Q15 三数之和
https://leetcode.com/problems/3sum/discuss/681295/Simple-3-pointer-(Similar-approach-to-number-of-triangles).
three pointer
// my solution
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public List> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List> res = new ArrayList>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
for(int cur = 0; cur < nums.length; cur++){
if(cur != 0 && nums[cur]== nums[cur-1]){
continue;
}
int l = cur + 1, r = nums.length-1;
while(l < r){
int sum = nums[l] + nums[r]+nums[cur];
if( sum == 0){
ArrayList each = new ArrayList();
each.add(nums[cur]);
each.add(nums[l]);
each.add(nums[r]);
res.add(each);
l++;
r--;
while(l < r && nums[l] == nums[l-1]){
l++;
}
while(l < r && nums[r] == nums[r+1]){
r--;
}
}else if(sum < 0){
l++;
}else{
r--;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
Q1139 最大的以1为边界的正方形
https://leetcode.com/problems/largest-1-bordered-square/discuss/345265/c%2B%2B-beats-100-(both-time-and-memory)-concise-with-algorithm-and-image
preprocess matrix
暴力解法的时间复杂度是O(nmmin(n,m)min(n,m)),使用预处理矩阵后的时间复杂度是O(nm*min(n,m))
Q14 最长公共前缀
longest-common-prefix 没有找到总结性的题解。
总结了一下这道题目的最优解法应该有两种,假设字符串个数为n,字符串中字符的个数为m。
最优解1
分治法。每次将字符串数组划分为两部分,不断分治问题直到子问题中包含两个字符串时可以直接求解最长公共子串。如果子问题中只有一个字符串,那么这种特殊情况直接返回字符串。时间复杂度为O(mlogn)
最优解2
二分法。首先找到最短的那个字符串ss,对它进行二分[low, mid, hi],如果ss[low: mid]是所有字符串的前缀,那么真正最长公共前缀的最后一个字符的位置一定在mid和hi的右边,否则在其左边(包括mid)。时间复杂度O(x*n*logm),其中x是判断二分的字符串是否是一个字符串前缀的时间复杂度,x不好估算,这种解法相比最优解1更加适合m比n大得多的情况。
Q297 二叉树的序列化和反序列化
二叉树的序列化有四种方法:先,中,后,层序。它们就是二叉树的四种遍历方法。但是二叉树的反序列化可行的只有三种方法:先,后,层序。中序无法完成反序列化的原因在于:对于中序序列你无法找到一棵树的根,先,后序反序列化本质还是递归算法(先找到一个根节点,反序列化这个根节点,然后递归的反序列化根的左子树和右子树)。代码上先/后/层序反序列化的代码在逻辑上都是一样的,进行X序反序列化就是重做X序遍历,层序反序列化中需要注意设置两个队列childQueue和parentQueue,并且空节点不要放入到队列中。
Q1014 最佳观光组合
https://leetcode.com/problems/best-sightseeing-pair/discuss/260850/JavaC%2B%2BPython-One-Pass
解法的思路借鉴题解,但是题解中的说明并不清晰。
/**
* max(A[i] + A[j] + i -j ) and i < j
* = max(A[i] + i -j + A[j])
* => max(A[j]) + max(A[i] + i - j ) 相当于对于每个位置j,找前面最大的A[i] + i -j
* 所以如果想在one-pass复杂度中得到结果,需要优化"找前面最大的A[i] + i -j"的过程,这个过程在代码中对应的就是maxpart2
*/
public class Q1014 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[] {8,1,5,2,6};
int res = maxScoreSightseeingPair(arr);
System.out.println(res);
}
public static int maxScoreSightseeingPair(int[] A) {
int maxpart2= 0;
int res = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int i = 0; i< A.length; i++){
if( i == 0){
maxpart2 = A[0] - 1;
}else{
res = Math.max(res, A[i] + maxpart2);
// 减1的原因在于:
// 1.若果下一个景点i前面最优搭配的景点是景点i-1前面最优搭配的景点的化,距离会增加一个
// 2.如果下一个景点i前面最优搭配的景点是它前一个位置,距离为1
maxpart2 = Math.max(maxpart2 - 1, A[i] - 1);
}
}
return res;
}
}
Q221 最大正方形
https://leetcode.com/problems/maximal-square/discuss/61803/C%2B%2B-space-optimized-DP
坐标型动态规划
Q93 复原IP地址
一种解法(回溯法)的多种写法。约束条件较多的回溯问题如何解决。
// most votes 题解
public class Solution {
public List restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
List res = new ArrayList();
int len = s.length();
for(int i = 1; i<4 && i3 || s.length()==0 || (s.charAt(0)=='0' && s.length()>1) || Integer.parseInt(s)>255)
return false;
return true;
}
}
// My code
import java.util.*;
public class Q93 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//System.out.println(String.join("-", new String[]{"a","b"}));
