Spring事务管理,带你回顾数据库事务!
写在前面: 本文将告诉你:数据库事务,以及如何使用Spring整理事务,以及用注解开发事务。 作者是一个学生,没有能力写得太深,需要的可以去看看大佬们的 手撕Spring源码。
如果对你有帮助可以点赞支持一下^ _ ^
作者公众号:小白编码
本文目录
- 数据库事务介绍
- 事务的ACID属性
- 数据库的并发问题
- 四种隔离级别
- Spring事务控制
- 基于xml配置事务控制
- 基于注解配置事务控制
- 写在后边:
数据库事务介绍
-
事务:一组逻辑操作单元,使数据从一种状态变换到另一种状态。
-
事务处理(事务操作):保证所有事务都作为一个工作单元来执行,即使出现了故障,都不能改变这种执行方式。当在一个事务中执行多个操作时,要么所有的事务都被提交(commit),那么这些修改就永久地保存下来;要么数据库管理系统将放弃所作的所有修改,整个事务**回滚(rollback)**到最初状态。
-
为确保数据库中数据的一致性,数据的操纵应当是离散的成组的逻辑单元:当它全部完成时,数据的一致性可以保持,而当这个单元中的一部分操作失败,整个事务应全部视为错误,所有从起始点以后的操作应全部回退到开始状态。
事务的ACID属性
-
原子性(Atomicity)
原子性是指事务是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务中的操作要么都发生,要么都不发生。 -
一致性(Consistency)
事务必须使数据库从一个一致性状态变换到另外一个一致性状态。 -
隔离性(Isolation)
事务的隔离性是指一个事务的执行不能被其他事务干扰,即一个事务内部的操作及使用的数据对并发的其他事务是隔离的,并发执行的各个事务之间不能互相干扰。 -
持久性(Durability)
持久性是指一个事务一旦被提交,它对数据库中数据的改变就是永久性的,接下来的其他操作和数据库故障不应该对其有任何影响。
数据库的并发问题
-
对于同时运行的多个事务, 当这些事务访问数据库中相同的数据时, 如果没有采取必要的隔离机制, 就会导致各种并发问题:
- 脏读: 对于两个事务 T1, T2, T1 读取了已经被 T2 更新但还没有被提交的字段。之后, 若 T2 回滚, T1读取的内容就是临时且无效的。
- 不可重复读: 对于两个事务T1, T2, T1 读取了一个字段, 然后 T2 更新了该字段。之后, T1再次读取同一个字段, 值就不同了。
- 幻读: 对于两个事务T1, T2, T1 从一个表中读取了一个字段, 然后 T2 在该表中插入了一些新的行。之后, 如果 T1 再次读取同一个表, 就会多出几行。
-
数据库事务的隔离性: 数据库系统必须具有隔离并发运行各个事务的能力, 使它们不会相互影响, 避免各种并发问题。
-
一个事务与其他事务隔离的程度称为隔离级别。数据库规定了多种事务隔离级别, 不同隔离级别对应不同的干扰程度, 隔离级别越高, 数据一致性就越好, 但并发性越弱。
四种隔离级别
-
数据库提供的4种事务隔离级别:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-m7zu5UHE-1590579555991)(C:/Users/JUN/Desktop/生产力工具/笔记/JDBC/尚硅谷_宋红康_JDBC.assets/1555586275271.png)]
-
Oracle 支持的 2 种事务隔离级别:READ COMMITED, SERIALIZABLE。 Oracle 默认的事务隔离级别为: READ COMMITED 。
-
Mysql 支持 4 种事务隔离级别。Mysql 默认的事务隔离级别为: REPEATABLE READ。
Spring事务控制
事务的传播行为:
REQUIRED:如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中。一般的选择(默认值)
SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行(没有事务)
MANDATORY:使用当前的事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常 REQUERS_NEW:新建事务,如果当前在事务中,把当前事务挂起。
NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起
NEVER:以非事务方式运行,如果当前存在事务,抛出异常
NESTED:如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行REQUIRED类似的操作。
设置超时时间默认是没有超时限制,默认值是-1,以秒为单位.
