自动泊车(之三)车位线定位(视觉定位)
1 引言
在前篇博客中,小博介绍了车位检测得一些方法,当车位识别出来其实就是将车位在图像坐标系中得坐标(u,v)给找出来,但是给出图像坐标是无法提供给决策层去倒车入库得,我们需要提供得是3D坐标,接下来本篇略浅得讲下视觉定位的知识,如何从鱼眼相机2D图像坐标到3D坐标。在看此文之前需要具备基本得相机模型知识,我在前面博文讲过不少双目相机标定得知识,可参考前面得知识。
本文参考博客
http://www.cnblogs.com/singlex/p/pose_estimation_1.html
一篇写的非常实用得博客
首先我们看下鱼眼图像
2视觉定位基础知识
首先我们知道车子是一个随动坐标系,与机器人相同,我们定义车子四轮中心为世界坐标系原点,则车位在世界坐标系中有一个坐标,记为(X,Y,Z),同样在相机为原点得坐标系中也有一个相机坐标(x,y,z),我们需要获得两个坐标系之间得关系,及求出两个坐标系得旋转与平移向量。
利用多个控制点在三维场景中的坐标及其在图像中的透视投影坐标即可求解出摄像机坐标系与表示三维场景结构的世界坐标系之间的绝对位姿关系,包括绝对平移向量t以及旋转矩阵R,该类求解方法统称为N点透视位姿求解(Perspective-N-Point,PNP问题)。这里的控制点是指准确知道三维空间坐标位置,同时也知道对应图像平面坐标的点。对于透视投影来说,要使得PNP问题有确定解,需要至少三组控制点。
opencv中提供了接口函数,Opencv中PNP的求解函数
void solvePnP(InputArray objectPoints, InputArray imagePoints, InputArray cameraMatrix, InputArray distCoeffs, OutputArray rvec, OutputArray tvec, bool useExtrinsicGuess=false, int flags = CV_ITERATIVE)
Parameters:
objectPoints - 世界坐标系下的控制点的坐标,vector的数据类型在这里可以使用
imagePoints - 在图像坐标系下对应的控制点的坐标。vector在这里可以使用
cameraMatrix - 相机的内参矩阵
distCoeffs - 相机的畸变系数
以上两个参数通过相机标定可以得到。相机的内参数的标定以前博文已经给出过代码
rvec - 输出的旋转向量。使坐标点从世界坐标系旋转到相机坐标系
tvec - 输出的平移向量。使坐标点从世界坐标系平移到相机坐标系
flags - 默认使用CV_ITERATIV迭代法
3 算法使用
(1) 求出 R T
由于opencv2以上版本已经提供了pnp算法的api,所以使用pnp的难点变成了如何构造场景使得能使用PNP算法。目前我们使用的最简单的方法就是使用五个点,四个点做为标定,一个点作为测试,使用物体方法使得场景中只出现这四个控制点。如图所示,我在标定板上选出了四个点,同时确定他在图像坐标系中得坐标u,v,与在车得世界坐标系坐标 X,Y,Z。我们通过求出两个坐标系之间得R,T

原理图如下

(2)求出S,尺度
下式为图像坐标与世界坐标的转换公式,第一个矩阵为相机内参数矩阵,第二个矩阵为相机外参数矩阵,该式中图像坐标已知,相机内参数矩阵通过标定已获取,还欠缺s。
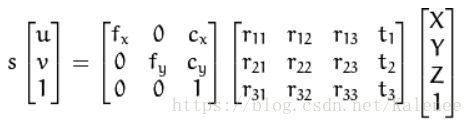
转换公式转换为如下左式,其中M为相机内参数矩阵,R为旋转矩阵,t为平移矩阵,Z为实际坐标系原点与相机坐标系原点在Z轴上的距离。左式进行转换后可得出右式,在右式中,当R,M,t和Z已知时,s为唯一变量,所以可以求得s
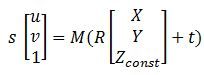