List res = new Q93().restoreIpAddresses("010010");
System.out.println(res);
}
public List restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
ArrayList res = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList each = new ArrayList<>();
backtrack(s,res,each,0);
return res;
}
public void backtrack(String s, ArrayList res, ArrayList each, int start){
if(each.size() == 3){
String substr = s.substring(start);
if(isValid(substr)){
each.add(substr);
res.add(String.join(".", each));
each.remove(each.size() -1);
}
return;
}
for(int point = start + 1; point <= start + 3 && point <= s.length(); point++ ){
String substr = s.substring(start, point);
if(isValid(substr)){
each.add(substr);
backtrack(s,res,each,point);
each.remove(each.size() -1 );
}
}
}
public boolean isValid(String s){
if(s.length() == 0){
return false;
}
if(s.charAt(0) == '0' && s.length() != 1){
return false;
}
if(s.length() > 3){
return false;
}
if(Integer.valueOf(s) > 255){
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
Q11盛最多水的容器
和Q42接雨水进行区分,注意两者盛水的方式是不同的,但是都可以使用双指针解决
class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int l = 0, r = height.length -1;
int res = 0;
int curarea = 0;
while(l < r){
if(height[l] <= height[r]){
curarea = (r - l)* height[l];
res = Math.max(res, curarea);
//因为[l] < [r],所以此时把r向左移动只会减少盛水量
l++;
}else{
curarea = (r - l)* height[r];
res = Math.max(res, curarea);
r--;
}
}
return res;
}
}
Q42接雨水
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
if(height.length == 0){
return 0;
}
int l = 0, r = height.length - 1;
int lmax = height[l], rmax = height[r];
int res = 0;
int cur = 0;
while(l < r){
if(height[l] < height[r]){
cur = Math.max(0, lmax - height[l]);
res += cur;
lmax = Math.max(lmax, height[l]);
l ++;
}else{
cur = Math.max(0, rmax - height[r]);
res += cur;
rmax = Math.max(rmax, height[r]);
r --;
}
}
return res;
}
}
Q48 旋转图像
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[][] matrix) {
int tr = 0, tc = 0, dr = matrix.length-1, dc = matrix.length-1;
while(tr < dr){
rotateALoop(matrix, tr,tc,dr,dc);
tr++; tc++;
dr--; dc--;
}
}
void rotateALoop(int[][] mat, int tr, int tc, int dr, int dc){
//tr,tc为左上顶点的行和列坐标;dr,dc为右下顶点的行和列的坐标
if(tr==dr) {// mat中有条件是nxn
return;
}
int[] temp = {Integer.MAX_VALUE};
for(int i =0 ; i < dc - tc; i++){ // 仔细思考这里i从0循环的意图
swap(mat, tr,tc+i,temp); // i再col上增加
swap(mat, tr + i, dc,temp); //i再row上增加
swap(mat, dr, dc-i,temp); //i在col上减少
swap(mat, dr-i,tc,temp); //i在row上减少
swap(mat, tr,tc+i,temp); // 补一次
}
return;
}
void swap(int[][] mat, int sr, int sc, int[] temp){
int _temp = mat[sr][sc];
mat[sr][sc] = temp[0];
temp[0] = _temp;
}
}
Q50 pow(x, n)
我估计牛客面试不会考这题,太简单了。
class Solution {
public double myPow(double x, long n) { // 注意这里n的类型为long,虽然题目中表示n是32位有符号整数,但是如果n = Integer.MIN_VALUE;第10行代码中-n其实就会发生int溢出。造成的结果就是负数取反后还是负数,从而引发无限递归造成栈溢出。
if(n == 0){
return 1;
}
if(x == 1){
return 1;
}
if(n < 0){
return 1.0/myPow(x,-n);
}
if(n % 2 == 0){
double ret = myPow(x, n/2);
return ret * ret;
}else{
double ret = myPow(x, n/2);
return ret * ret * x;
}
}
}
Q57 插入区间
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jeKvO1JS-4w
class Solution {
public int[][] insert(int[][] intervals, int[] newInterval) {
List listRes = new ArrayList<>();