查询的时候设为只读
基于xml配置事务控制
spring中基于XML的声明式事务控制配置步骤
1、配置事务管理器
2、配置事务的通知
此时我们需要导入事务的约束 tx名称空间和约束,同时也需要aop的
使用tx:advice标签配置事务通知
属性:
id:给事务通知起一个唯一标识
transaction-manager:给事务通知提供一个事务管理器引用
3、配置AOP中的通用切入点表达式
4、建立事务通知和切入点表达式的对应关系
5、配置事务的属性
是在事务的通知tx:advice标签的内部
配置事务的属性
isolation: 用于指定事务的隔离级别。默认值是DEFAULT,表示使用数据库的默认隔离级别。
propagation: 用于指定事务的传播行为。默认值是REQUIRED,表示一定会有事务,增删改的选择。查询方法可以选择SUPPORTS。
read-only: 用于指定事务是否只读。只有查询方法才能设置为true。默认值是false,表示读写。
timeout: 用于指定事务的超时时间,默认值是-1,表示永不超时。如果指定了数值,以秒为单位。
rollback-for: 用于指定一个异常,当产生该异常时,事务回滚,产生其他异常时,事务不回滚。没有默认值。表示任何异常都回滚。
no-rollback-for: 用于指定一个异常,当产生该异常时,事务不回滚,产生其他异常时事务回滚。没有默认值。表示任何异常都回滚。
依赖注入:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-contextartifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbcartifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-txartifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-testartifactId>
<version>5.0.2.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>5.1.6version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectjgroupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaverartifactId>
<version>1.8.7version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>4.12version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>1.18.12version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
环境搭建:
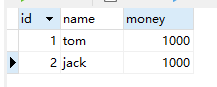
Account表:
CREATE TABLE `account` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL,
`money` float DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=11 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
对应javaBean:
@Data
public class Account implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Float money;
}
Dao:自行编写接口
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
@Override
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where id = ?", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class), accountId);
//判断是否空,如果空返回null,如果非空返回指定id的
return accounts.isEmpty() ? null : accounts.get(0);
}
@Override
public Account findAccountByName(String accountName) {
List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where name = ?", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Account.class), accountName);
if (accounts.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
if (accounts.size() > 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("结果集不唯一");
}
return accounts.get(0);
}
@Override
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?", account.getName(), account.getMoney(), account.getId());
}
}
Service:
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
@Override
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
return accountDao.findAccountById(accountId);
}
@Override
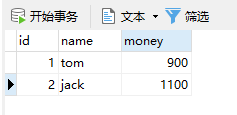
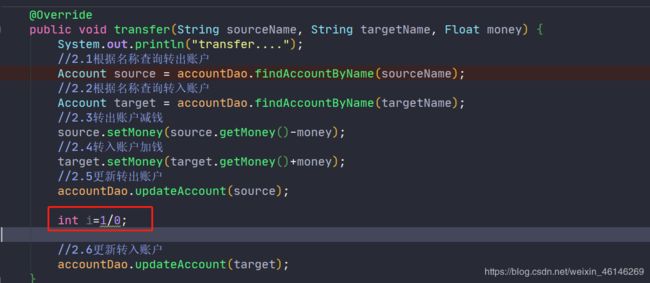
public void transfer(String sourceName, String targetName, Float money) {
System.out.println("transfer....");
//2.1根据名称查询转出账户
Account source = accountDao.findAccountByName(sourceName);
//2.2根据名称查询转入账户
Account target = accountDao.findAccountByName(targetName);
//2.3转出账户减钱
source.setMoney(source.getMoney()-money);
//2.4转入账户加钱
target.setMoney(target.getMoney()+money);
//2.5更新转出账户
accountDao.updateAccount(source);
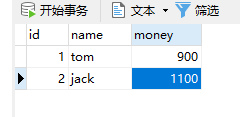
// int i=1/0;
//2.6更新转入账户
accountDao.updateAccount(target);
}
}
xml事务配置
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean id="accountService" class="cn.codewhite.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao">property>
bean>
<bean id="accountDao" class="cn.codewhite.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver">property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:2001/spring">property>
<property name="username" value="root">property>
<property name="password" value="20010303">property>
bean>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"> property>
bean>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="find*" propagation="SUPPORTS" read-only="true"/>
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pt1" expression="execution(* cn.codewhite.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pt1">aop:advisor>
aop:config>
beans>
测试方法:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:bean.xml")
public class AccountDaoTest {
@Autowired
AccountService as;
@Test
public void test() {
as.transfer("tom","jack",100f);
}
}
基于注解配置事务控制
Xml:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.codewhite">context:component-scan>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver">property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:2001/spring">property>
<property name="username" value="root">property>
<property name="password" value="20010303">property>
bean>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager">tx:annotation-driven>
beans>
运行环境:在xml的基础上:
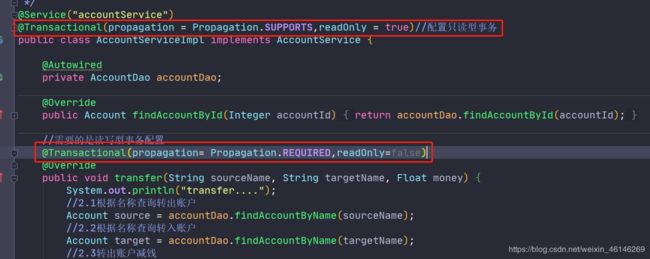
ServiceImpl配置:
accountDao:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:bean.xml")
public class AccountDaoTest {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("accountService")
private AccountService as;
@Test
public void test() {
// ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
as.transfer("tom","jack",100f);
}
}
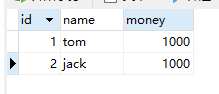
运行:转账成功:
此时我在Service中加入除零异常:
写在后边:
写得不好,请见谅,如果需要PDF版的可以找我。