1)
output3 = conv2d('d_conv_2', output2, ksize=5, out_dim=2*DEPTH)
output4 = lrelu('d_lrelu_2', output3)
output5 = conv2d('d_conv_3', output4, ksize=5, out_dim=4*DEPTH)
output6 = lrelu('d_lrelu_3', output5)
chanel = output6.get_shape().as_list()
output9 = tf.reshape(output6, [batch_size, chanel[1]*chanel[2]*chanel[3]])
output0 = fully_connected('d_fc', output9, 1)
return output0
def generator(name, reuse=False):
with tf.variable_scope(name, reuse=reuse):
noise = tf.random_normal([batch_size, 128])#.astype('float32')
noise = tf.reshape(noise, [batch_size, 128], 'noise')
output = fully_connected('g_fc_1', noise, 2*2*8*DEPTH)
output = tf.reshape(output, [batch_size, 2, 2, 8*DEPTH], 'g_conv')
output = deconv2d('g_deconv_1', output, ksize=5, outshape=[batch_size, 4, 4, 4*DEPTH])
output = tf.nn.relu(output)
output = tf.reshape(output, [batch_size, 4, 4, 4*DEPTH])
output = deconv2d('g_deconv_2', output, ksize=5, outshape=[batch_size, 7, 7, 2* DEPTH])
output = tf.nn.relu(output)
output = deconv2d('g_deconv_3', output, ksize=5, outshape=[batch_size, 14, 14, DEPTH])
output = tf.nn.relu(output)
output = deconv2d('g_deconv_4', output, ksize=5, outshape=[batch_size, OUTPUT_SIZE, OUTPUT_SIZE, 1])
# output = tf.nn.relu(output)
output = tf.nn.sigmoid(output)
return tf.reshape(output,[-1,784])
def save_images(images, size, path):
# 图片归一化
img = (images + 1.0) / 2.0
h, w = img.shape[1], img.shape[2]
merge_img = np.zeros((h * size[0], w * size[1], 3))
for idx, image in enumerate(images):
i = idx % size[1]
j = idx // size[1]
merge_img[j * h:j * h + h, i * w:i * w + w, :] = image
return scipy.misc.imsave(path, merge_img)
LAMBDA = 10
EPOCH = 40
def train(mnist):
# print os.getcwd()
with tf.variable_scope(tf.get_variable_scope()):
# real_data = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[-1, OUTPUT_SIZE*OUTPUT_SIZE*3])
path = os.getcwd()
'''获得数据'''
real_data = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[batch_size,784])
with tf.variable_scope(tf.get_variable_scope()):
fake_data = generator('gen',reuse=False)
disc_real = Discriminator('dis_r',real_data,reuse=False)
disc_fake = Discriminator('dis_r',fake_data,reuse=True)
t_vars = tf.trainable_variables()
d_vars = [var for var in t_vars if 'd_' in var.name]
g_vars = [var for var in t_vars if 'g_' in var.name]
'''计算损失'''
gen_cost = tf.reduce_mean(disc_fake)
disc_cost = -tf.reduce_mean(disc_fake) + tf.reduce_mean(disc_real)
alpha = tf.random_uniform(
shape=[batch_size, 1],minval=0.,maxval=1.)
differences = fake_data - real_data
interpolates = real_data + (alpha * differences)
gradients = tf.gradients(Discriminator('dis_r',interpolates,reuse=True), [interpolates])[0]
slopes = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(gradients), reduction_indices=[1]))
gradient_penalty = tf.reduce_mean((slopes - 1.) ** 2)
disc_cost += LAMBDA * gradient_penalty
with tf.variable_scope(tf.get_variable_scope(), reuse=None):
gen_train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(
learning_rate=1e-4,beta1=0.5,beta2=0.9).minimize(gen_cost,var_list=g_vars)
disc_train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(
learning_rate=1e-4,beta1=0.5,beta2=0.9).minimize(disc_cost,var_list=d_vars)
saver = tf.train.Saver()
# os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = str(0)#gpu环境
# config = tf.ConfigProto()
# config.gpu_options.per_process_gpu_memory_fraction = 0.5#调用50%GPU资源
# sess = tf.InteractiveSession(config=config)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
if not os.path.exists('img'):
os.mkdir('img')
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# init = tf.initialize_all_variables()
sess.run(init)
for epoch in range (1, EPOCH):
idxs = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size
for iters in range(1, idxs):
img, _ = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
#训练D网络
for x in range (0,5):
_, d_loss = sess.run([disc_train_op, disc_cost], feed_dict={real_data: img})
#训练G网络
_, g_loss = sess.run([gen_train_op, gen_cost])
if(iters%10==0):
print("[%2d:%4d/%4d] d_loss: %.8f, g_loss: %.8f"%(epoch, iters, idxs, d_loss, g_loss))
with tf.variable_scope(tf.get_variable_scope()):
samples = generator('gen', reuse=True)
samples = tf.reshape(samples, shape=[batch_size, 28,28,1])
samples=sess.run(samples)
save_images(samples, [8,8], os.getcwd()+'/img/'+'sample_%d_epoch.png' % (epoch))
if epoch>=39:
checkpoint_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(),'my_wgan-gp.ckpt')
saver.save(sess, checkpoint_path, global_step=epoch)
print('model saved')
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
sess.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("mnist_data", one_hot=True)
train(mnist)
代码部分参考于:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_25737169/article/details/76695935