for(int [] it : intervals){
if( newInterval == null || it[1] < newInterval[0]){
listRes.add(it);
}else if(newInterval[1] < it[0]){
listRes.add(newInterval);
newInterval = null;
listRes.add(it);
}else{ // newInterval[0] <= it[1] && newInterval[1] >= it[0] 这是newInterval和it区间有交集的情况。
newInterval[0] = Math.min(newInterval[0], it[0]);
newInterval[1] = Math.max(newInterval[1], it[1]);
}
}
if(newInterval == null) return listToArray(listRes);
listRes.add(newInterval);
return listToArray(listRes);
}
int[][] listToArray(List list){
int[][] res = new int[list.size()][2];
int idx = 0;
for(int[] it: list){
res[idx++] = it;
}
return res;
}
}
Q60 第k个排列
class Solution {
private HashMap memo = new HashMap<>();
public String getPermutation(int n, int k) {
ArrayList candidates = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList res = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 1; i<=n; i++){
candidates.add(i);
}
getPerm(candidates, res, k-1); // k做offset的原因见33、34行注释
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int i: res){
sb.append(i);
}
return sb.toString();
}
private void getPerm(ArrayList candidates, ArrayList res, int remainOfK){
if(candidates.size()==1){ // 此时remainOfK == 0
res.add(candidates.remove(0));
return;
}
int nSubGroup = computePermNum(candidates.size() - 1);
int idx = remainOfK / nSubGroup;
remainOfK = remainOfK % nSubGroup;
//注意因为idx从0开始计数,而remainOfK从1开始计数,所以要对上面的取余运算做一些调整
//当然也可以不做调整,在传入remainOfK参数时直接offset做-1的处理,这里的代码使用这种方法。
res.add(candidates.remove(idx));
getPerm(candidates, res, remainOfK);
return;
}
private int computePermNum(int n){
if(n == 1){
return 1;
}
if(memo.containsKey(n)){
return memo.get(n);
}
int res = n * computePermNum(n-1);
memo.put(n, res);
return res;
}
}
这题含有一个非常普遍的处理技巧:
int n; // 从1开始计数
int k = n / div; // 这里的k其实是从0开始计数
int r = n % div; // 这里的r其实也是从0开始计数
如果我们需要将r的值赋给n进行多次迭代,那么这其实是会出现错误的:比如n = 5,div = 5,计算后r = 0,实际上对应从1开始计数的第一个数1。解决这个错误的办法可以从两个角度来解决:
- 每次计算后对k和r进行修正:
//修正代码
k = k + 1;
if(r == 0){
k = k - 1;
r = 1;
}else{
r = r + 1;
}
- 直接修正n,在传入参数时选择传入n-1;
显然第二种方法更简洁。
Q139 单词拆分
序列型动态规划+遍历型(划分型)动态规划
class Solution {
public boolean wordBreak(String s, List wordDict) {
// dp[i]表示s中前0个字符是否满足题目条件
boolean[] dp = new boolean[s.length()+1];
dp[0] = true;
for(int i = 1; i<= s.length(); i++){
for(int j = 0; j < i; j++){
if(dp[j] && wordDict.contains(s.substring(j,i))){
dp[i] = true;
break;
}
}
}
return dp[s.length()];
}
}
Q116 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
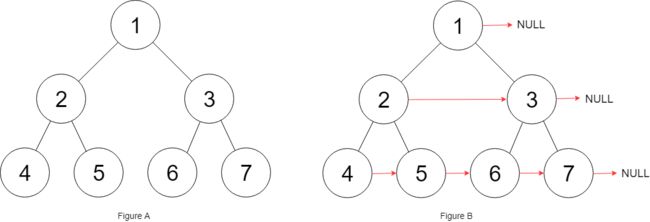
也就是要构造上图中的红色指针,本质上还是层序遍历的一个变式,解答略。
Q136 只出现一次的数字
某个元素只出现一次,其他元素都出现两次,找出这个出现一次的元素。
类似题目:
Q137某个元素出现一次,其他元素出现三次,找出出现一次的元素。
对于这种某个元素出现一次,其他元素出现k次,找出出现一次的元素的题目。有统一的解法:
逐位操作,如果所有数在当前位上0的个数可以整除k,那么目标数在当前位上的二进制值为1,否则为0
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int [] zeroCount = new int[32];
for(int n: nums){
for(int i = 0; i< 32; i++){
if(((n >> i) & 1) == 0){
zeroCount[i]++;
}
}
}
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i< 31; i++){
if(zeroCount[i] % 3 == 0){
res+= Math.pow(2,i);
}
}
if(zeroCount[31] % 3 == 0){
res += -Math.pow(2,31);
}
return res;
}
}
Q260 只出现一次的数字III
首先求数组的xor sum,这个值肯定是要找的两个数的异或和。因为这两个元素不同,所以异或和中其中一位肯定为1,找到这个位置,也就是说两个数在这一位上有不同的二进制值,通过这个可以将原数组分为两个部分,两个目标数在不同部分中,从而将问题转化两个Q136的子问题。