4 算法实现
二、程序实现
(1)计算参数s和旋转平移矩阵,需要输入一系列的世界坐标系的点及其对应的图像坐标系的点
objectPoints与 imagePoints为图像坐标与真实世界坐标(2)根据输入的图像坐标计算世界坐标。
//输入参数
Mat cameraMatrix = Mat(3, 3, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0)); /* 摄像机内参数矩阵 */
Mat distCoeffs = Mat(1, 5, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(0)); /* 摄像机的5个畸变系数:k1,k2,p1,p2,k3 */
double zConst = 0;//实际坐标系的距离
//计算参数
double s;
Mat rotationMatrix = Mat (3, 3, DataType<double>::type);
Mat tvec = Mat (1, 3, cv::DataType<double>::type);
void calcParameters(vector<cv::Point2f> imagePoints, vector<cv::Point3f> objectPoints)
{
//计算旋转和平移矩阵
Mat rvec(1, 3, cv::DataType<double>::type);
cv::solvePnP(objectPoints, imagePoints, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, rvec, tvec);
cv::Rodrigues(rvec, rotationMatrix);
cv::Mat imagePoint = cv::Mat::ones(3, 1, cv::DataType<double>::type); //u,v=1,1,1
//计算参数S
cv::Mat tempMat, tempMat2;
tempMat = rotationMatrix.inv() * cameraMatrix.inv() * imagePoint;
tempMat2 = rotationMatrix.inv() * tvec;
s = zConst + tempMat2.at<double>(2, 0);
s /= tempMat.at<double>(2, 0);
}
(2)根据输入的图像坐标计算世界坐标。接下来我们给入一个图像坐标,即会输出真实世界中坐标
Point3f getWorldPoints(Point2f inPoints)
{
cv::Mat imagePoint = cv::Mat::ones(3, 1, cv::DataType<double>::type); //u,v,1
imagePoint.at<double>(0, 0) = inPoints.x;
imagePoint.at<double>(1, 0) = inPoints.y;
Mat wcPoint = rotationMatrix.inv() * (s * cameraMatrix.inv() * imagePoint - tvec);
Point3f worldPoint(wcPoint.at<double>(0, 0), wcPoint.at<double>(1, 0), wcPoint.at<double>(2, 0));
return worldPoint;
}
求R T,旋转角等完整代码
#include 5 相比于C++版本,python版本真是简单了好多啊。。。
import cv2
from numpy import *
import numpy as np
import math
object_3d_points = np.array(([2750, 890, 0],
[3500, 450, 0],
[3620, -50, 0],
[2790, -240, 0]), dtype=np.double)
object_2d_point = np.array(([558, 259],
[629, 212],
[693, 209],
[744, 260]), dtype=np.double)
camera_matrix = np.array(([328.47364883, 0, 629.0359318],
[0, 328.4303046, 340.13011656],
[0, 0, 1.0]), dtype=np.double)
# dist_coefs = np.array([0.06147452, 0.03188344, -0.00678974, 0, 0], dtype=np.double)
dist_coefs = np.array([0.06147452, 0.03188344, 0, 0, -0.00678974], dtype=np.double)
# 求解相机位姿
found, rvec, tvec = cv2.solvePnP(object_3d_points, object_2d_point, camera_matrix, dist_coefs)
# print(rvec, tvec)
rotM = cv2.Rodrigues(rvec)[0]
camera_postion = -np.matrix(rotM).T * np.matrix(tvec)
# print(camera_postion.T)
# 验证根据博客http://www.cnblogs.com/singlex/p/pose_estimation_1.html提供方法求解相机位姿
# 计算相机坐标系的三轴旋转欧拉角,旋转后可以转出世界坐标系。旋转顺序z,y,x
thetaZ = math.atan2(rotM[1, 0], rotM[0, 0])*180.0/math.pi
thetaY = math.atan2(-1.0*rotM[2, 0], math.sqrt(rotM[2, 1]**2 + rotM[2, 2]**2))*180.0/math.pi
thetaX = math.atan2(rotM[2, 1], rotM[2, 2])*180.0/math.pi
# 相机坐标系下值
x = tvec[0]
y = tvec[1]
z = tvec[2]
# 进行三次旋转
def RotateByZ(Cx, Cy, thetaZ):
rz = thetaZ*math.pi/180.0
outX = math.cos(rz)*Cx - math.sin(rz)*Cy
outY = math.sin(rz)*Cx + math.cos(rz)*Cy
return outX, outY
def RotateByY(Cx, Cz, thetaY):
ry = thetaY*math.pi/180.0
outZ = math.cos(ry)*Cz - math.sin(ry)*Cx
outX = math.sin(ry)*Cz + math.cos(ry)*Cx
return outX, outZ
def RotateByX(Cy, Cz, thetaX):
rx = thetaX*math.pi/180.0
outY = math.cos(rx)*Cy - math.sin(rx)*Cz
outZ = math.sin(rx)*Cy + math.cos(rx)*Cz
return outY, outZ
(x, y) = RotateByZ(x, y, -1.0*thetaZ)
(x, z) = RotateByY(x, z, -1.0*thetaY)
(y, z) = RotateByX(y, z, -1.0*thetaX)
Cx = x*-1
Cy = y*-1
Cz = z*-1
# 输出相机位置
print(Cx, Cy, Cz)
# 输出相机旋转角
print(thetaX, thetaY, thetaZ)
# 对第五个点进行验证
Out_matrix = np.concatenate((rotM, tvec), axis=1)
pixel = np.dot(camera_matrix, Out_matrix)
pixel1 = np.dot(pixel, np.array([4120, 270, 0, 1], dtype=np.double))
pixel2 = pixel1/pixel1[2]
# print(pixel1[2])
print(pixel2)
# 计算参数S
temmat = mat(rotM).I * mat(camera_matrix).I * mat([754, 217, 1]).T
temmat2 = mat(rotM).I * mat(tvec)
# print(temmat, temmat2)
s = temmat2[2]
s = s/temmat[2]
# print(s)
# 计算世界坐标
wcpoint = mat(rotM).I * (s[0, 0] * mat(camera_matrix).I * mat([754, 217, 1]).T - mat(tvec))
print(wcpoint)